Unveiling The Waterscape: A Comprehensive Look At Water Quality Atlas Maps
Unveiling the Waterscape: A Comprehensive Look at Water Quality Atlas Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Waterscape: A Comprehensive Look at Water Quality Atlas Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Waterscape: A Comprehensive Look at Water Quality Atlas Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Waterscape: A Comprehensive Look at Water Quality Atlas Maps
Water, the lifeblood of our planet, faces an array of challenges. Pollution, climate change, and unsustainable practices threaten its quality, impacting ecosystems, human health, and economic prosperity. To effectively address these challenges, comprehensive and accessible information about water quality is paramount. Enter the water quality atlas map, a powerful tool for visualizing, understanding, and managing the health of our aquatic resources.
The Essence of Water Quality Atlas Maps
A water quality atlas map is a specialized geographic information system (GIS) tool that presents a spatial overview of water quality data. It acts as a visual repository, integrating diverse data sources to depict the condition of water bodies across a region, country, or even globally. These maps are not simply static representations; they are dynamic platforms that allow users to explore, analyze, and interact with water quality data in a user-friendly manner.
Components of a Water Quality Atlas Map
A comprehensive water quality atlas map typically incorporates several key elements:
- Spatial Data: The foundation of the map lies in geographic data, often obtained from remote sensing, field surveys, or existing databases. This data includes information on water bodies, their boundaries, and surrounding land use patterns.
- Water Quality Parameters: The map integrates various water quality indicators, such as dissolved oxygen levels, pH, nutrient concentrations, heavy metal content, and microbial contamination. These parameters are collected through sampling, monitoring programs, and laboratory analysis.
- Temporal Data: To understand the dynamics of water quality, the atlas map incorporates time-series data. This allows users to observe trends, seasonal variations, and the impact of specific events on water quality over time.
- Spatial Analysis Tools: The atlas map goes beyond simple visualization. It provides analytical tools to assess patterns, identify areas of concern, and evaluate the effectiveness of management strategies. These tools can include spatial statistics, geostatistical analysis, and modeling techniques.
- User Interface: A user-friendly interface allows users to navigate the map, select data layers, zoom in on specific areas, and generate reports. The interface should be intuitive and accessible to a wide range of users, including scientists, policymakers, and the general public.
The Significance of Water Quality Atlas Maps
Water quality atlas maps serve as indispensable tools for various stakeholders:
- Environmental Monitoring and Management: These maps provide a comprehensive overview of water quality across vast areas, enabling environmental agencies to identify pollution hotspots, assess the effectiveness of conservation efforts, and prioritize areas for remediation.
- Water Resource Management: By visualizing water quality data, water resource managers can optimize water allocation, identify areas vulnerable to contamination, and implement strategies for sustainable water use.
- Public Health Protection: Atlas maps aid in understanding the relationship between water quality and human health. They can identify areas at risk of waterborne diseases and guide public health interventions.
- Research and Education: Researchers utilize these maps to investigate the drivers of water quality changes, develop predictive models, and conduct scientific studies. Atlas maps also serve as valuable educational tools, raising awareness about water quality issues and promoting citizen science initiatives.
- Policy Development: Atlas maps provide policymakers with the necessary data to inform legislation, develop regulations, and allocate resources effectively for water quality protection.
Benefits of Water Quality Atlas Maps
The use of water quality atlas maps offers numerous benefits:
- Improved Data Visualization: Atlas maps present complex water quality data in a readily understandable format, facilitating communication and collaboration among stakeholders.
- Enhanced Spatial Understanding: By visualizing data geographically, users gain a deeper understanding of spatial patterns, identifying areas of high or low water quality, and understanding the influence of surrounding land use practices.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Atlas maps provide a solid foundation for informed decision-making. They enable users to identify areas of concern, prioritize resources, and evaluate the effectiveness of management actions.
- Increased Transparency and Accountability: Publicly accessible atlas maps promote transparency by making water quality data readily available to all stakeholders. This fosters accountability and encourages citizen participation in water quality monitoring and management.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Atlas maps can help optimize resource allocation by identifying areas where management efforts are most needed. This can lead to more efficient and cost-effective water quality protection programs.
FAQs about Water Quality Atlas Maps
1. What data sources are used in water quality atlas maps?
Water quality atlas maps draw upon a diverse range of data sources, including:
- Field Monitoring Data: This includes water samples collected at various locations and analyzed in laboratories for specific parameters.
- Remote Sensing Data: Satellite imagery and aerial photography can provide information on water quality parameters like turbidity, chlorophyll levels, and algal blooms.
- GIS Databases: Existing spatial databases containing information on land use, topography, and hydrological features contribute to the map’s context.
- Citizen Science Data: Data collected by volunteers and citizen science initiatives can supplement official monitoring efforts, providing valuable insights into local water quality conditions.
2. How can I access water quality atlas maps?
Water quality atlas maps are increasingly available online, often through government agencies, research institutions, and environmental organizations. Many atlases are interactive, allowing users to explore data, generate reports, and download information.
3. What are the limitations of water quality atlas maps?
While powerful tools, water quality atlas maps have limitations:
- Data Availability and Quality: The accuracy and completeness of the map depend on the quality and availability of input data. Gaps in data coverage can limit the map’s effectiveness.
- Spatial Resolution: The resolution of the data used can influence the level of detail depicted on the map. Fine-scale features might be missed if data is collected at coarser spatial scales.
- Temporal Resolution: The frequency of data collection and analysis can impact the ability to capture short-term fluctuations or event-driven changes in water quality.
- Interpretation and Bias: Interpreting data presented on the map requires expertise in water quality assessment and understanding potential biases in data collection and analysis.
Tips for Utilizing Water Quality Atlas Maps Effectively
- Understand the Data: Familiarize yourself with the data sources, parameters measured, and limitations of the atlas map before drawing conclusions.
- Explore the Tools: Utilize the map’s interactive features to analyze data, zoom in on specific areas, and generate customized reports.
- Consider Context: Interpret data within the broader context of land use, climate, and other environmental factors influencing water quality.
- Collaborate with Experts: Engage with water quality experts, scientists, and environmental professionals to interpret data and develop informed management strategies.
- Promote Public Awareness: Share information from the atlas map with the community, fostering public engagement in water quality protection efforts.
Conclusion: A Vision for Sustainable Waters
Water quality atlas maps are invaluable tools for understanding, managing, and protecting our precious water resources. By visualizing data, facilitating analysis, and promoting collaboration, these maps empower stakeholders to make informed decisions, implement effective management strategies, and strive towards a future where our waters are healthy, sustainable, and accessible to all. As technology advances and data collection methods improve, the potential of water quality atlas maps to guide us towards a more sustainable water future continues to grow.

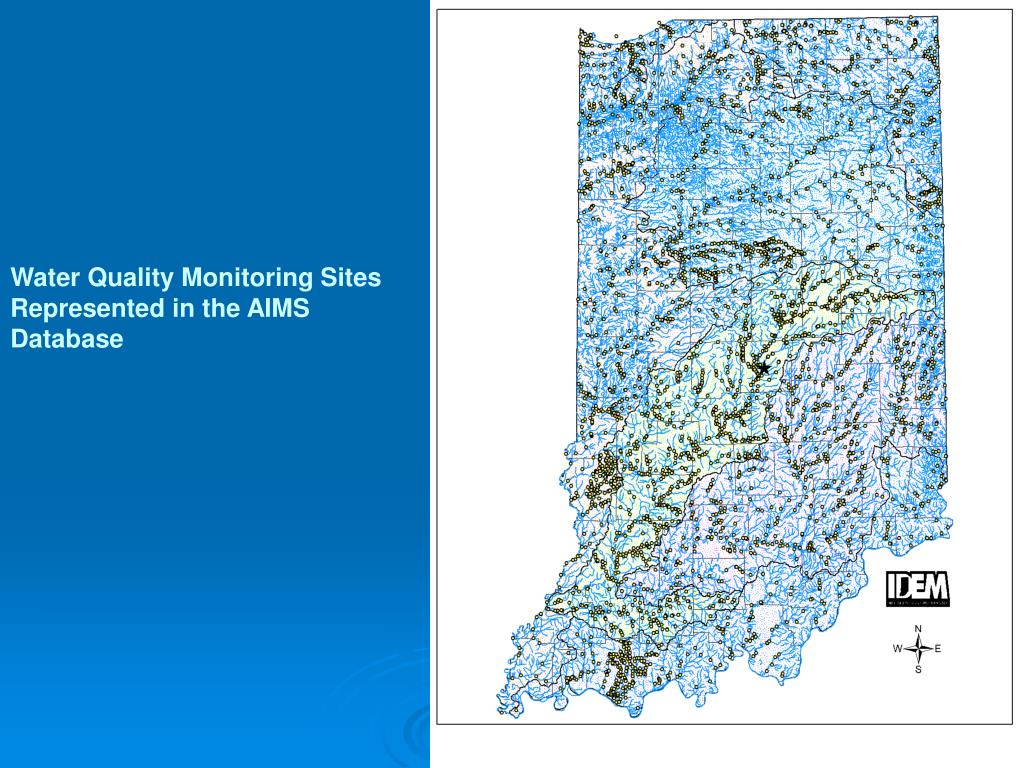

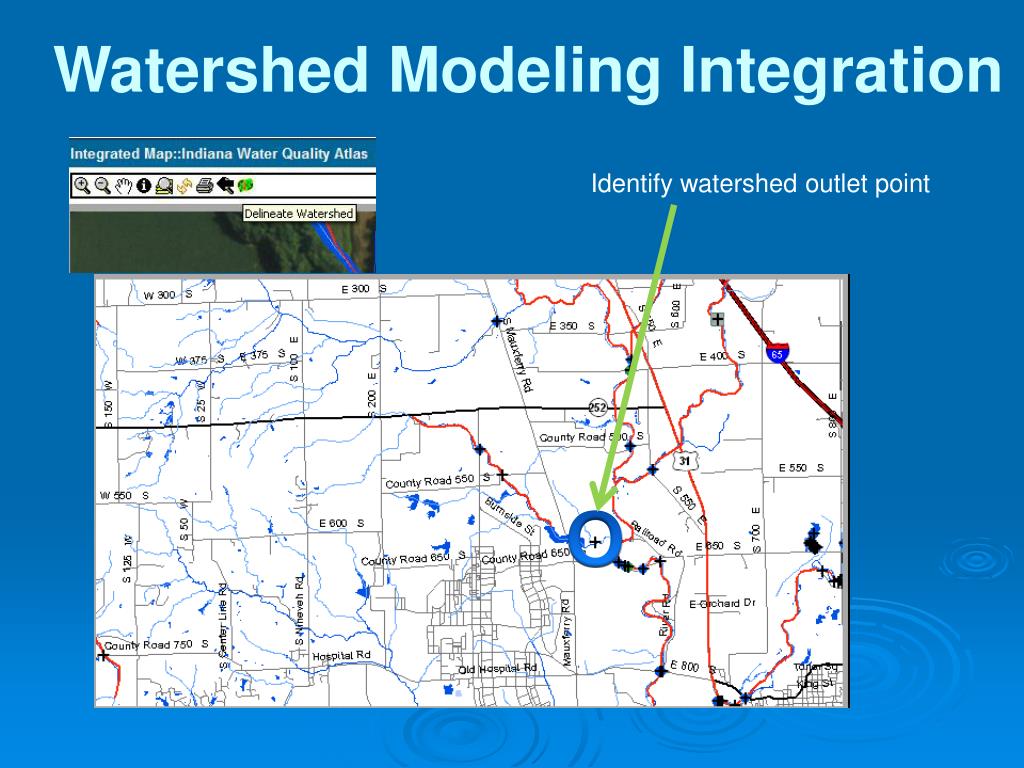
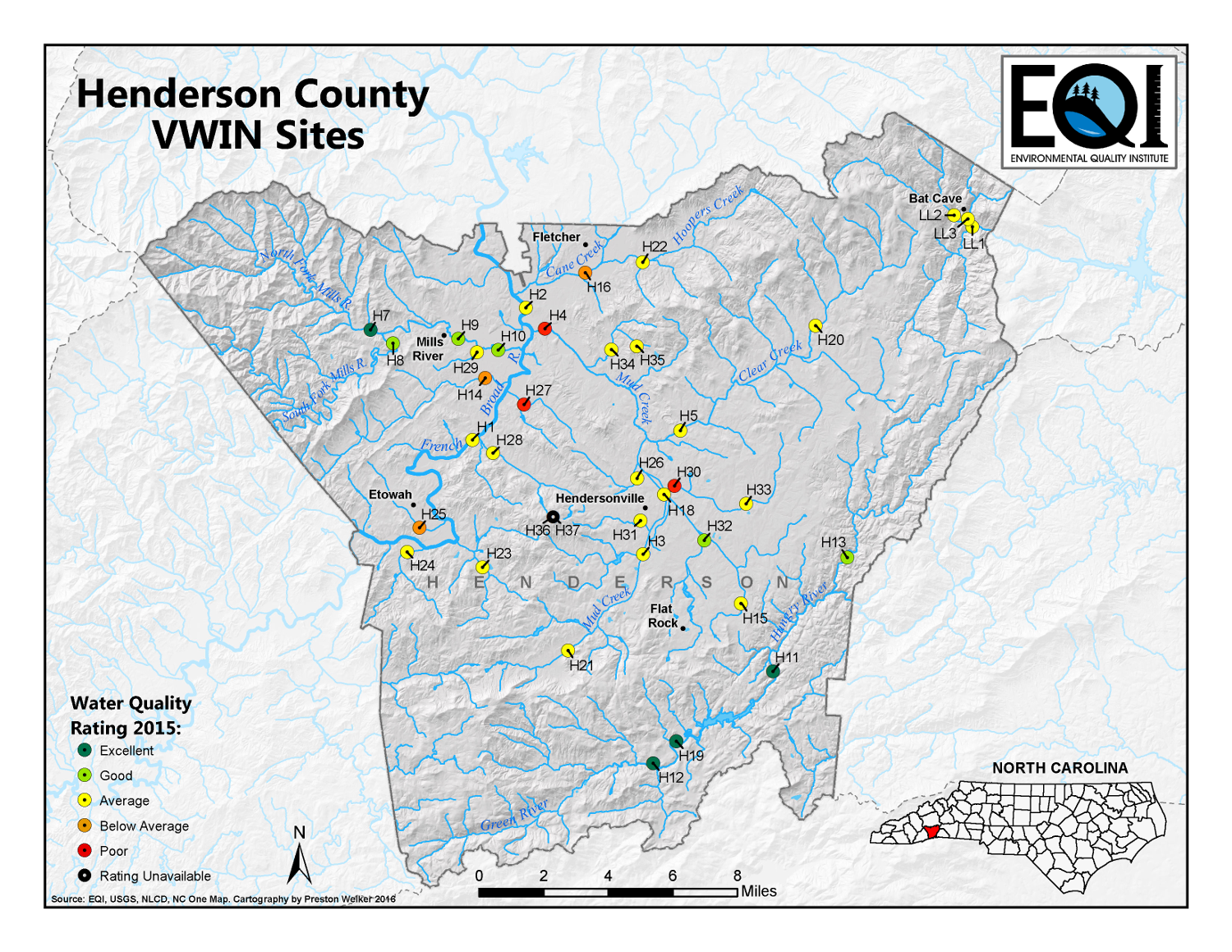



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Waterscape: A Comprehensive Look at Water Quality Atlas Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!