Unmasking The Geography Of Hepatitis B And C Mortality: A County-Level Perspective
Unmasking the Geography of Hepatitis B and C Mortality: A County-Level Perspective
Related Articles: Unmasking the Geography of Hepatitis B and C Mortality: A County-Level Perspective
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unmasking the Geography of Hepatitis B and C Mortality: A County-Level Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unmasking the Geography of Hepatitis B and C Mortality: A County-Level Perspective

Hepatitis B and C, viral infections that primarily affect the liver, pose a significant global health burden. While substantial progress has been made in combating these diseases, they continue to claim lives, particularly in certain geographic regions and demographic groups. Understanding the spatial distribution of hepatitis-related deaths is crucial for informing public health interventions, resource allocation, and targeted prevention efforts.
Visualizing the Impact: County-Level Mortality Maps
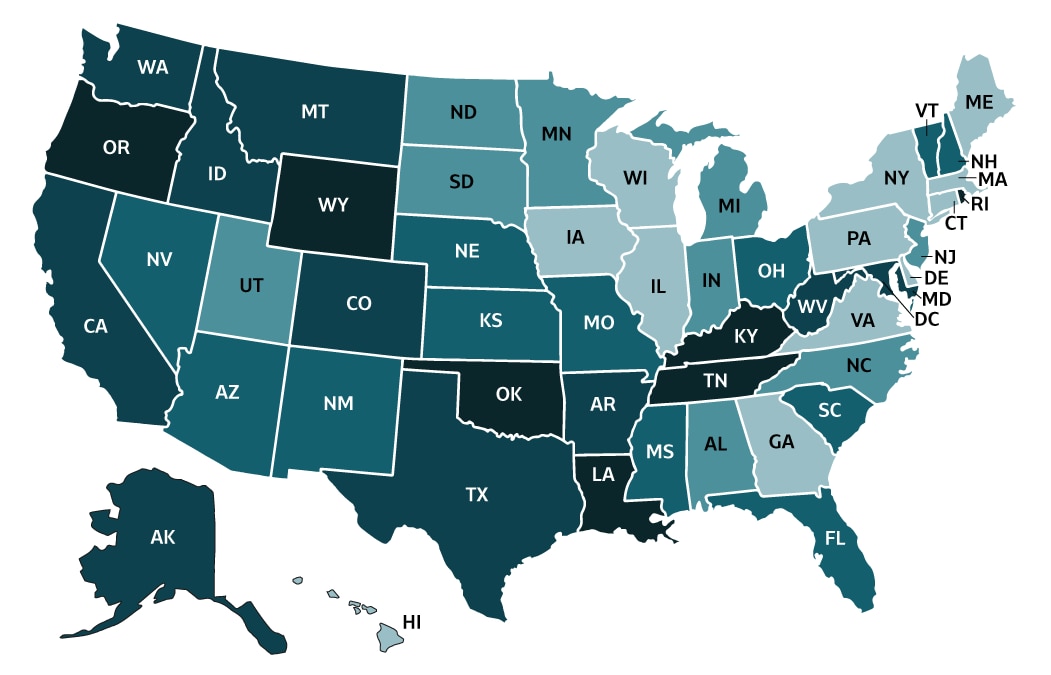
County-level mortality maps, which depict the number of deaths attributed to hepatitis B and C in each county, provide a powerful visual representation of the disease’s impact across different geographic areas. These maps serve as essential tools for:
- Identifying High-Risk Areas: By highlighting counties with disproportionately high mortality rates, these maps pinpoint areas where the need for increased public health resources and intervention programs is most acute.
- Understanding Spatial Trends: The maps reveal geographical patterns of hepatitis-related deaths, allowing researchers and public health officials to identify potential contributing factors such as socioeconomic disparities, access to healthcare, and prevalence of risk factors like injection drug use.
- Monitoring Progress: Over time, comparing mortality maps from different years can help track the effectiveness of public health initiatives and identify areas where interventions may need to be adjusted.
Interpreting the Data: Key Insights and Considerations
When analyzing county-level hepatitis B and C mortality maps, it is essential to consider several factors that can influence the data:
- Population Density: Counties with higher population densities may naturally have higher death counts, even if the mortality rate per capita is lower.
- Data Availability and Accuracy: The quality and completeness of mortality data can vary across counties, potentially affecting the accuracy of the map.
- Underlying Risk Factors: The map alone does not reveal the root causes of hepatitis-related deaths. Further investigation is needed to understand the specific risk factors and social determinants of health driving mortality in each county.
Beyond the Map: A Deeper Dive into Contributing Factors
While county-level maps provide a valuable snapshot of hepatitis B and C mortality, they do not tell the full story. To address these complex public health challenges, it is crucial to delve deeper into the underlying factors contributing to these deaths. These factors may include:
- Socioeconomic Disparities: Lower socioeconomic status, limited access to healthcare, and lack of health insurance are often associated with higher rates of hepatitis infection and mortality.
- Injection Drug Use: Sharing needles for injecting drugs is a major route of transmission for hepatitis B and C. Communities with higher rates of injection drug use may experience higher mortality rates.
- Access to Healthcare: Limited access to testing, treatment, and preventive services can contribute to delayed diagnosis and missed opportunities for early intervention.
- Stigma and Discrimination: Stigma associated with hepatitis B and C can hinder individuals from seeking testing and treatment, leading to delayed diagnosis and increased risk of complications.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: How are hepatitis B and C deaths classified and recorded?
A: Deaths are classified based on the underlying cause of death reported on death certificates. If hepatitis B or C is identified as the primary or contributing cause of death, the case is included in the mortality data.
Q: How often are these county-level maps updated?
A: The frequency of updates depends on the data source and the specific jurisdiction. In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) releases mortality data annually.
Q: What are some limitations of county-level mortality maps?
A: As with any data visualization, county-level maps have limitations. They may not accurately reflect the mortality burden in smaller geographic areas or within specific demographic groups. Additionally, the data may not capture all hepatitis-related deaths, particularly those not attributed to the disease on death certificates.
Tips: Utilizing County-Level Mortality Maps for Public Health Action
- Identify High-Risk Counties: Prioritize counties with elevated mortality rates for targeted interventions and resource allocation.
- Collaborate with Local Partners: Engage with local public health agencies, community organizations, and healthcare providers to develop tailored strategies.
- Address Underlying Risk Factors: Implement programs addressing socioeconomic disparities, injection drug use, and access to healthcare.
- Promote Stigma Reduction: Raise awareness about hepatitis B and C, promote testing and treatment, and combat stigma through public education campaigns.
- Monitor Progress: Regularly review mortality data to assess the effectiveness of interventions and adjust strategies as needed.
Conclusion: A Call for Action
County-level mortality maps provide a powerful visual tool for understanding the geographic distribution of hepatitis B and C deaths. By highlighting areas of high mortality, these maps can guide public health efforts to address the disease’s impact, prevent future deaths, and improve the lives of those affected. However, it is crucial to remember that the maps are only one piece of the puzzle. A comprehensive approach that considers the complex interplay of social, economic, and healthcare factors is essential to combat this ongoing public health challenge. By utilizing these maps to inform targeted interventions, promote access to care, and address underlying risk factors, we can strive to reduce hepatitis-related deaths and improve health outcomes for all.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unmasking the Geography of Hepatitis B and C Mortality: A County-Level Perspective. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!