Unveiling The Secrets Of The Atlantic Ocean Floor: A Comprehensive Look At Its Relief Map
Unveiling the Secrets of the Atlantic Ocean Floor: A Comprehensive Look at its Relief Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the Atlantic Ocean Floor: A Comprehensive Look at its Relief Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of the Atlantic Ocean Floor: A Comprehensive Look at its Relief Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of the Atlantic Ocean Floor: A Comprehensive Look at its Relief Map

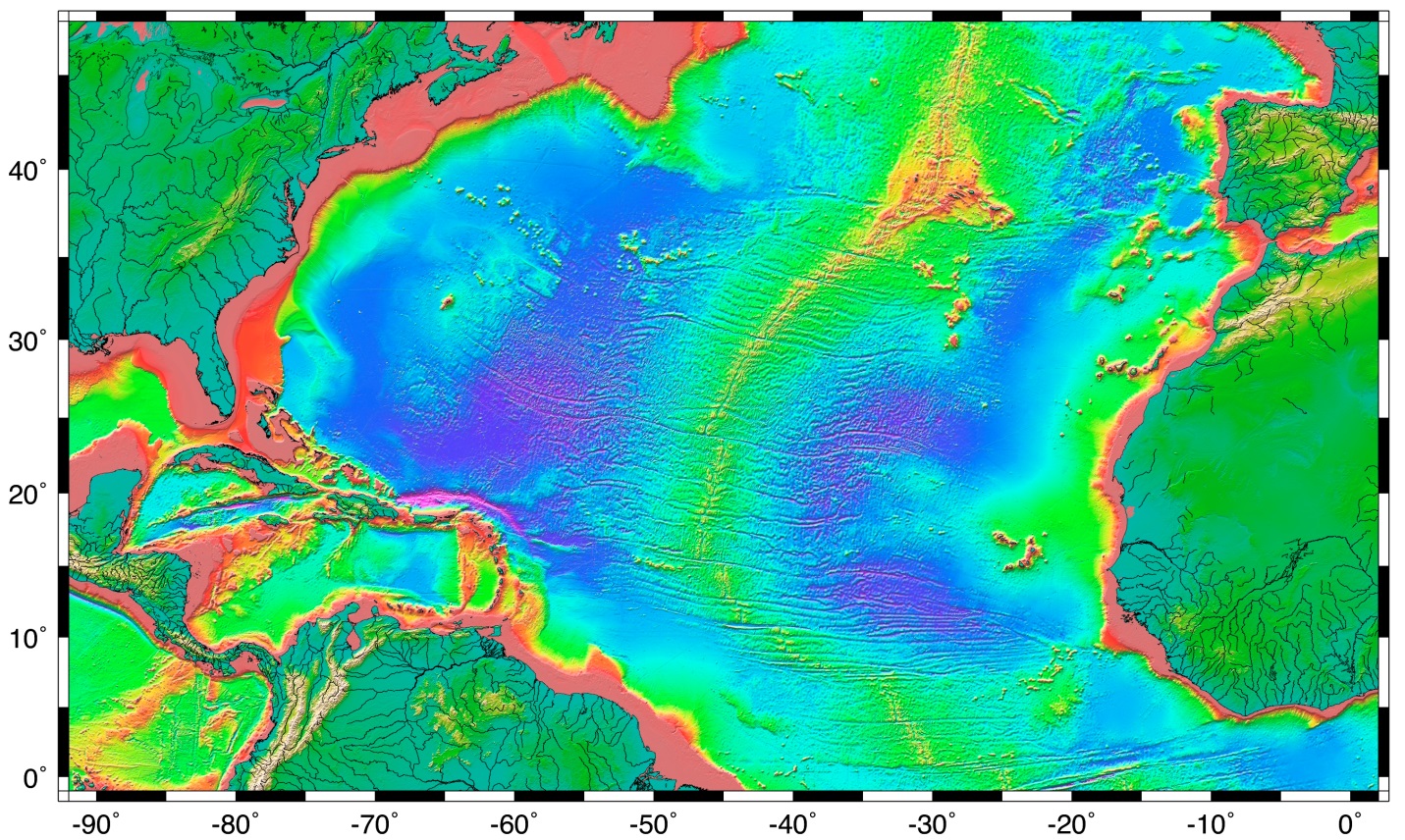
The Atlantic Ocean, a vast expanse of water covering over 20% of the Earth’s surface, holds within its depths a complex and dynamic landscape. This submerged terrain, known as the ocean floor, is sculpted by a multitude of geological forces, resulting in a diverse array of features that significantly influence ocean currents, marine life, and even the global climate. Understanding the topography of the Atlantic Ocean floor, often visualized through relief maps, is crucial for comprehending these intricate interactions and unlocking the secrets of this watery world.
The Atlantic Ocean Floor: A Tapestry of Diverse Features
An Atlantic Ocean relief map reveals a captivating story of geological history, showcasing a remarkable array of features:
-
Mid-Atlantic Ridge: This prominent undersea mountain range, stretching from the Arctic Ocean to the South Atlantic, marks the boundary between the North American and Eurasian plates, and the South American and African plates. It is a site of active volcanism and seafloor spreading, where new oceanic crust is constantly being generated.
-
Fracture Zones: These linear zones of weakness, perpendicular to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, represent areas where the ocean floor has been broken and offset by tectonic movements. They often act as barriers to ocean currents, creating distinct water masses and influencing marine life distribution.
-
Abyssal Plains: Vast, flat expanses of sediment-covered seabed lie between the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the continental margins. These plains are formed by the slow accumulation of fine-grained sediments, carried by ocean currents and deposited over millions of years.
-
Seamounts and Guyots: Isolated volcanic mountains rising from the ocean floor, seamounts are often extinct volcanoes, while guyots are flat-topped seamounts, eroded by wave action when they were above sea level. These features provide valuable habitats for a variety of marine organisms, including deep-sea corals and fish.
-
Trenches: Deep, narrow depressions in the ocean floor, trenches are formed at convergent plate boundaries where one tectonic plate is subducted beneath another. The Puerto Rico Trench, the deepest point in the Atlantic Ocean, is a prime example.
-
Continental Margins: These transition zones between the continents and the ocean floor are characterized by a series of features, including continental shelves, slopes, and rises. The continental shelf, a relatively shallow and gently sloping area, is an important habitat for marine life, while the continental slope marks a steeper descent into the deep ocean.
Unveiling the Importance of Atlantic Ocean Relief Maps
Understanding the topography of the Atlantic Ocean floor is paramount for several reasons:
-
Ocean Circulation and Climate: The relief map reveals the intricate network of underwater mountains and valleys that influence ocean currents. These currents play a vital role in distributing heat and nutrients around the globe, significantly impacting weather patterns and climate regulation.
-
Marine Ecosystem Dynamics: The diverse features of the Atlantic Ocean floor create a mosaic of habitats, supporting a wide array of marine life. From shallow-water coral reefs to the deep-sea hydrothermal vents, each feature harbors unique ecosystems with specialized organisms adapted to their specific environment.
-
Resource Exploration and Management: The relief map provides valuable insights into the distribution of natural resources, such as oil, gas, and minerals, found beneath the ocean floor. This information is crucial for responsible resource exploration and management, ensuring sustainable use and minimizing environmental impact.
-
Navigation and Safety: Knowledge of the ocean floor topography is essential for safe and efficient navigation, particularly for submarines, underwater vehicles, and ships operating in shallow waters. Relief maps help identify potential hazards, such as submerged mountains, trenches, and wrecks, allowing for safer passage.
-
Scientific Research and Understanding: The relief map serves as a fundamental tool for scientific research, providing a visual representation of the ocean floor’s complex structure and geological processes. This information is crucial for understanding plate tectonics, seafloor spreading, and the evolution of the Earth’s oceans.
FAQs about Atlantic Ocean Relief Maps
Q: What are the primary methods used to create Atlantic Ocean relief maps?
A: Modern relief maps are created using a combination of techniques, including:
- Sonar (Sound Navigation and Ranging): This technology emits sound waves that bounce off the ocean floor, allowing scientists to measure the depth and topography of the seabed.
- Satellite Altimetry: Satellites equipped with radar can measure the height of the ocean surface, providing data about the underlying seafloor topography.
- Remote Sensing: Techniques like aerial photography and multispectral imaging can be used to map certain features of the ocean floor, such as shallow-water reefs and coastal areas.
Q: What are some of the challenges in mapping the Atlantic Ocean floor?
A: Despite advancements in technology, mapping the entire ocean floor remains a significant challenge due to:
- Vastness of the Ocean: The Atlantic Ocean is incredibly vast, making it time-consuming and expensive to map its entire topography.
- Technical Limitations: Some areas of the ocean, such as deep trenches and canyons, are difficult to map accurately due to limitations in sonar and satellite technology.
- Environmental Conditions: Harsh weather conditions, strong currents, and limited visibility can hinder mapping operations.
Q: How do Atlantic Ocean relief maps contribute to our understanding of climate change?
A: Relief maps provide valuable insights into ocean currents, which play a crucial role in regulating global climate. By studying the interaction between ocean currents and the ocean floor topography, scientists can better understand how changes in ocean circulation patterns might impact climate change and its effects.
Tips for Utilizing Atlantic Ocean Relief Maps
- Choose the Right Map: Different relief maps are designed for different purposes. Select a map that is appropriate for your specific needs, considering factors such as scale, detail, and data sources.
- Interpret the Data: Understanding the symbols and conventions used on relief maps is essential for accurately interpreting the data they present.
- Integrate with Other Data: Combining relief maps with other data sources, such as oceanographic measurements, marine life surveys, and climate models, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the Atlantic Ocean.
- Explore Online Resources: Numerous online resources, including interactive maps and databases, provide access to a wealth of information about the Atlantic Ocean floor.
Conclusion
The Atlantic Ocean relief map is a powerful tool that unveils the hidden secrets of this vast and dynamic body of water. It provides a visual representation of the complex and diverse topography of the ocean floor, offering valuable insights into ocean currents, marine ecosystems, resource distribution, navigation, and scientific research. As technology advances and our understanding of the ocean deepens, the Atlantic Ocean relief map will continue to play a crucial role in unraveling the mysteries of this underwater world and guiding our efforts towards responsible stewardship of this vital resource.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of the Atlantic Ocean Floor: A Comprehensive Look at its Relief Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!