The Power Of Spatial Analysis: Unveiling Insights With Map Calculators
The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unveiling Insights with Map Calculators
Related Articles: The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unveiling Insights with Map Calculators
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unveiling Insights with Map Calculators. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unveiling Insights with Map Calculators
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unveiling Insights with Map Calculators
- 3.1 What is a Map Calculator?
- 3.2 The Essence of Spatial Analysis: Unveiling Hidden Patterns
- 3.3 Beyond Calculations: A Toolkit for Spatial Transformation
- 3.4 The Importance of Map Calculators: A Bridge Between Data and Insights
- 3.5 Applications of Map Calculators: A Diverse Spectrum of Possibilities
- 3.6 Unveiling the Power of Map Calculators: FAQs
- 3.7 Tips for Effective Use of Map Calculators
- 3.8 Conclusion: Unleashing the Power of Spatial Analysis
- 4 Closure
The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unveiling Insights with Map Calculators

The world is a complex tapestry woven with intricate relationships between physical and human phenomena. Understanding these connections, visualizing their interplay, and drawing meaningful conclusions requires tools capable of analyzing spatial data. Enter the map calculator, a powerful tool within Geographic Information Systems (GIS) that enables users to perform calculations and manipulations on spatial data, unlocking a world of possibilities for spatial analysis.
What is a Map Calculator?
At its core, a map calculator is a function within GIS software that allows users to perform mathematical operations, logical expressions, and data transformations on spatial data. This data can encompass a wide range of attributes, from elevation and population density to land cover types and environmental variables. By applying calculations to these attributes, users can derive new information, analyze patterns, and gain deeper insights into the relationships between spatial phenomena.
The Essence of Spatial Analysis: Unveiling Hidden Patterns
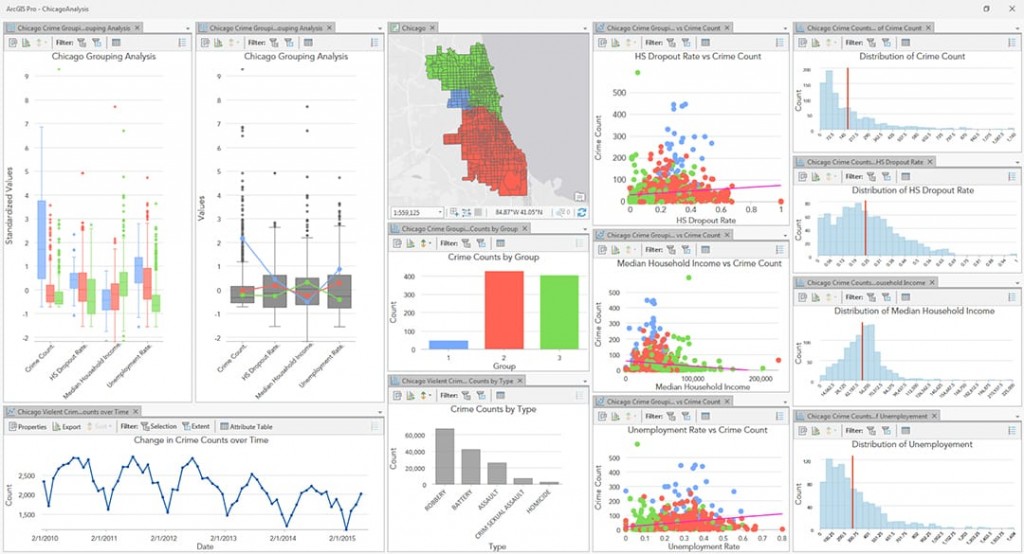
The map calculator serves as a powerful engine for spatial analysis, a critical aspect of GIS that focuses on understanding the spatial distribution and relationships of phenomena. This analysis goes beyond simple map visualization, delving into the ‘why’ and ‘how’ behind spatial patterns. Through map calculators, users can:
- Derive New Data: Calculate distances between features, create new layers based on existing data, and generate derived variables such as population density or slope.
- Identify Relationships: Analyze the correlation between different spatial variables, revealing how factors like land cover and elevation influence population distribution.
- Perform Spatial Queries: Extract data based on specific criteria, such as identifying areas with high flood risk or locating suitable locations for infrastructure development.
- Model Spatial Processes: Simulate the spread of disease, predict environmental impacts, or analyze the effects of climate change on land use patterns.
Beyond Calculations: A Toolkit for Spatial Transformation
The map calculator is not merely a tool for mathematical operations. It empowers users to transform data, manipulate spatial relationships, and create new layers with unique properties. This versatility extends its application beyond simple analysis, enabling users to:
- Reclassify Data: Group data into meaningful categories, such as classifying land cover types into forest, urban, and agricultural areas.
- Create Buffer Zones: Generate areas around features based on a specified distance, useful for analyzing proximity to roads, rivers, or other points of interest.
- Perform Overlay Analysis: Combine multiple layers to identify areas that meet specific criteria, such as finding suitable locations for wind farms based on wind speed, land availability, and proximity to power grids.
- Create Raster Mosaics: Combine multiple raster datasets into a single, continuous layer, useful for creating seamless maps of elevation or land cover.
The Importance of Map Calculators: A Bridge Between Data and Insights
The map calculator plays a pivotal role in bridging the gap between raw spatial data and meaningful insights. It allows users to:
- Extract Value from Data: Transform raw data into valuable information, revealing hidden patterns and relationships that might otherwise remain obscured.
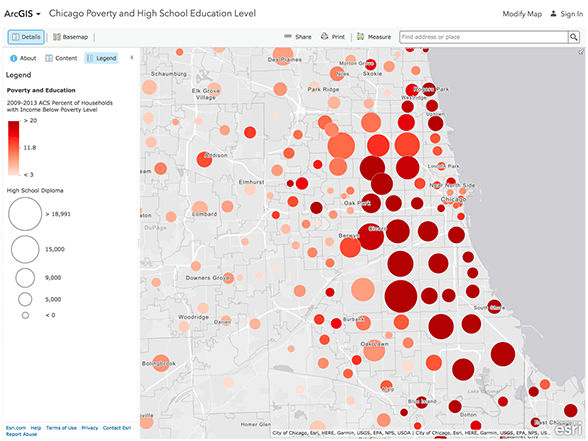
- Visualize Complex Relationships: Represent complex spatial relationships through maps and charts, making complex data accessible and understandable to a wider audience.
- Support Decision-Making: Provide quantitative evidence to support informed decision-making in various fields, including urban planning, environmental management, and resource allocation.
- Advance Research: Enable researchers to analyze spatial data, test hypotheses, and develop new models to understand complex spatial processes.
Applications of Map Calculators: A Diverse Spectrum of Possibilities
The versatility of map calculators extends its application across diverse fields:
- Environmental Management: Analyzing the impact of pollution on water quality, mapping areas vulnerable to deforestation, and identifying suitable locations for renewable energy projects.
- Urban Planning: Optimizing transportation networks, identifying areas for urban renewal, and analyzing the impact of infrastructure development on population density.
- Resource Management: Assessing the availability of natural resources, managing agricultural lands, and optimizing the distribution of water resources.
- Disaster Response: Mapping areas affected by natural disasters, identifying evacuation routes, and assessing the potential impact of future disasters.
- Public Health: Analyzing the spread of diseases, identifying areas with high risk of outbreaks, and planning public health interventions.
Unveiling the Power of Map Calculators: FAQs
1. What are the different types of calculations that can be performed using a map calculator?
Map calculators support a wide range of calculations, including:
- Mathematical Operations: Addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, modulo, and exponentiation.
- Logical Operations: AND, OR, NOT, XOR, and conditional statements.
- Data Transformations: Reclassification, buffer creation, and overlay analysis.
- Trigonometric Functions: Sin, cos, tan, asin, acos, atan.
- Statistical Functions: Mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and variance.
2. What are the different types of data that can be used with a map calculator?
Map calculators can handle various data types, including:
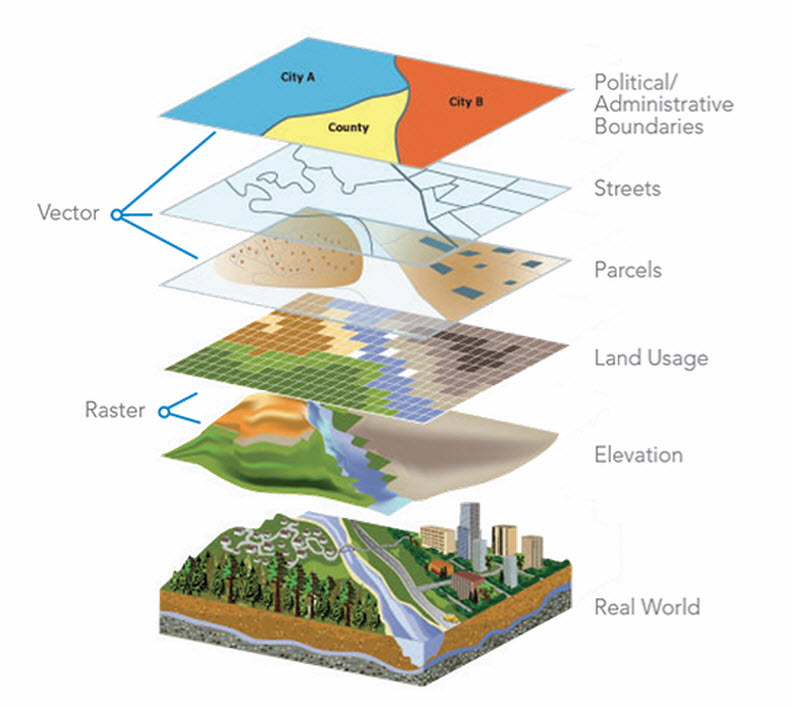
- Vector Data: Points, lines, and polygons representing features on the Earth’s surface.
- Raster Data: Gridded data representing continuous variables like elevation, temperature, and precipitation.
- Attribute Data: Tables containing information associated with spatial features.
3. How can I learn to use a map calculator effectively?
Most GIS software provides comprehensive documentation and tutorials on using map calculators. Additionally, online resources, forums, and training courses offer valuable guidance and practical examples.
4. What are the limitations of map calculators?
While powerful, map calculators have limitations:
- Computational Complexity: Complex calculations can be computationally intensive, requiring significant processing power.
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of results depends on the accuracy of the input data.
- User Expertise: Effective use of map calculators requires a basic understanding of GIS concepts and spatial analysis techniques.
Tips for Effective Use of Map Calculators
- Understand Your Data: Familiarize yourself with the data types, units, and attributes before performing calculations.
- Start Simple: Begin with basic calculations to understand the syntax and functionality of the map calculator.
- Test Your Results: Verify the accuracy of your calculations by comparing results with known values or applying visual inspection.
- Document Your Work: Keep a record of your calculations, including the formulas used, input data, and output results.
- Seek Guidance: Consult documentation, online resources, or experts for assistance with complex calculations or specific applications.
Conclusion: Unleashing the Power of Spatial Analysis
The map calculator is an essential tool for unlocking the potential of spatial data. By empowering users to perform calculations, transformations, and analysis on spatial data, it facilitates the discovery of hidden patterns, the understanding of complex relationships, and the generation of valuable insights. Whether applied to environmental management, urban planning, resource management, or any field involving spatial data, map calculators serve as a cornerstone for informed decision-making and a powerful instrument for advancing our understanding of the world around us.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unveiling Insights with Map Calculators. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!