Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 The Significance of Mean Arterial Pressure
- 3.2 Calculating Mean Arterial Pressure
- 3.3 Applications of Mean Arterial Pressure Measurement
- 3.4 Factors Influencing Mean Arterial Pressure
- 3.5 Interpretation of Mean Arterial Pressure
- 3.6 FAQs Regarding Mean Arterial Pressure
- 3.7 Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Mean Arterial Pressure
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide
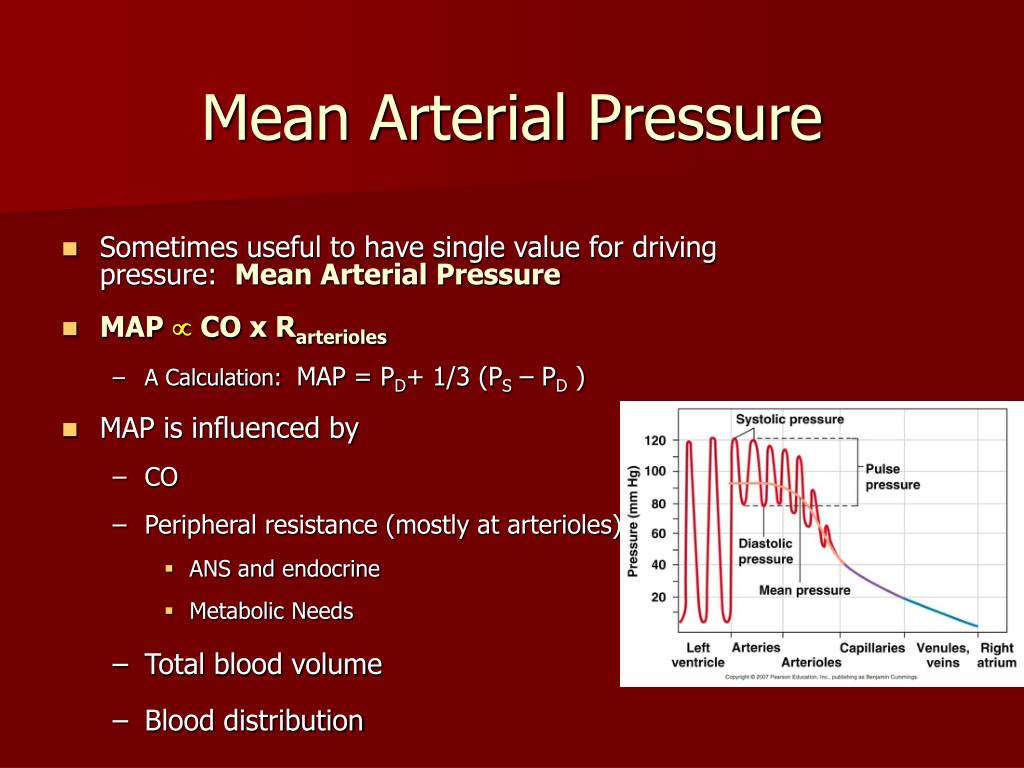
Mean arterial pressure (MAP) is a crucial measure in cardiovascular health, representing the average pressure exerted by the blood against the walls of arteries during a single cardiac cycle. While systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings are familiar, MAP provides a more comprehensive picture of overall cardiovascular function, offering valuable insights into organ perfusion and risk assessment.
The Significance of Mean Arterial Pressure
MAP plays a pivotal role in maintaining adequate blood flow to vital organs. It dictates the pressure gradient driving blood from the heart to the periphery, ensuring the delivery of oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products. Insufficient MAP can lead to inadequate tissue perfusion, potentially causing organ damage and dysfunction. Conversely, persistently elevated MAP can strain the cardiovascular system, contributing to conditions like hypertension and heart disease.
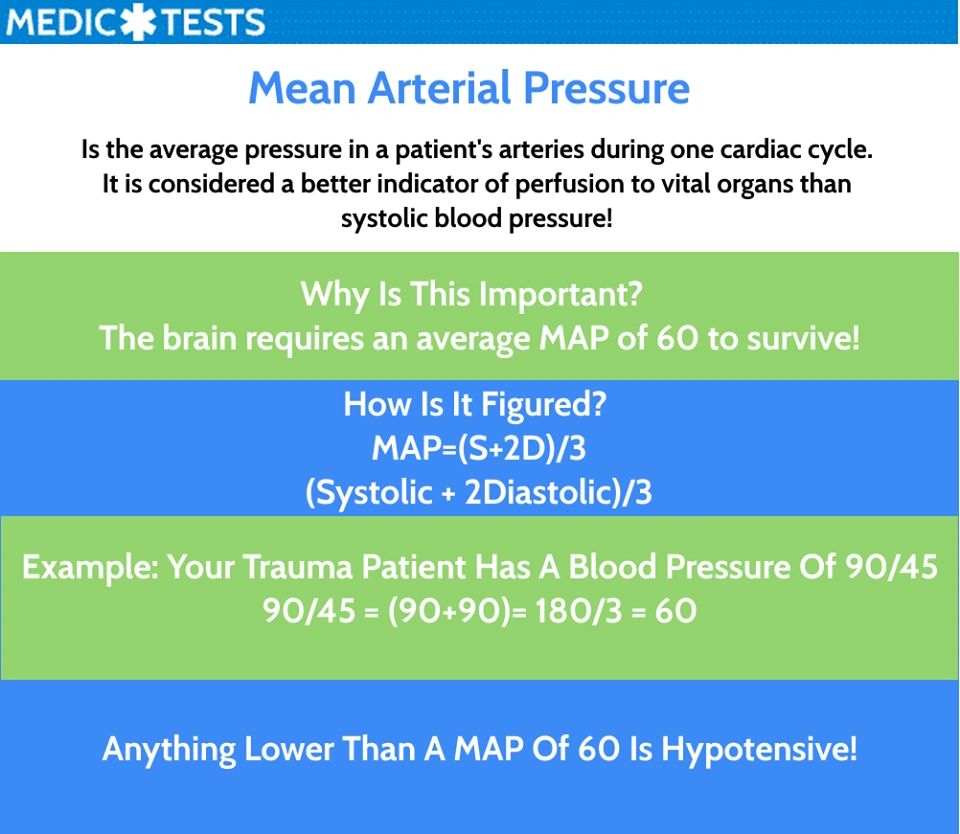
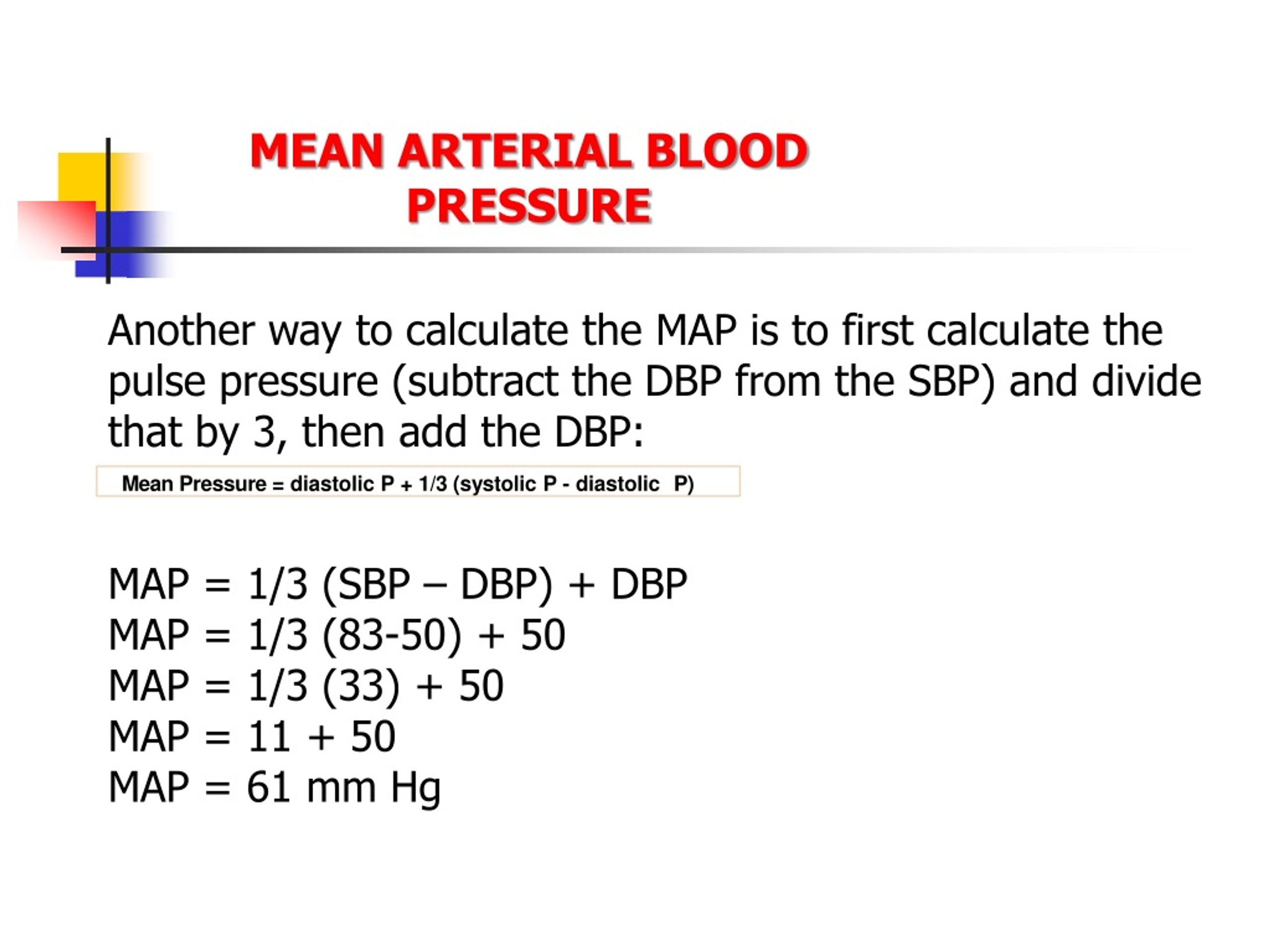
Calculating Mean Arterial Pressure
MAP is not directly measured but rather calculated using a simple formula:
*MAP = Diastolic Blood Pressure + (1/3) (Systolic Blood Pressure – Diastolic Blood Pressure)**
This formula considers the time spent in each phase of the cardiac cycle. Diastolic pressure represents the pressure during the relaxation phase of the heart, lasting the longest portion of the cycle. Systolic pressure, reflecting the pressure during the contraction phase, is only present for a shorter duration. The formula weights the diastolic pressure more heavily, reflecting its longer presence in the cardiac cycle.
Applications of Mean Arterial Pressure Measurement
MAP calculation finds applications in various clinical settings:
- Hypertension Management: Assessing MAP provides a more accurate gauge of cardiovascular risk than isolated systolic or diastolic readings. It helps clinicians tailor treatment plans for patients with hypertension, aiming to maintain optimal MAP levels.
- Organ Perfusion Assessment: MAP is particularly relevant in monitoring patients with critical illnesses, such as sepsis or trauma. Adequate MAP ensures sufficient blood flow to vital organs, especially the brain and kidneys.
- Anesthesia and Intensive Care: Anesthesiologists and intensivists closely monitor MAP during surgery and critical care, adjusting medications and fluids to maintain optimal blood flow and organ function.
- Research and Clinical Trials: MAP is a crucial parameter in cardiovascular research, aiding in the evaluation of new treatments and understanding disease progression.
Factors Influencing Mean Arterial Pressure
Several factors influence MAP, including:
- Cardiac Output: The amount of blood pumped by the heart per minute directly impacts MAP. Higher cardiac output leads to increased MAP.
- Peripheral Vascular Resistance: The resistance to blood flow in the arteries influences MAP. Increased resistance, often associated with vasoconstriction, elevates MAP.
- Blood Volume: The total volume of blood in the circulatory system affects MAP. Increased blood volume, as in hypervolemia, tends to raise MAP.
- Hormonal Factors: Hormones such as adrenaline and noradrenaline can influence MAP by constricting blood vessels.
Interpretation of Mean Arterial Pressure
While a normal MAP range exists, interpretation depends on individual factors and clinical context. Generally, a MAP below 60 mmHg suggests potential tissue perfusion issues, while a MAP above 100 mmHg may indicate elevated cardiovascular risk. However, it’s crucial to consider other factors like age, medical history, and current medications for a comprehensive interpretation.
FAQs Regarding Mean Arterial Pressure
Q: What are the normal ranges for MAP?
A: The normal MAP range varies with age, but generally falls between 70-100 mmHg. However, individual factors and clinical context play a crucial role in interpretation.
Q: Can MAP be measured directly?
A: MAP is not directly measured but rather calculated using the formula mentioned earlier.
Q: What are the potential risks of low MAP?
A: Low MAP can lead to inadequate tissue perfusion, potentially causing organ damage and dysfunction.
Q: What are the potential risks of high MAP?
A: Sustained high MAP can strain the cardiovascular system, contributing to conditions like hypertension and heart disease.
Q: How can I lower my MAP?
A: Lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and a balanced diet can help lower MAP. Consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Q: Can MAP be influenced by medications?
A: Yes, various medications can affect MAP. Consult with your healthcare provider regarding potential interactions and adjustments.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Mean Arterial Pressure
- Adopt a healthy lifestyle: Engage in regular physical activity, maintain a balanced diet low in sodium and saturated fats, and manage stress effectively.
- Monitor your blood pressure: Regularly check your blood pressure and consult with your healthcare provider about any concerning readings.
- Follow your doctor’s recommendations: Adhere to prescribed medications and lifestyle modifications tailored to your individual needs.
- Stay informed: Understand the importance of MAP and its role in overall cardiovascular health.
Conclusion
Mean arterial pressure is a valuable indicator of cardiovascular health, offering insights into organ perfusion and risk assessment. Understanding the significance of MAP and its influencing factors allows individuals and healthcare professionals to make informed decisions regarding prevention, management, and treatment of cardiovascular conditions. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, monitoring blood pressure, and seeking professional guidance, individuals can contribute to maintaining a healthy MAP and overall cardiovascular well-being.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Mean Arterial Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!