Unveiling The Power Of Resource Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Utilizing Atlases
Unveiling the Power of Resource Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Atlases
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Resource Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Atlases
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Resource Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Atlases. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Resource Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Atlases
In an increasingly interconnected and resource-constrained world, the ability to effectively manage and utilize resources is paramount. Atlas resource maps, often referred to simply as resource maps, provide a powerful tool for achieving this goal. These maps are not mere static representations of geographical locations; they are dynamic, interactive visualizations that offer a holistic understanding of resource distribution, availability, and utilization across various scales.
Understanding the Essence of Atlas Resource Maps
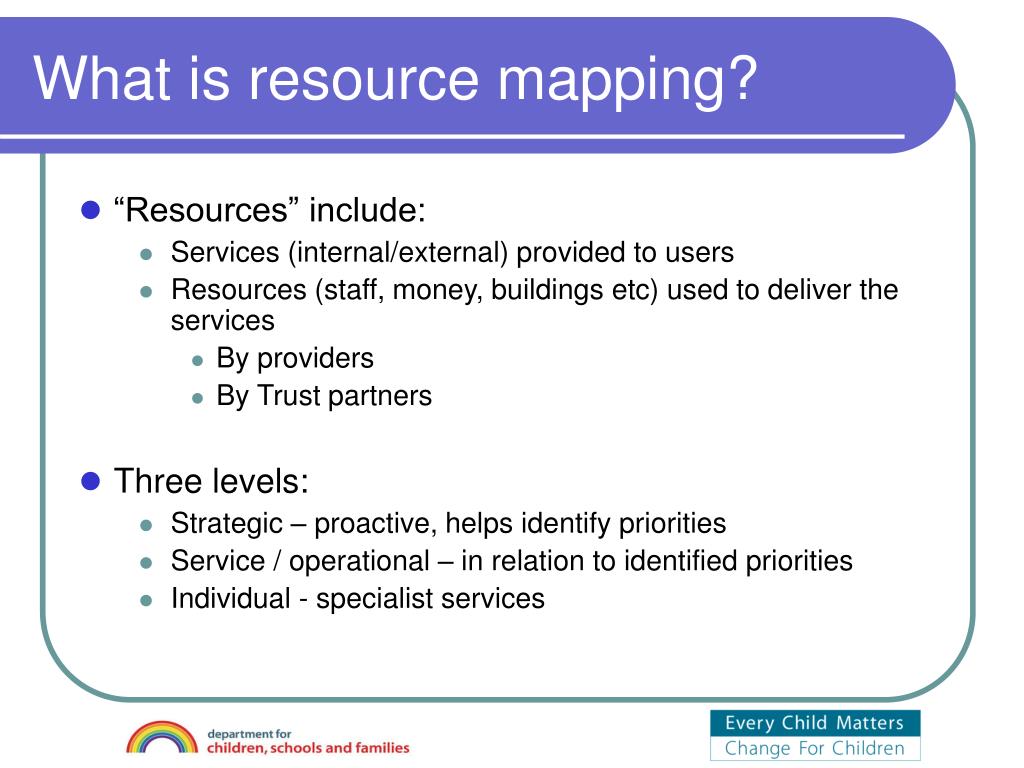
At their core, resource maps are visual representations of the spatial distribution of resources. These resources can encompass a wide spectrum, ranging from natural resources like minerals, water, and forests to human capital, infrastructure, and even intangible assets such as knowledge and innovation. The maps act as a visual bridge, connecting the physical world with data and information, providing a comprehensive overview of resource availability and potential.
Key Components of a Resource Map
A comprehensive resource map typically comprises the following key elements:
- Base Map: This forms the foundation of the map, providing a geographical context. It can be a simple outline of a region or a detailed representation with various geographical features like rivers, roads, and elevation contours.
- Resource Layers: These layers represent different types of resources. Each layer can be customized to display specific data, such as the location of oil fields, the density of population, or the availability of renewable energy sources.
- Data Visualization: Resource maps utilize various data visualization techniques, such as color-coding, symbols, and charts, to represent resource characteristics like quantity, quality, and accessibility.
- Interactive Functionality: Modern resource maps often incorporate interactive features, allowing users to zoom, pan, and query the data, providing deeper insights and enabling tailored analysis.
Beyond Simple Visualization: The Power of Resource Mapping
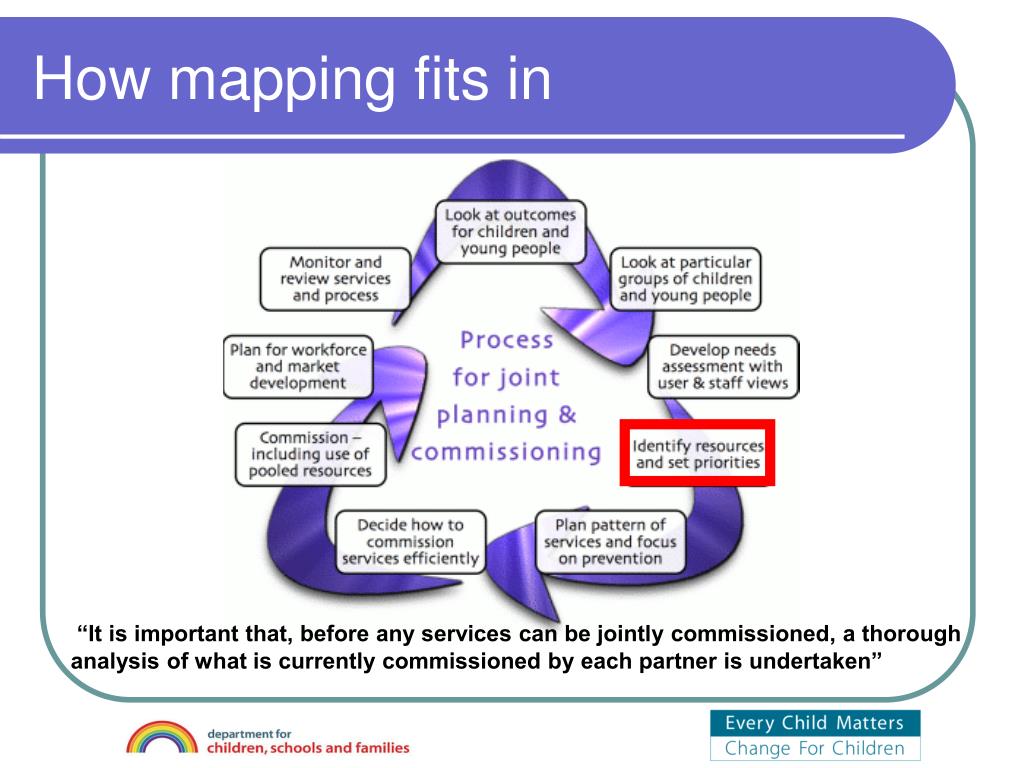
Resource maps are more than just static visual representations; they serve as powerful analytical tools, enabling users to:
- Identify Resource Hotspots: By overlaying different resource layers, users can identify areas with high concentrations of specific resources, guiding resource extraction, development, and conservation efforts.
- Assess Resource Availability: Maps can be used to analyze resource availability across different regions, informing strategic planning and decision-making in resource management.
- Predict Resource Needs: By considering factors like population growth, economic development, and climate change, resource maps can project future resource demands, enabling proactive planning and resource allocation.
- Optimize Resource Utilization: By visualizing resource flow and consumption patterns, maps can highlight areas of inefficient resource use, prompting optimization strategies and promoting sustainable practices.
- Facilitate Collaboration: Resource maps can serve as a common platform for sharing resource information, fostering collaboration among stakeholders, and promoting informed decision-making in resource management.
Applications of Resource Mapping: A Wide Spectrum of Possibilities
The applications of resource mapping are as diverse as the resources they represent. Some key areas where resource maps find significant use include:
- Environmental Management: Assessing biodiversity, identifying pollution hotspots, and monitoring deforestation are crucial for effective environmental management, and resource maps play a vital role in these processes.
- Natural Resource Management: From oil and gas exploration to sustainable forestry and water resource management, resource maps provide invaluable insights into the distribution, availability, and potential of natural resources.
- Urban Planning: Understanding population distribution, infrastructure availability, and service access is essential for sustainable urban development, and resource maps provide valuable insights for city planners.
- Disaster Management: Resource maps can be used to assess vulnerability to natural disasters, identify critical infrastructure, and plan for efficient resource allocation during emergencies.
- Economic Development: Identifying resource-rich areas, understanding resource potential, and optimizing resource utilization are essential for promoting economic growth, and resource maps play a crucial role in these processes.
FAQs on Resource Mapping
1. What are the benefits of using resource maps?
Resource maps offer numerous benefits, including:
- Improved resource management: By providing a comprehensive understanding of resource distribution and availability, maps enable more effective resource planning and utilization.
- Enhanced decision-making: Resource maps provide valuable data and insights that support informed decision-making in resource management, development, and conservation.
- Increased collaboration: Maps act as a common platform for sharing resource information, fostering collaboration among stakeholders and promoting coordinated resource management efforts.
- Reduced resource waste: By identifying areas of inefficient resource use, maps enable the development of strategies to optimize resource utilization and minimize waste.
- Improved sustainability: Resource maps facilitate the development of sustainable resource management practices, ensuring the long-term availability and responsible use of resources.
2. What are some common challenges associated with resource mapping?
Despite their numerous benefits, resource mapping faces certain challenges, including:
- Data availability and accuracy: Ensuring the availability of accurate and up-to-date data is crucial for creating effective resource maps. Data gaps and inconsistencies can limit the accuracy and reliability of the maps.
- Data integration and standardization: Integrating data from various sources, often with different formats and standards, can be challenging. Establishing standardized data formats and protocols can enhance data integration and map accuracy.
- Technical expertise: Creating and utilizing resource maps effectively requires technical expertise in data management, spatial analysis, and map design. Access to skilled personnel is essential for successful resource mapping.
- Public access and awareness: Ensuring public access to resource maps and promoting awareness of their benefits is crucial for leveraging their potential in decision-making and resource management.
3. What are some tips for effective resource mapping?
To create and utilize resource maps effectively, consider the following tips:
- Define clear objectives: Clearly define the purpose and objectives of the resource mapping project to guide data collection, analysis, and map design.
- Identify relevant data sources: Identify and access reliable and up-to-date data sources relevant to the targeted resources and geographical areas.
- Ensure data accuracy and quality: Verify the accuracy and consistency of data before incorporating it into the resource map. Implement quality control measures to ensure data reliability.
- Choose appropriate visualization techniques: Select data visualization techniques that effectively represent the resource characteristics and facilitate clear understanding.
- Incorporate interactive features: Include interactive features in the resource map to enable users to explore data, perform analysis, and generate customized reports.
- Promote user engagement: Design the resource map interface to be user-friendly and intuitive, encouraging users to explore the map and utilize its data.
- Disseminate map information: Share the resource map with relevant stakeholders, promoting its use in decision-making and resource management.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Resource Mapping for a Sustainable Future
Atlas resource maps are not merely static representations of geographical information; they are powerful tools for understanding, managing, and utilizing resources effectively. By providing a holistic view of resource distribution, availability, and utilization, these maps enable informed decision-making, promoting sustainable resource management and fostering a more equitable and prosperous future. As we navigate the challenges of a resource-constrained world, embracing the power of resource mapping is essential for ensuring the responsible and sustainable use of our planet’s resources for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Resource Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Atlases. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!