The Power Of Spatial Analysis: Unlocking Insights With Map Calculator Equations
The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unlocking Insights with Map Calculator Equations
Related Articles: The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unlocking Insights with Map Calculator Equations
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unlocking Insights with Map Calculator Equations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unlocking Insights with Map Calculator Equations
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unlocking Insights with Map Calculator Equations
- 3.1 Understanding Map Calculator Equations
- 3.2 Applications of Map Calculator Equations
- 3.3 Benefits of Using Map Calculator Equations
- 3.4 FAQs about Map Calculator Equations
- 3.5 Tips for Using Map Calculator Equations Effectively
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unlocking Insights with Map Calculator Equations

Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are powerful tools for analyzing and visualizing spatial data. One of the most valuable features within GIS software is the ability to perform calculations directly on spatial data using map calculator equations. These equations, often referred to as "raster calculator" or "field calculator" depending on the software, enable users to manipulate and derive new information from existing data layers. This article delves into the world of map calculator equations, exploring their functionality, applications, and the profound impact they have on spatial analysis.
Understanding Map Calculator Equations
Map calculator equations are essentially mathematical expressions that operate on spatial data. They allow users to perform a wide range of operations, from simple arithmetic calculations to complex statistical and logical operations. These equations are written using a syntax specific to the GIS software, often employing a combination of:
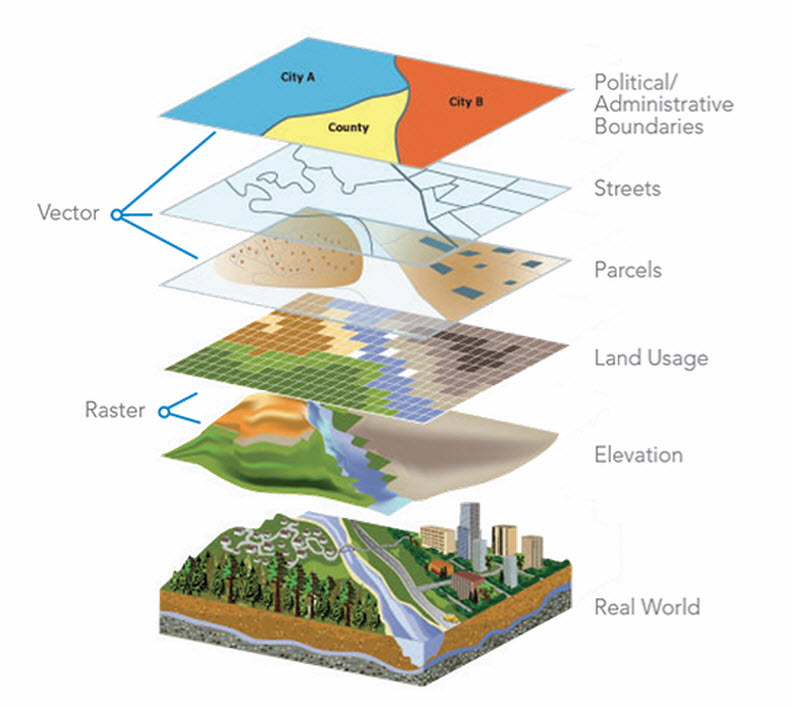
- Spatial data layers: These are the input datasets, representing features like land cover, elevation, population density, or any other geographically referenced information.
-
Operators: These are symbols that define the mathematical or logical operations to be performed on the data. Common operators include:
- Arithmetic operators: +, -, *, /, % (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, modulus)
- Comparison operators: ==, !=, >, <, >=, <= (equal to, not equal to, greater than, less than, greater than or equal to, less than or equal to)
- Logical operators: AND, OR, NOT (logical conjunction, disjunction, negation)
- Functions: These are pre-defined routines that perform specific operations on data, such as calculating distances, performing statistical analysis, or converting data units.
The beauty of map calculator equations lies in their ability to work directly on spatial data. This means that calculations are not limited to individual values but can be applied across entire datasets, allowing for analysis of spatial patterns and relationships.
Applications of Map Calculator Equations
The applications of map calculator equations are vast and extend across numerous domains. Here are some prominent examples:
1. Deriving New Data Layers:
- Slope and Aspect: Calculating slope and aspect from a digital elevation model (DEM) provides crucial information for hydrological analysis, land management, and infrastructure planning.
- Distance to Features: Determining the distance from each point in a dataset to the nearest feature, such as a road, river, or city, can be used for accessibility analysis, proximity studies, and service area delineation.
- Buffer Zones: Creating buffer zones around features like protected areas, pollution sources, or infrastructure can be achieved by calculating distances and generating new polygons.
2. Performing Spatial Analysis:
- Suitability Analysis: Combining multiple data layers representing factors like elevation, soil type, and rainfall can be used to assess the suitability of an area for specific land uses, such as agriculture, forestry, or urban development.
- Overlay Analysis: Combining multiple data layers to identify areas where specific conditions are met. For example, overlaying a land cover map with a rainfall map can identify areas susceptible to flooding.
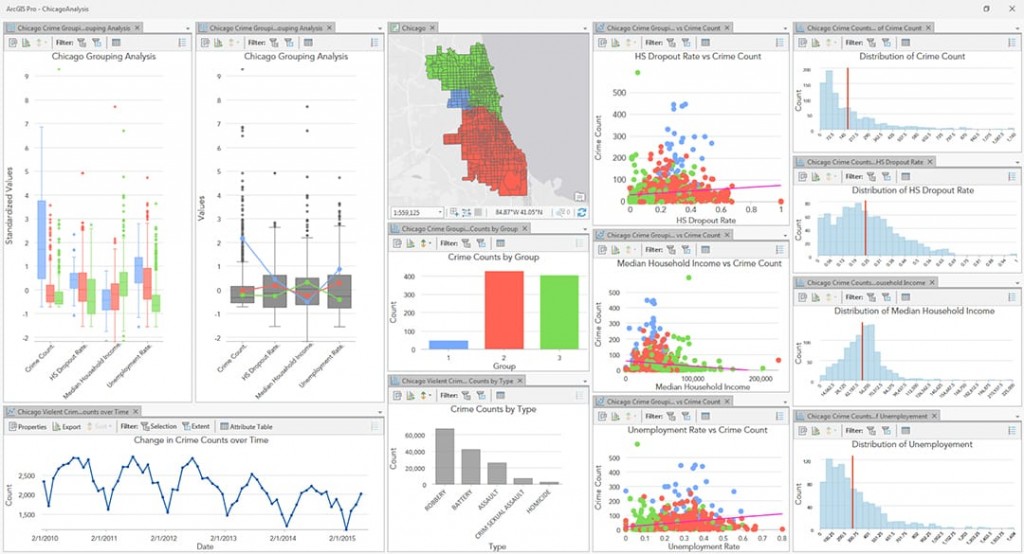
- Spatial Statistics: Calculating statistics like mean, standard deviation, and spatial autocorrelation for specific areas or across the entire dataset can reveal spatial patterns and relationships.
3. Data Transformation and Manipulation:
- Reclassifying Data: Converting data values into different categories based on specific criteria, such as reclassifying land cover types into broad categories like urban, forest, and water.
- Data Aggregation: Combining data from multiple cells into larger units, such as aggregating rainfall data into monthly totals or combining population density data into regional averages.
- Data Normalization: Adjusting data values to a common scale, allowing for comparisons between datasets with different units or ranges.
4. Creating Visualizations and Maps:
- Generating thematic maps: Using map calculator equations to create new data layers that can be visualized on maps, such as maps showing areas with high population density, areas with high risk of flooding, or areas suitable for specific land uses.
- Creating symbology: Applying custom symbology based on calculated values, such as using different colors or sizes to represent different levels of pollution or risk.
- Generating data visualizations: Using map calculator equations to create charts, graphs, and other visualizations that highlight spatial patterns and relationships.
Benefits of Using Map Calculator Equations
Utilizing map calculator equations offers several advantages for spatial analysis:
- Increased Accuracy and Precision: By performing calculations directly on spatial data, map calculator equations ensure that results are accurate and reflect the true spatial relationships within the data.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: The ability to create custom equations allows users to tailor analyses to specific research questions and project objectives.
- Efficiency and Automation: Performing calculations within the GIS software streamlines the analysis process, automating tasks that would otherwise require manual data manipulation.
- Reduced Error Potential: Automating calculations minimizes the risk of human error, ensuring consistent and reliable results.
- Enhanced Data Exploration and Discovery: Map calculator equations empower users to explore data in new ways, revealing hidden patterns and relationships that might not be apparent through simple visualization alone.
FAQs about Map Calculator Equations
1. What are the limitations of map calculator equations?
While powerful, map calculator equations have limitations:
- Data format restrictions: Most GIS software require data to be in specific formats, such as raster or vector, limiting the types of operations that can be performed.
- Computational complexity: Complex calculations can require significant processing power, especially when dealing with large datasets.
- Syntax and programming knowledge: Writing map calculator equations requires understanding the syntax and logic of the specific GIS software.
2. How can I learn to write map calculator equations?
Learning to write map calculator equations involves:
- Understanding the syntax of the GIS software: Familiarize yourself with the specific syntax used for operators, functions, and data references.
- Exploring available functions: Refer to the software documentation to discover the range of functions available for calculations.
- Practicing with simple examples: Start with basic calculations and gradually increase complexity as you gain confidence.
- Seeking online resources and tutorials: Numerous online resources and tutorials offer guidance on using map calculator equations for specific tasks.
3. Can I use map calculator equations for multiple data layers at once?
Yes, map calculator equations can be used to perform calculations on multiple data layers simultaneously. This allows for complex spatial analysis, such as overlay analysis or weighted sum calculations.
4. What are some common errors to avoid when writing map calculator equations?
- Incorrect data types: Ensure that the data types used in the equation are compatible.
- Typographical errors: Double-check the spelling and syntax of operators, functions, and data references.
- Missing parentheses: Use parentheses to define the order of operations correctly.
- Incorrect data units: Ensure that all data layers are using the same units before performing calculations.
Tips for Using Map Calculator Equations Effectively
- Start simple: Begin with basic calculations to understand the syntax and logic of the software.
- Break down complex tasks: Divide complex calculations into smaller, manageable steps.
- Use comments: Add comments to your equations to explain the logic and purpose of each step.
- Test your equations: Run test calculations on small datasets to ensure that the equations are working as intended.
- Document your work: Keep a record of your equations and their results for future reference.
Conclusion
Map calculator equations are an indispensable tool for spatial analysis, providing a powerful means to manipulate, analyze, and derive new information from spatial data. By leveraging the capabilities of these equations, users can unlock insights into spatial patterns, relationships, and trends, enhancing their understanding of geographic phenomena and informing decision-making across various disciplines. As GIS technology continues to evolve, map calculator equations will play an increasingly crucial role in facilitating advanced spatial analysis and empowering users to make informed decisions based on the insights gleaned from spatial data.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unlocking Insights with Map Calculator Equations. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!