Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Calculation And Significance
Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Calculation and Significance
Related Articles: Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Calculation and Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Calculation and Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Calculation and Significance
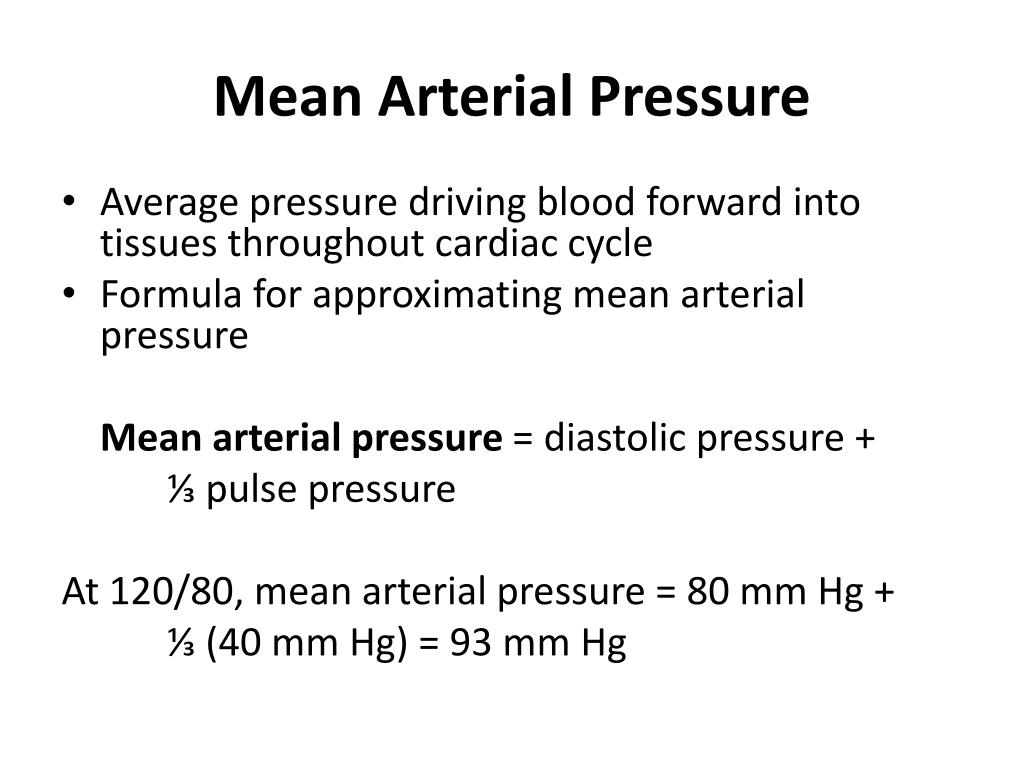
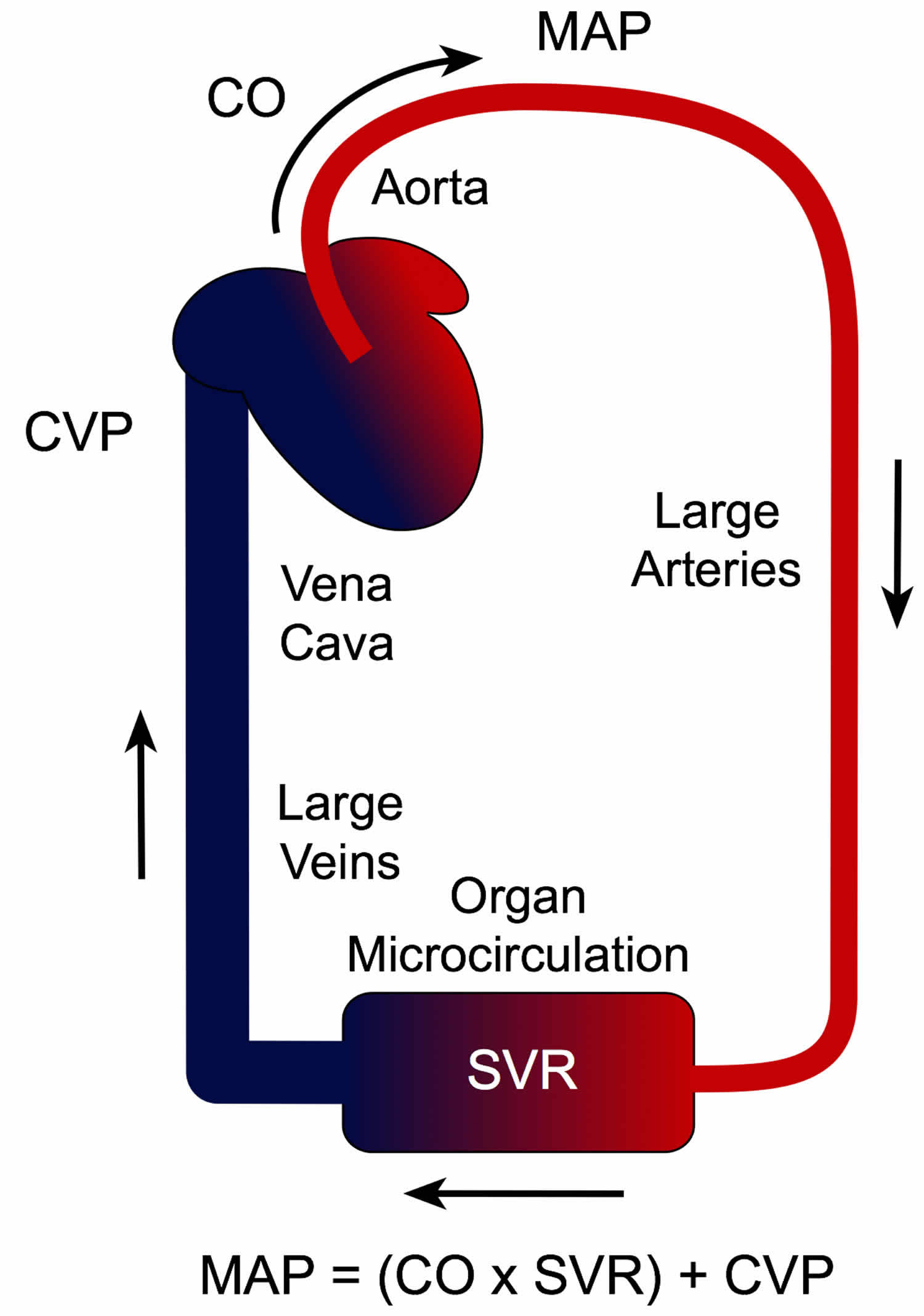
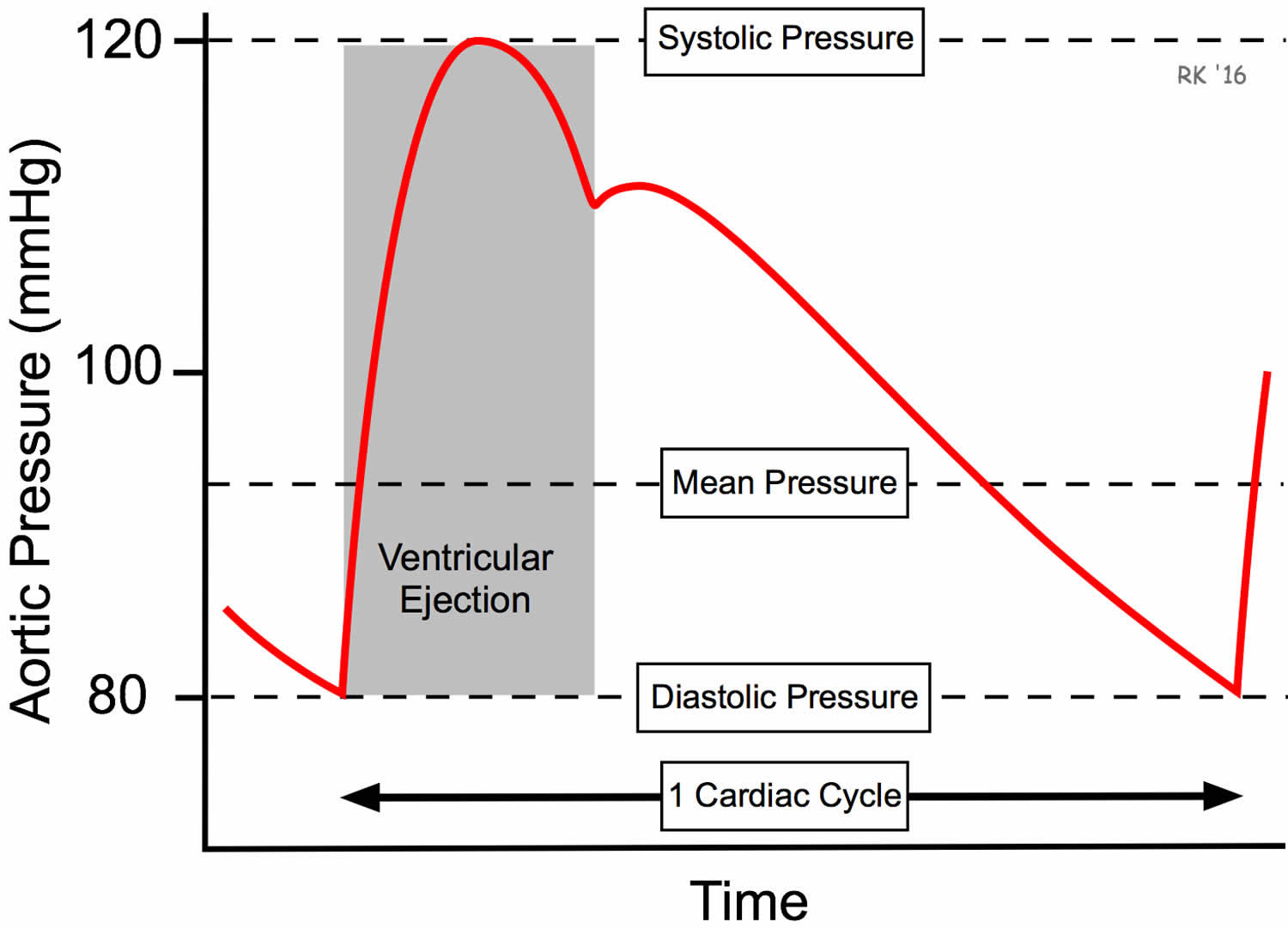
Mean arterial pressure (MAP) represents the average pressure exerted by the blood against the walls of the arteries during a single cardiac cycle. It is a crucial indicator of cardiovascular health, as it reflects the overall perfusion pressure driving blood flow to vital organs. Unlike systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings, which represent peak and minimum pressures respectively, MAP provides a more holistic picture of the circulatory system’s performance.
Calculating Mean Arterial Pressure: A Simple Formula
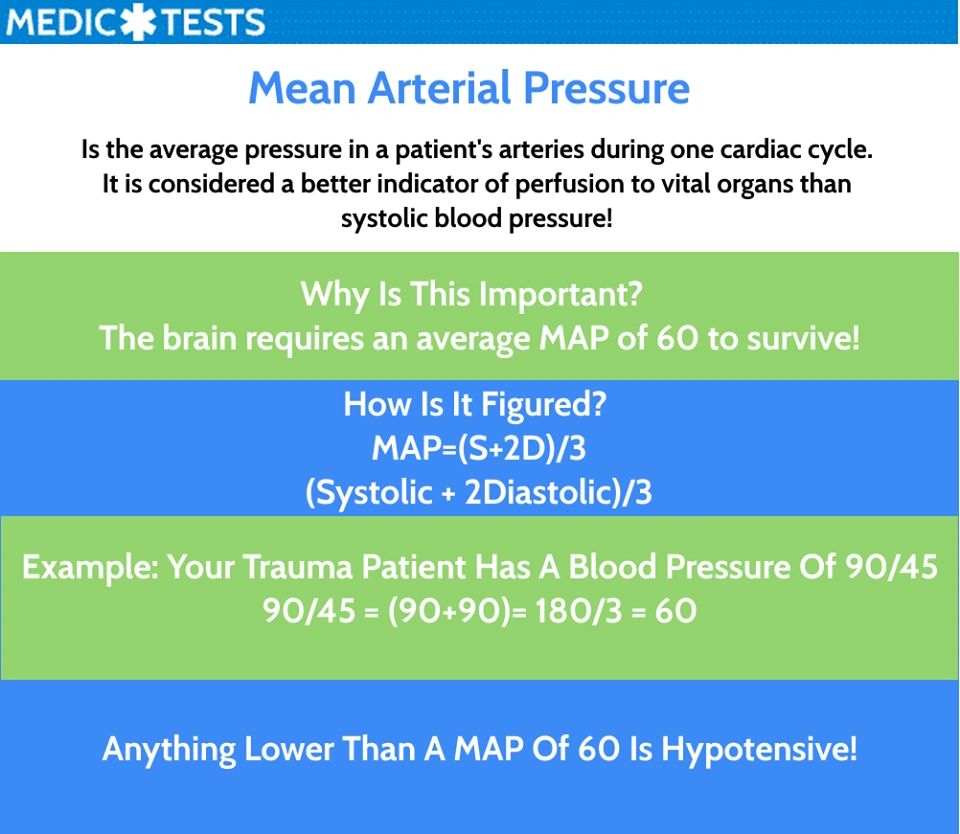
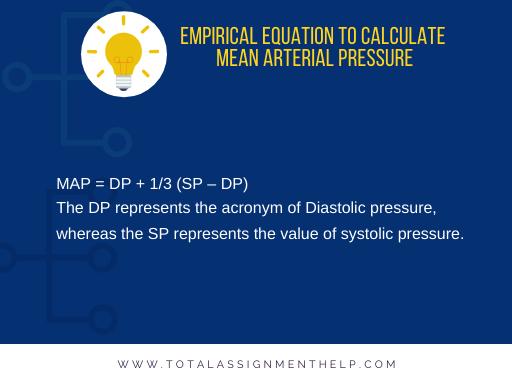
The most commonly used formula for calculating MAP is:
MAP = Diastolic Blood Pressure + 1/3 (Systolic Blood Pressure – Diastolic Blood Pressure)
This formula takes into account both the diastolic pressure, which represents the pressure when the heart is relaxed, and the systolic pressure, which represents the pressure when the heart contracts. The difference between these two pressures, known as the pulse pressure, is then weighted by 1/3 to account for the fact that the heart spends more time in diastole than in systole.
Interpreting Mean Arterial Pressure: A Guide to Normal Values and Risks
The normal range for MAP varies slightly depending on individual factors such as age and medical conditions. Generally, a MAP of 70-100 mmHg is considered normal for most adults. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
A MAP below 60 mmHg may indicate insufficient blood flow to vital organs, potentially leading to complications like organ dysfunction or even failure. Conversely, a MAP above 100 mmHg may signal an increased risk of cardiovascular events such as stroke, heart attack, and aneurysm.
The Importance of Mean Arterial Pressure Monitoring: A Crucial Tool for Cardiovascular Health
Monitoring MAP is crucial for several reasons:
- Early Detection of Cardiovascular Issues: Elevated or low MAP readings can serve as early warning signs of potential cardiovascular problems. Regular monitoring can help identify individuals at risk of developing complications.
- Effective Management of Cardiovascular Conditions: For individuals with existing cardiovascular conditions, monitoring MAP is vital for adjusting medication dosages and ensuring optimal treatment outcomes.
- Assessing the Effectiveness of Treatments: MAP measurements can help assess the effectiveness of various treatments, including medications and lifestyle modifications.
- Personalized Care and Risk Assessment: By providing a comprehensive picture of circulatory health, MAP measurements can contribute to personalized care plans and accurate risk assessments for cardiovascular disease.
Factors Influencing Mean Arterial Pressure: A Multifaceted Perspective
Several factors can influence MAP, including:
- Heart Rate: A faster heart rate generally leads to a higher MAP, as the heart pumps blood more frequently.
- Blood Volume: An increased blood volume, often due to fluid retention, can elevate MAP.
- Arterial Stiffness: As arteries become less flexible with age or due to conditions like atherosclerosis, MAP tends to increase.
- Peripheral Resistance: Narrowing of blood vessels, often caused by conditions like hypertension, can increase resistance to blood flow and raise MAP.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as vasoconstrictors or stimulants, can influence MAP.
- Lifestyle Factors: Factors like smoking, stress, and lack of physical activity can contribute to elevated MAP.
Frequently Asked Questions about Mean Arterial Pressure
Q: Can I measure my own MAP at home?
A: While home blood pressure monitors can measure systolic and diastolic pressures, they typically do not calculate MAP. Consulting a healthcare professional is recommended for accurate MAP measurements.
Q: What are the risks of having a high or low MAP?
A: High MAP can increase the risk of stroke, heart attack, and aneurysm. Low MAP can lead to insufficient blood flow to vital organs, potentially causing organ dysfunction or failure.
Q: How can I lower my MAP if it is high?
A: Lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management can help lower MAP. In some cases, medication may be necessary.
Q: What are the benefits of monitoring my MAP?
A: Monitoring MAP can help detect early signs of cardiovascular problems, ensure effective treatment for existing conditions, and assess the effectiveness of interventions.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Mean Arterial Pressure
- Regular Blood Pressure Checks: Schedule regular checkups with your healthcare provider to monitor your blood pressure and MAP.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Engage in regular physical activity, maintain a balanced diet, and manage stress effectively.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and can elevate MAP.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can damage the heart and blood vessels, potentially leading to high MAP.
- Manage Underlying Conditions: If you have conditions like diabetes, high cholesterol, or thyroid disease, manage them effectively as they can impact MAP.
Conclusion: The Significance of Mean Arterial Pressure in Cardiovascular Health
Mean arterial pressure is a crucial indicator of cardiovascular health, providing a more comprehensive picture of circulatory system performance than traditional systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings. Monitoring MAP can help identify individuals at risk of developing cardiovascular complications, facilitate effective management of existing conditions, and assess the effectiveness of treatments. By understanding the importance of MAP and adopting healthy lifestyle choices, individuals can proactively contribute to their cardiovascular well-being.

.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Calculation and Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!