Unveiling Health Disparities: A Comprehensive Look At Health Atlas Maps
Unveiling Health Disparities: A Comprehensive Look at Health Atlas Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling Health Disparities: A Comprehensive Look at Health Atlas Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Health Disparities: A Comprehensive Look at Health Atlas Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling Health Disparities: A Comprehensive Look at Health Atlas Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling Health Disparities: A Comprehensive Look at Health Atlas Maps
- 3.1 Defining the Scope: What are Health Atlas Maps?
- 3.2 The Power of Visualization: Benefits of Health Atlas Maps
- 3.3 Applications Across Healthcare Domains: Unveiling the Versatility
- 3.4 Unveiling the Data: Understanding the Components of Health Atlas Maps
- 3.5 Navigating the Landscape: FAQs on Health Atlas Maps
- 3.6 Navigating the Path: Tips for Effective Use of Health Atlas Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Health Equity
- 4 Closure
Unveiling Health Disparities: A Comprehensive Look at Health Atlas Maps
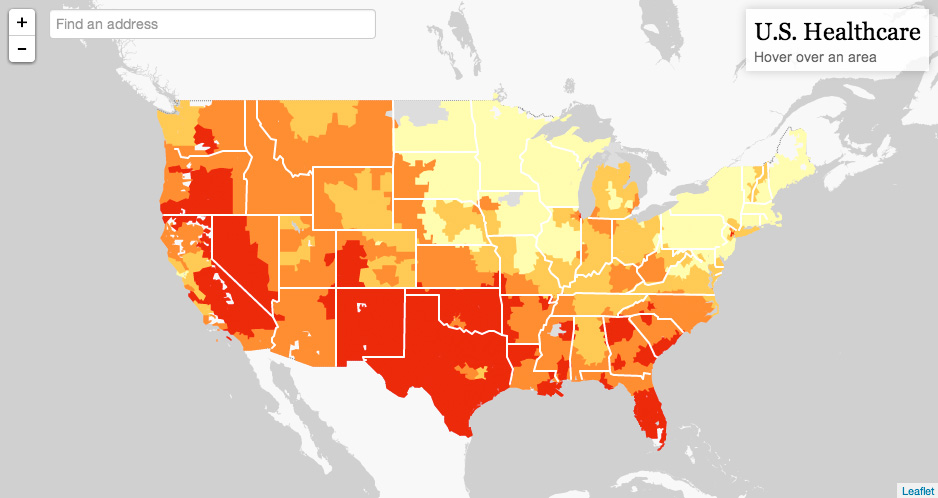
Health atlas maps, visual representations of health data across geographical regions, serve as powerful tools for understanding and addressing health disparities. They provide a comprehensive overview of health indicators, revealing patterns and trends that might otherwise remain hidden, ultimately informing policy decisions and resource allocation. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of health atlas maps, exploring their significance, benefits, and applications in various healthcare domains.
Defining the Scope: What are Health Atlas Maps?
Health atlas maps, also known as health geographic information systems (GIS), utilize geospatial technology to overlay health data onto geographical maps. This integration allows for a visual representation of health indicators, such as disease prevalence, mortality rates, access to healthcare services, and population demographics, across different geographical areas. The resulting maps serve as a visual guide to understanding health trends, identifying areas of need, and informing interventions.
The Power of Visualization: Benefits of Health Atlas Maps
Health atlas maps offer a unique advantage by transforming complex health data into easily digestible visual representations. This visual approach facilitates a deeper understanding of health trends and disparities, leading to several benefits:
-
Identification of Health Disparities: By visualizing health indicators across regions, these maps highlight disparities in health outcomes, access to care, and disease prevalence. This identification of disparities enables targeted interventions and resource allocation to address specific needs.
-
Informed Policy Development: Health atlas maps provide policymakers with valuable insights into health trends and disparities, informing the development of effective healthcare policies. This data-driven approach ensures that policies are tailored to address specific regional needs and improve overall health outcomes.
-
Resource Allocation and Prioritization: By identifying areas with high disease prevalence, limited access to care, or poor health outcomes, health atlas maps guide the allocation of resources to areas of greatest need. This efficient allocation optimizes resource utilization and maximizes impact.
-
Improved Health Service Delivery: By understanding the geographical distribution of health services and population demographics, health atlas maps enable the optimization of service delivery. This includes identifying areas with limited access to healthcare facilities, facilitating the establishment of new clinics or mobile health units.
-
Public Health Surveillance: Health atlas maps play a crucial role in public health surveillance, allowing for the monitoring of disease outbreaks, tracking the spread of infections, and identifying areas requiring immediate intervention. This real-time data visualization enables rapid response and containment efforts.
Applications Across Healthcare Domains: Unveiling the Versatility
Health atlas maps have proven to be versatile tools with applications across various healthcare domains, including:
-
Chronic Disease Management: By identifying geographic clusters of individuals with chronic diseases, health atlas maps facilitate targeted interventions and resource allocation. This includes promoting health education, providing access to specialized care, and supporting community-based initiatives.
-
Maternal and Child Health: Health atlas maps are instrumental in understanding geographical variations in maternal and child health indicators, such as birth rates, infant mortality rates, and access to prenatal care. This data-driven approach informs interventions aimed at improving maternal and child health outcomes.
-
Mental Health Services: By visualizing the distribution of mental health services and the prevalence of mental health conditions, health atlas maps enable the identification of gaps in service provision and the development of targeted interventions. This ensures equitable access to mental healthcare for all.
-
Environmental Health: Health atlas maps are valuable tools for understanding the relationship between environmental factors and health outcomes. By overlaying environmental data, such as air pollution levels or water quality, with health data, these maps reveal potential environmental risk factors and guide interventions aimed at mitigating environmental health hazards.
-
Disaster Response and Preparedness: Health atlas maps play a vital role in disaster preparedness and response by identifying vulnerable populations, mapping evacuation routes, and facilitating the distribution of aid. This data-driven approach ensures efficient and targeted disaster response efforts.
Unveiling the Data: Understanding the Components of Health Atlas Maps
Health atlas maps are built upon a foundation of various health data sources, including:
-
Disease Registries: Data from disease registries provides information on the prevalence and incidence of specific diseases within defined geographical areas.
-
Mortality Data: Mortality data, often obtained from death certificates, offers insights into the leading causes of death and geographical variations in mortality rates.
-
Health Service Utilization Data: Data on healthcare service utilization, such as hospital admissions, doctor visits, and prescription fills, reveals patterns in access to care and potential disparities in healthcare utilization.
-
Demographic Data: Census data and population statistics provide information on population density, age distribution, socioeconomic status, and other demographic factors that influence health outcomes.
-
Environmental Data: Environmental data, such as air pollution levels, water quality, and proximity to hazardous waste sites, can be integrated with health data to identify potential environmental risk factors.
Navigating the Landscape: FAQs on Health Atlas Maps
1. What are the limitations of health atlas maps?
While powerful tools, health atlas maps have limitations that must be considered. Data availability and quality can vary across regions, potentially leading to biases and inaccuracies. Additionally, the maps may not capture all relevant factors influencing health outcomes, such as social determinants of health or individual behavioral factors.
2. How can data privacy be protected when using health atlas maps?
Data privacy is a crucial consideration when working with sensitive health data. Health atlas maps should utilize anonymized data and employ robust data security measures to protect individual privacy. Ethical considerations and data governance practices are paramount in ensuring responsible data utilization.
3. What are the challenges associated with using health atlas maps?
Challenges in using health atlas maps include data collection and standardization, ensuring data quality and accuracy, and overcoming potential biases in data interpretation. Furthermore, translating data insights into actionable interventions requires collaboration between policymakers, healthcare providers, and communities.
4. What is the future of health atlas maps?
The future of health atlas maps holds immense potential. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies can enhance data analysis, predictive modeling, and the identification of hidden patterns in health data. This advancement will lead to more sophisticated and insightful health atlas maps, further informing healthcare decision-making and improving health outcomes.
Navigating the Path: Tips for Effective Use of Health Atlas Maps
-
Collaborate with Experts: Engage with experts in public health, GIS, and data analysis to ensure accurate data interpretation and the development of effective interventions.
-
Consider Data Quality: Assess the reliability and completeness of data sources to ensure the validity of the maps and the accuracy of derived insights.
-
Address Data Privacy: Implement robust data security measures and adhere to ethical guidelines for data collection and utilization to protect individual privacy.
-
Engage Communities: Involve communities in the development and implementation of interventions based on health atlas maps to ensure relevance and sustainability.
-
Continuously Monitor and Evaluate: Regularly monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions informed by health atlas maps to ensure ongoing improvement and adaptation.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Health Equity
Health atlas maps serve as invaluable tools for understanding and addressing health disparities. They provide a visual representation of health data, revealing patterns and trends that inform policy decisions, resource allocation, and the development of targeted interventions. By utilizing these maps effectively, we can strive towards a more equitable and healthier future for all.


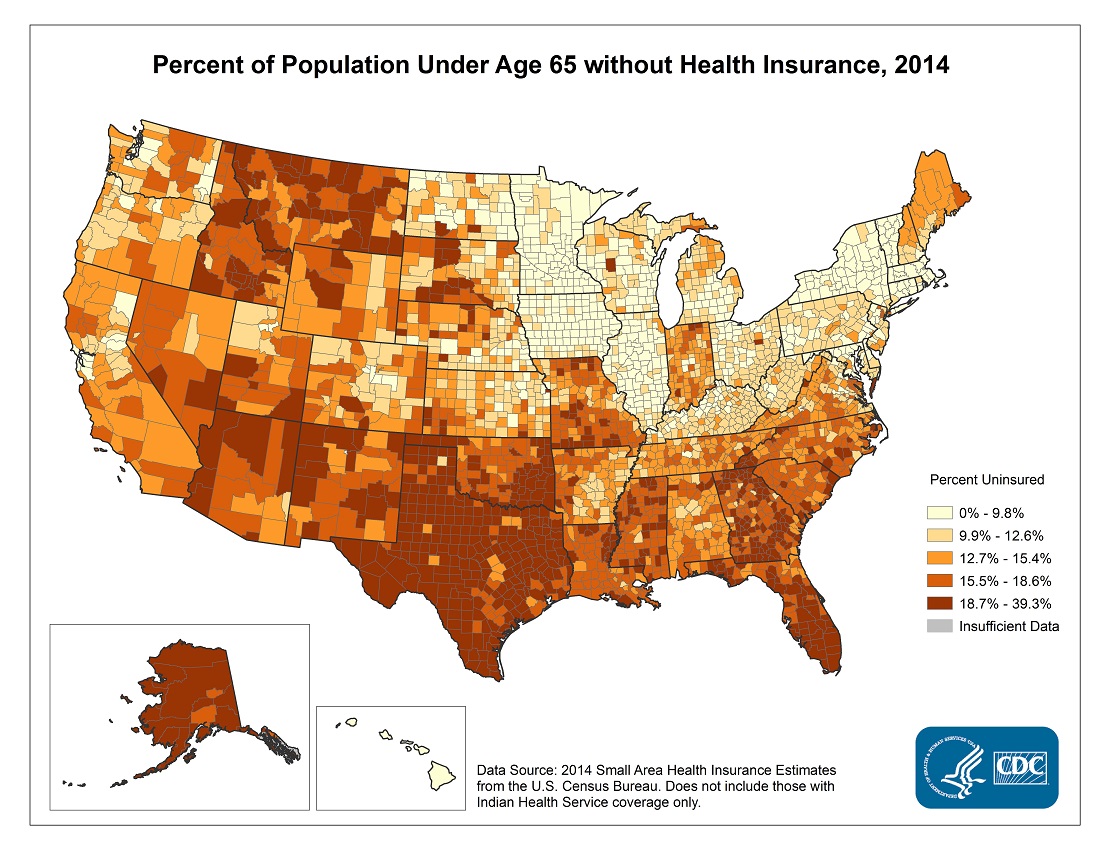



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Health Disparities: A Comprehensive Look at Health Atlas Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!