Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 The Importance of Mean Arterial Pressure
- 3.2 Calculating Mean Arterial Pressure
- 3.3 MAP Calculator: A Useful Tool for Healthcare Professionals
- 3.4 MAP in Clinical Practice
- 3.5 Factors Influencing Mean Arterial Pressure
- 3.6 The Importance of Maintaining a Healthy MAP
- 3.7 FAQs about Mean Arterial Pressure
- 3.8 Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Mean Arterial Pressure
- 3.9 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide
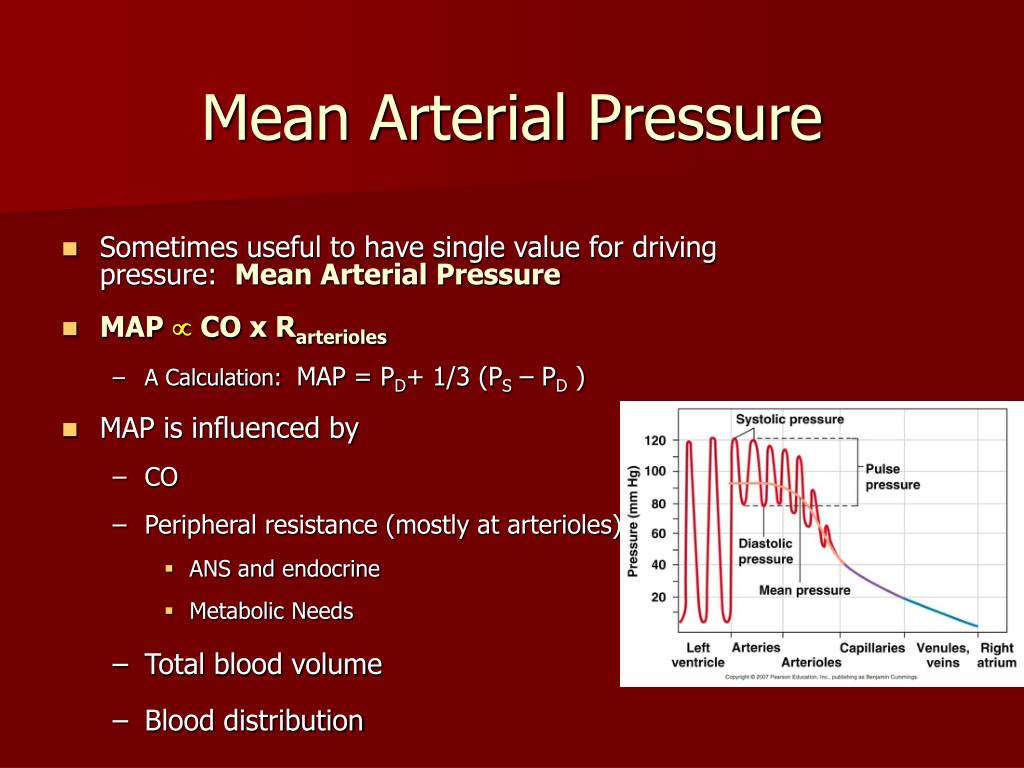
Mean arterial pressure (MAP) is a crucial indicator of cardiovascular health, representing the average pressure exerted by the blood against the walls of the arteries during a single cardiac cycle. It is a more accurate reflection of overall tissue perfusion than systolic or diastolic pressure alone, providing vital information about the body’s ability to deliver oxygen and nutrients to organs and tissues.
The Importance of Mean Arterial Pressure
MAP is a fundamental parameter used in clinical settings to assess the adequacy of blood flow to vital organs. Maintaining a healthy MAP is essential for:
- Adequate Tissue Perfusion: MAP directly influences the amount of blood delivered to tissues. A sufficient MAP ensures adequate oxygen and nutrient delivery, supporting proper cellular function.
- Organ Function: Organs like the brain, kidneys, and heart require a consistent blood supply to operate optimally. A healthy MAP ensures these organs receive the necessary blood flow to function effectively.
- Cardiovascular Health: Sustained high or low MAP can indicate underlying cardiovascular issues. Monitoring MAP helps identify potential problems early and facilitates timely interventions.
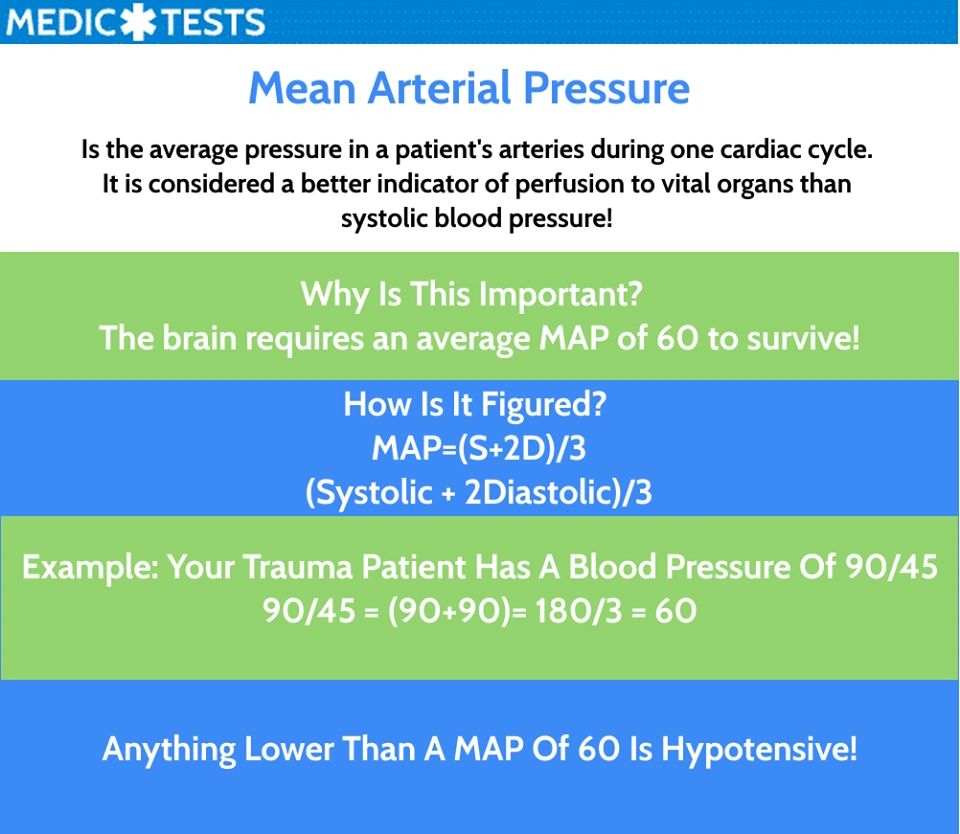
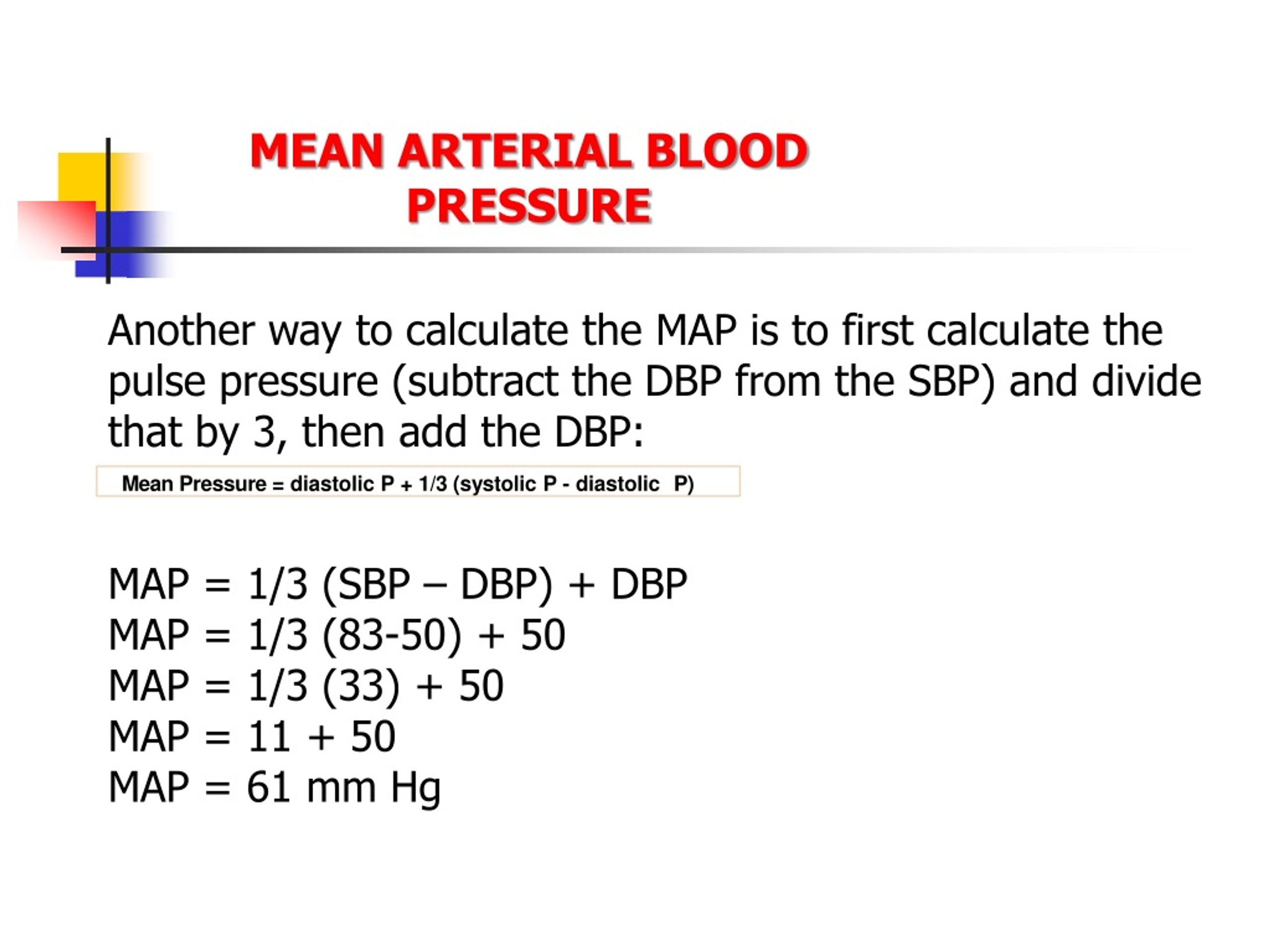
Calculating Mean Arterial Pressure
MAP is typically calculated using a simple formula:
*MAP = (Diastolic Pressure + (1/3 (Systolic Pressure – Diastolic Pressure)))**
This formula considers the time spent in diastole (the relaxation phase of the heart cycle) and systole (the contraction phase) to determine the average pressure.
MAP Calculator: A Useful Tool for Healthcare Professionals
MAP calculators are readily available online and in various medical software programs. These tools simplify the process of calculating MAP, eliminating the need for manual calculation and reducing the risk of errors. They are particularly valuable for:
- Rapid Assessment: MAP calculators provide immediate results, enabling quick assessment of a patient’s hemodynamic status.
- Accuracy and Consistency: Automated calculations ensure accuracy and consistency, minimizing potential variations in manual calculations.
- Convenience: MAP calculators are easily accessible, allowing for convenient and time-efficient calculations.
MAP in Clinical Practice
MAP is routinely monitored in various clinical settings, including:
- Critical Care: In intensive care units (ICUs), MAP is closely monitored to ensure adequate organ perfusion and guide fluid management.
- Emergency Medicine: MAP is a crucial parameter in emergency situations, aiding in the diagnosis and management of shock and other cardiovascular emergencies.
- Anesthesia: During surgical procedures, MAP is closely monitored to ensure adequate blood flow to vital organs and manage potential complications.
- Cardiology: In cardiology practice, MAP is monitored to assess cardiovascular health, guide treatment decisions, and track the effectiveness of interventions.
Factors Influencing Mean Arterial Pressure
Several factors can influence MAP, including:
- Cardiac Output: The amount of blood pumped by the heart per minute directly affects MAP. Increased cardiac output generally leads to higher MAP.
- Peripheral Vascular Resistance: The resistance to blood flow in the peripheral arteries influences MAP. Increased resistance, often due to vasoconstriction, increases MAP.
- Blood Volume: The total volume of blood in the circulatory system affects MAP. Increased blood volume, often due to fluid retention, typically elevates MAP.
The Importance of Maintaining a Healthy MAP
Maintaining a healthy MAP is essential for overall health and well-being. Factors contributing to an unhealthy MAP include:
- High Blood Pressure: Chronically elevated MAP can lead to various health problems, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and eye damage.
- Low Blood Pressure: Prolonged low MAP can cause dizziness, fatigue, and even organ damage.
- Medications: Some medications can affect MAP, requiring careful monitoring and adjustments.
FAQs about Mean Arterial Pressure
1. What is a normal mean arterial pressure?
A normal MAP for adults typically ranges between 70-100 mmHg. However, individual values may vary based on age, health status, and other factors.
2. What are the risks of high mean arterial pressure?
High MAP increases the risk of various cardiovascular complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
3. What are the risks of low mean arterial pressure?
Low MAP can lead to dizziness, fatigue, and organ damage, especially in the brain and kidneys.
4. How can I lower my mean arterial pressure?
Lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, weight management, and stress reduction, can help lower MAP. In some cases, medication may be necessary.
5. How can I increase my mean arterial pressure?
Increasing fluid intake, consuming salty foods, and avoiding certain medications can help increase MAP. However, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Mean Arterial Pressure
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Engage in regular physical activity, consume a balanced diet low in sodium and saturated fats, and manage stress effectively.
- Monitor Blood Pressure Regularly: Regularly check your blood pressure at home or consult your healthcare provider for professional monitoring.
- Follow Medical Advice: If diagnosed with high or low blood pressure, adhere to your healthcare provider’s recommendations for medication and lifestyle changes.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to maintain adequate blood volume and support healthy MAP.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of high blood pressure.
Conclusion
Mean arterial pressure is a vital indicator of cardiovascular health, reflecting the average pressure exerted by the blood against the arteries during a cardiac cycle. Understanding MAP and its significance is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals alike. Maintaining a healthy MAP through lifestyle modifications and medical management is essential for preventing cardiovascular complications and promoting overall well-being.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!