Visualizing Data: The Power Of County-Level Heat Maps
Visualizing Data: The Power of County-Level Heat Maps
Related Articles: Visualizing Data: The Power of County-Level Heat Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Visualizing Data: The Power of County-Level Heat Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Visualizing Data: The Power of County-Level Heat Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Visualizing Data: The Power of County-Level Heat Maps
- 3.1 Understanding Heat Maps: A Visual Representation of Data
- 3.2 County-Level Heat Maps: A Focus on Local Insights
- 3.3 Applications of County-Level Heat Maps: A Diverse Spectrum
- 3.4 Benefits of County-Level Heat Maps: Enhanced Insights and Decision-Making
- 3.5 Limitations of County-Level Heat Maps: Considerations for Interpretation
- 3.6 FAQs: Addressing Common Queries on County-Level Heat Maps
- 3.7 Tips for Effective Use of County-Level Heat Maps
- 3.8 Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Visualizing Geographic Data
- 4 Closure
Visualizing Data: The Power of County-Level Heat Maps
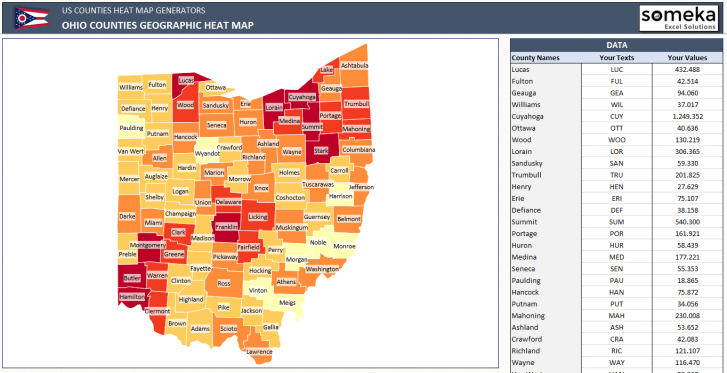
Heat maps, particularly those depicting data at the county level, offer a powerful tool for visualizing and understanding geographic patterns and trends. By representing data points with varying shades of color, heat maps provide an intuitive and visually compelling way to communicate complex information, making it accessible to a wider audience. This article delves into the significance of county-level heat maps, exploring their applications, benefits, and limitations.
Understanding Heat Maps: A Visual Representation of Data
A heat map is a graphical representation of data where values are depicted using color gradients. The intensity of the color corresponds to the magnitude of the data point, with higher values typically represented by warmer colors (e.g., red, orange) and lower values by cooler colors (e.g., blue, green). This visual representation allows for quick identification of areas with high or low values, revealing patterns and anomalies that might otherwise be obscured in tabular data.
County-Level Heat Maps: A Focus on Local Insights
When applied to county-level data, heat maps offer unique advantages. Counties, as administrative units, often reflect distinct geographic, demographic, and socioeconomic characteristics. Using county-level heat maps allows for:
- Highlighting Regional Differences: Heat maps can effectively illustrate how data varies across different counties, revealing regional disparities and trends. For example, a heat map showing unemployment rates by county might highlight areas with significantly higher unemployment, prompting further investigation into the underlying causes.
- Identifying Local Hotspots: Heat maps can pinpoint specific counties with exceptionally high or low values, indicating areas requiring targeted interventions or further analysis. For instance, a heat map depicting crime rates by county could identify counties with high crime rates, prompting authorities to allocate resources accordingly.
- Understanding Spatial Relationships: Heat maps facilitate the analysis of spatial relationships between data points. By visualizing data across counties, users can identify clusters of high or low values, suggesting potential correlations or underlying factors influencing the observed patterns.
Applications of County-Level Heat Maps: A Diverse Spectrum
County-level heat maps find applications across various fields, including:
1. Public Health:
- Disease Surveillance: Heat maps can visualize the distribution of diseases across counties, aiding in identifying outbreaks and allocating resources for public health interventions.
- Health Disparities: Heat maps can reveal disparities in health outcomes across counties, highlighting areas with higher rates of chronic diseases, infant mortality, or other health indicators.
2. Economics and Business:
- Market Analysis: Heat maps can identify counties with high concentrations of specific industries or consumer segments, assisting businesses in targeting marketing efforts and identifying potential growth areas.
- Economic Development: Heat maps can highlight counties with high economic growth or unemployment rates, guiding economic development initiatives and investment strategies.
3. Environmental Science:
- Air Pollution: Heat maps can illustrate the spatial distribution of air pollutants, identifying areas with high pollution levels and aiding in developing pollution control measures.
- Climate Change Impacts: Heat maps can visualize the projected impacts of climate change on different counties, informing adaptation strategies and resource allocation.
4. Social Sciences:
- Population Density: Heat maps can visualize population density across counties, aiding in understanding population distribution and planning infrastructure development.
- Social Inequality: Heat maps can reveal disparities in social indicators across counties, highlighting areas with higher poverty rates, crime rates, or educational attainment gaps.
5. Politics and Elections:
- Voting Patterns: Heat maps can visualize voting patterns across counties, revealing geographic trends and identifying key electoral districts.
- Political Polarization: Heat maps can illustrate the spatial distribution of political ideologies across counties, providing insights into regional divisions and political polarization.
Benefits of County-Level Heat Maps: Enhanced Insights and Decision-Making
County-level heat maps offer numerous benefits, making them invaluable tools for researchers, policymakers, and decision-makers:
- Data Visualization: Heat maps present complex data in a clear and concise manner, facilitating understanding and communication.
- Pattern Recognition: Heat maps enable the identification of geographic patterns and trends, highlighting areas with high or low values.
- Targeted Interventions: Heat maps help pinpoint specific counties requiring targeted interventions, ensuring resource allocation is efficient and effective.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Heat maps provide a visual representation of data, supporting evidence-based decision-making and informed policy development.
- Public Engagement: Heat maps can be used to engage the public in understanding complex issues and promoting awareness of regional disparities.
Limitations of County-Level Heat Maps: Considerations for Interpretation
While heat maps offer significant advantages, it is important to acknowledge their limitations:
- Data Availability: The availability of reliable county-level data is crucial for generating accurate and meaningful heat maps. Data gaps or inconsistencies can lead to misleading interpretations.
- Spatial Resolution: County-level data may not capture fine-grained spatial variations within counties, potentially masking local trends or hotspots.
- Data Aggregation: Heat maps often involve aggregating data across counties, potentially obscuring individual cases or specific characteristics within counties.
- Correlation vs. Causation: Heat maps can reveal correlations between variables, but they cannot establish causal relationships. Further analysis is required to understand the underlying factors driving observed patterns.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries on County-Level Heat Maps
1. What data can be visualized using county-level heat maps?
County-level heat maps can visualize a wide range of data, including demographic data (population density, age distribution), socioeconomic data (income levels, poverty rates), health data (disease prevalence, mortality rates), environmental data (air quality, water quality), and crime data (crime rates, police presence).
2. How are heat map colors chosen for county-level data?
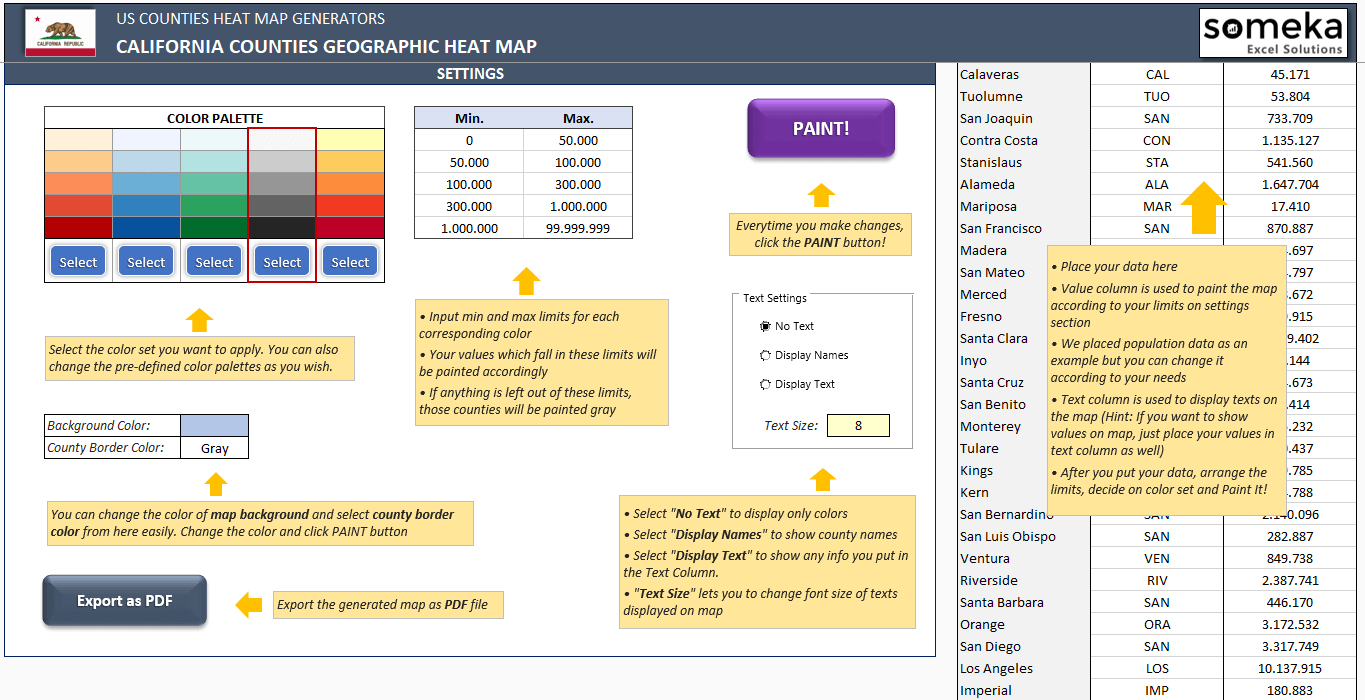
The choice of colors for heat maps depends on the specific data being visualized and the intended message. Generally, warmer colors (red, orange) represent higher values, while cooler colors (blue, green) represent lower values. It is important to use a consistent color scheme throughout the map to avoid confusion.
3. How can I create a county-level heat map?
There are various software tools available for creating heat maps, including:
- Geographic Information System (GIS) Software: ArcGIS, QGIS, and other GIS software offer advanced features for creating and analyzing heat maps.
- Data Visualization Software: Tableau, Power BI, and other data visualization tools provide user-friendly interfaces for creating interactive heat maps.
- Online Mapping Platforms: Google Maps, Mapbox, and other online platforms allow users to create basic heat maps using their data.
4. What are some best practices for creating effective county-level heat maps?
- Use clear and concise labels: Ensure that county names and data values are clearly visible and legible.
- Select an appropriate color scheme: Choose colors that are visually appealing and effectively convey the data.
- Provide a legend: Include a legend explaining the meaning of different colors and data ranges.
- Consider the target audience: Tailor the map’s complexity and presentation to the intended audience.
5. What are some potential applications of county-level heat maps in my field?
To identify potential applications, consider the specific data available in your field and the questions you are trying to answer. For example, if you are a public health professional, you might use heat maps to visualize disease prevalence, identify areas with high vaccination rates, or assess access to healthcare services.
Tips for Effective Use of County-Level Heat Maps
- Ensure Data Accuracy: Verify the accuracy and reliability of the data used to create the heat map.
- Consider Data Granularity: Explore the trade-offs between using county-level data and more granular data (e.g., zip code level).
- Communicate Context: Provide context for the data being visualized, explaining the underlying factors influencing the observed patterns.
- Engage with the Audience: Encourage interaction and discussion around the heat map to facilitate understanding and promote informed decision-making.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Visualizing Geographic Data
County-level heat maps offer a powerful tool for visualizing and understanding geographic patterns and trends. By representing data with varying shades of color, heat maps provide an intuitive and visually compelling way to communicate complex information, revealing regional differences, identifying local hotspots, and facilitating spatial analysis. Their applications span various fields, including public health, economics, environmental science, social sciences, and politics. By leveraging the benefits of heat maps and understanding their limitations, researchers, policymakers, and decision-makers can utilize this tool to gain valuable insights, support data-driven decision-making, and promote informed public engagement.

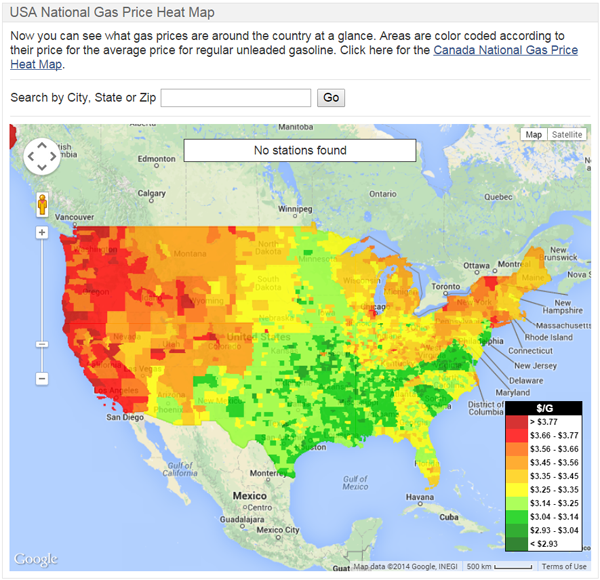


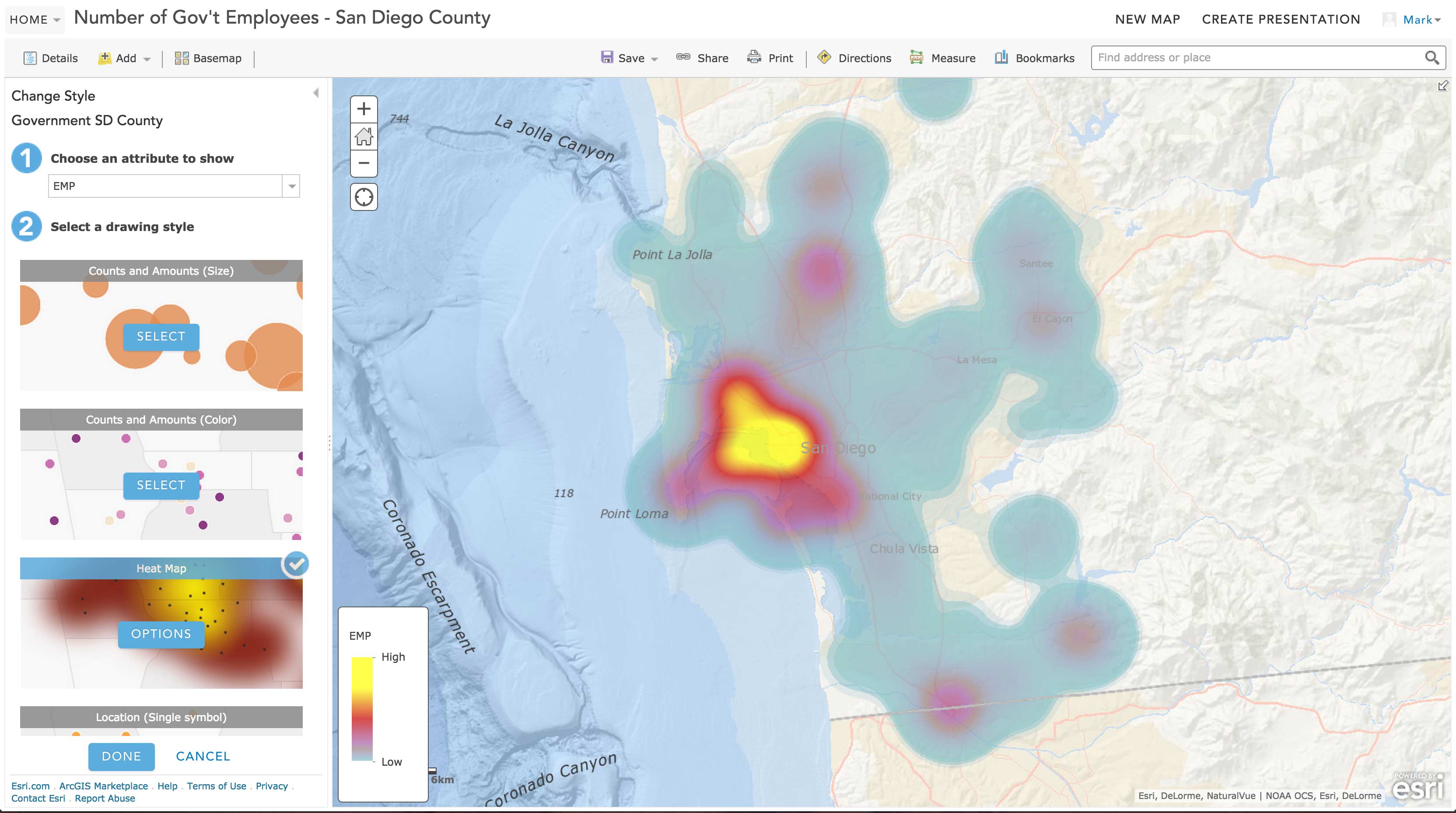

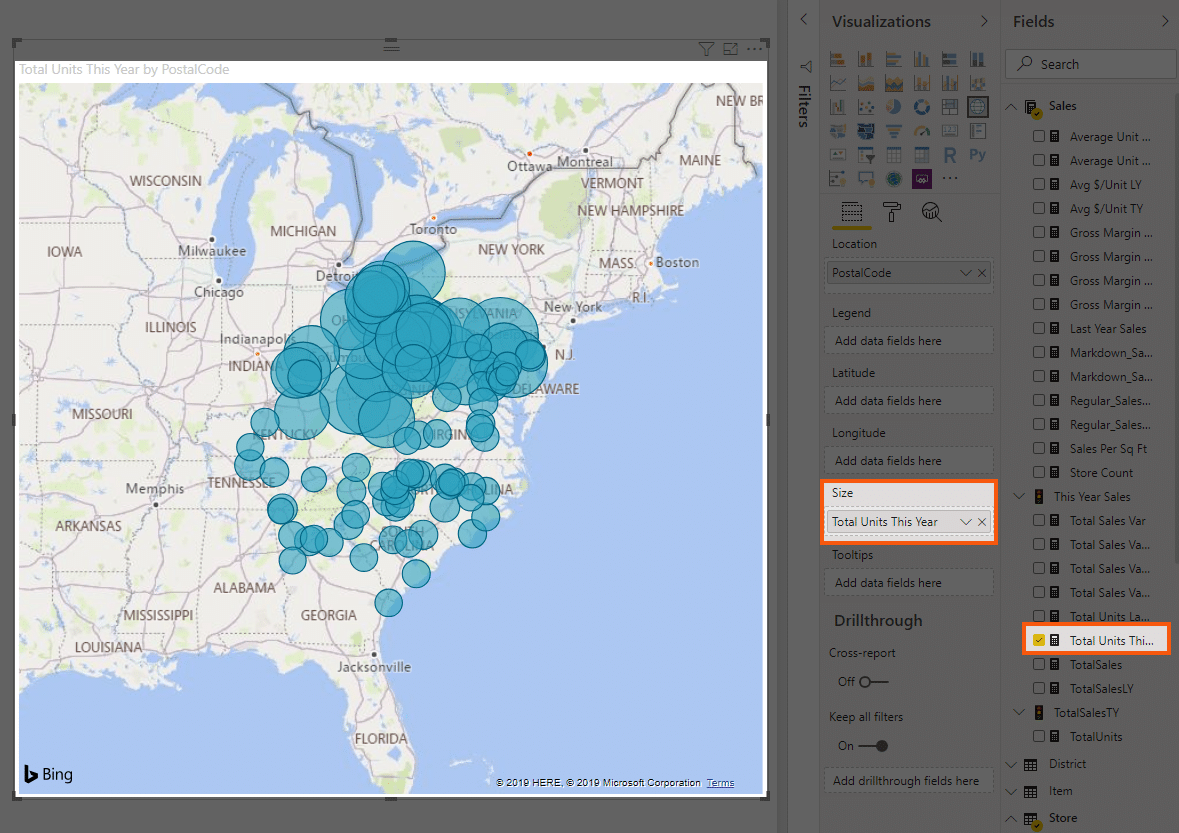
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Visualizing Data: The Power of County-Level Heat Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!