Unraveling The Earth: A Journey Through Latitude And Longitude
Unraveling the Earth: A Journey Through Latitude and Longitude
Related Articles: Unraveling the Earth: A Journey Through Latitude and Longitude
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Earth: A Journey Through Latitude and Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Earth: A Journey Through Latitude and Longitude

The world, in its vastness and complexity, can be daunting to comprehend. Yet, beneath the seemingly chaotic arrangement of continents, oceans, and landscapes lies an intricate grid system – a framework that enables us to pinpoint any location on Earth with remarkable accuracy. This system, known as latitude and longitude, is the foundation upon which our understanding of geography and global connectivity is built.
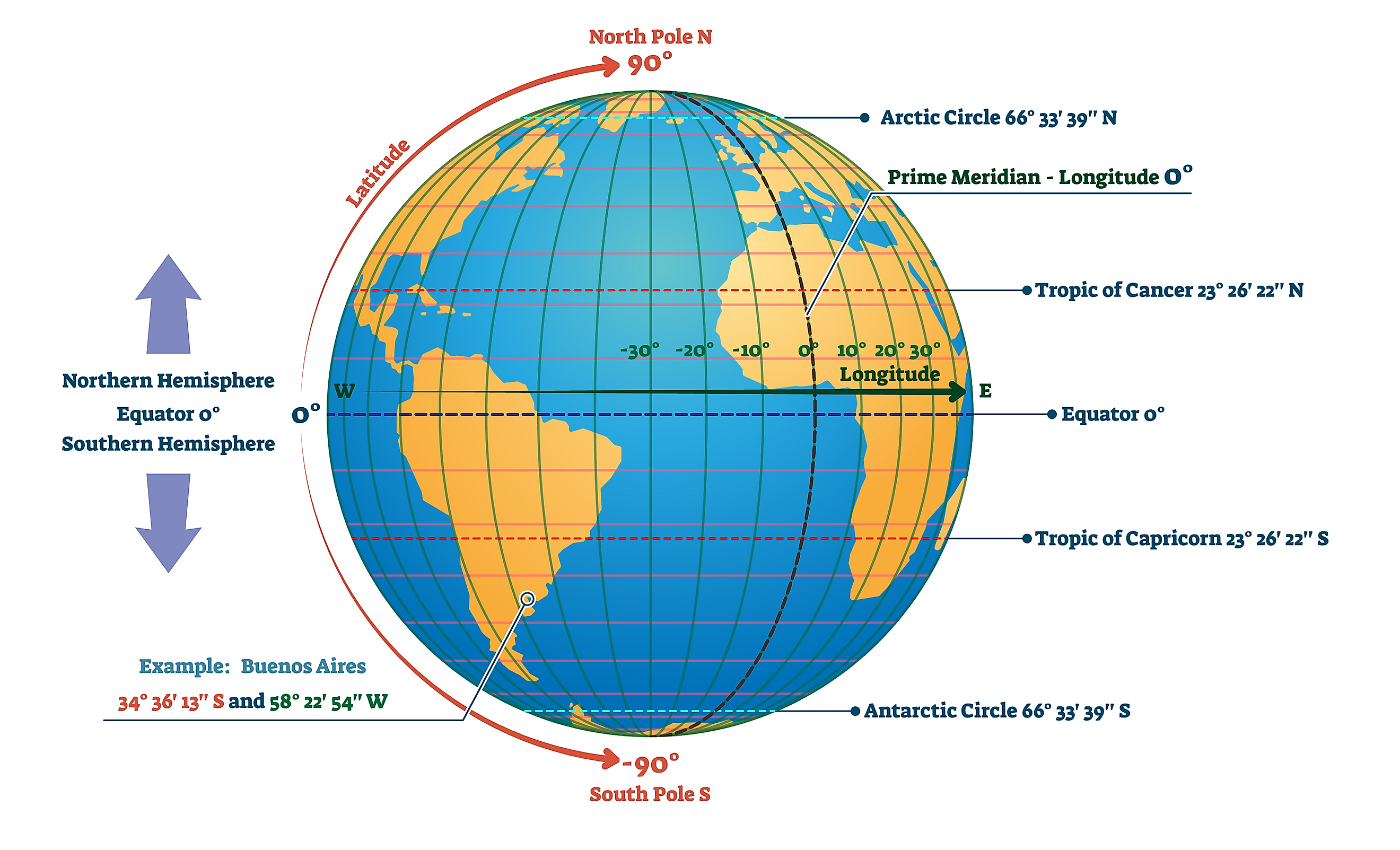
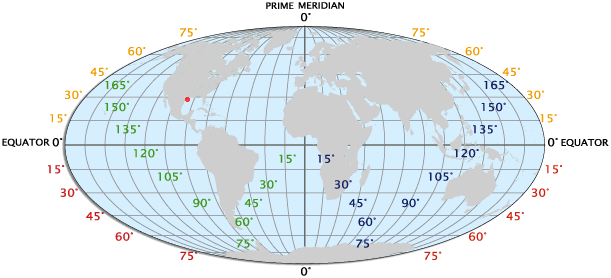
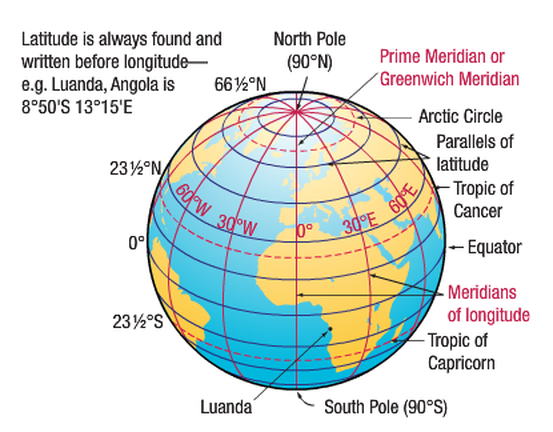
Latitude: Tracing the Horizontal Lines
Imagine slicing the Earth like a giant orange, with each slice representing a parallel circle running east to west. These circles, known as lines of latitude, are the horizontal lines on a map. The equator, the imaginary line that circles the Earth at zero degrees, divides the globe into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Each degree of latitude north or south of the equator represents approximately 111 kilometers (69 miles).
Latitude plays a crucial role in determining a location’s climate. Regions closer to the equator, with higher latitude values, receive more direct sunlight and experience warmer temperatures. Conversely, areas closer to the poles, with lower latitude values, receive less direct sunlight and experience colder temperatures.
Longitude: Charting the Vertical Lines
Now imagine slicing the Earth from the North Pole to the South Pole, each slice representing a semi-circle that runs from pole to pole. These semi-circles, known as lines of longitude, are the vertical lines on a map. The Prime Meridian, the imaginary line that passes through Greenwich, England, serves as the zero-degree longitude line and divides the globe into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. Each degree of longitude east or west of the Prime Meridian represents approximately 111 kilometers (69 miles) at the equator, gradually decreasing towards the poles.
Longitude is essential for determining a location’s time zone. As the Earth rotates on its axis, different parts of the globe experience sunrise and sunset at different times. The lines of longitude are used to divide the Earth into 24 time zones, each representing one hour of the Earth’s rotation.
The Power of Intersection: Pinpointing Locations
When lines of latitude and longitude intersect, they create a unique point on the Earth’s surface. This intersection, expressed as a pair of coordinates (latitude, longitude), provides a precise location for any place on the planet. For example, the coordinates 40.7128° N, 74.0060° W pinpoint the location of Times Square in New York City.
Beyond Navigation: The Significance of Latitude and Longitude
While latitude and longitude are fundamental for navigation, their significance extends far beyond simply finding one’s way around. They are crucial tools for:
- Mapping and Cartography: Latitude and longitude form the basis of all maps, allowing cartographers to accurately represent the Earth’s surface on a flat plane.
- Geographical Research: Scientists use latitude and longitude to study the distribution of flora and fauna, analyze climate patterns, and understand geological formations.
- Global Communication: Latitude and longitude are essential for satellite navigation systems, enabling us to pinpoint our location and navigate with precision.
- Weather Forecasting: Meteorologists use latitude and longitude to track weather patterns, predict storms, and issue warnings.
- Resource Management: Governments and organizations utilize latitude and longitude to manage natural resources, track deforestation, and monitor environmental changes.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
A: Latitude measures the angular distance north or south of the equator, while longitude measures the angular distance east or west of the Prime Meridian. Latitude lines are horizontal, while longitude lines are vertical.
Q: How do latitude and longitude affect climate?
A: Latitude directly influences climate by determining the amount of direct sunlight a region receives. Regions closer to the equator, with higher latitude values, experience warmer temperatures due to more direct sunlight.
Q: Why is the Prime Meridian located at Greenwich, England?
A: The Prime Meridian was established at Greenwich, England, in the 19th century because the Royal Observatory at Greenwich was a leading center for astronomical research.
Q: How are latitude and longitude used in satellite navigation systems?
A: Satellite navigation systems, such as GPS, use latitude and longitude to calculate a device’s precise location on Earth. They do this by receiving signals from multiple satellites, which transmit their own latitude and longitude coordinates.
Q: What are some examples of how latitude and longitude are used in everyday life?
A: Latitude and longitude are used in a variety of everyday applications, such as:
- Smartphone navigation apps: These apps utilize latitude and longitude to provide directions and real-time traffic updates.
- Weather forecasts: Weather reports often include latitude and longitude coordinates to pinpoint the location of storms or other weather events.
- Online mapping services: Websites like Google Maps and Bing Maps use latitude and longitude to display locations and provide directions.
Tips
- Understanding the Grid System: Familiarize yourself with the concept of latitude and longitude as a grid system, with lines of latitude running horizontally and lines of longitude running vertically.
- Using a World Atlas: Refer to a world atlas to visualize how latitude and longitude lines are displayed on maps and how they intersect to pinpoint locations.
- Practice with Coordinates: Practice identifying locations based on their latitude and longitude coordinates. This will help you develop a better understanding of the system.
- Exploring Online Tools: Utilize online mapping tools, such as Google Earth, to explore the globe and experiment with latitude and longitude coordinates.
Conclusion
The system of latitude and longitude is an essential framework for understanding our planet. It provides a universal language for describing locations, enabling us to navigate, map, and study the Earth with precision. From navigating the vast oceans to tracking weather patterns, latitude and longitude are integral to our understanding of the world and our place within it. As we continue to explore and interact with our planet, the importance of this fundamental grid system will only grow.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Earth: A Journey Through Latitude and Longitude. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!