The Power Of Spatial Analysis: Understanding And Utilizing Map Calculator
The Power of Spatial Analysis: Understanding and Utilizing Map Calculator
Related Articles: The Power of Spatial Analysis: Understanding and Utilizing Map Calculator
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Spatial Analysis: Understanding and Utilizing Map Calculator. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Spatial Analysis: Understanding and Utilizing Map Calculator

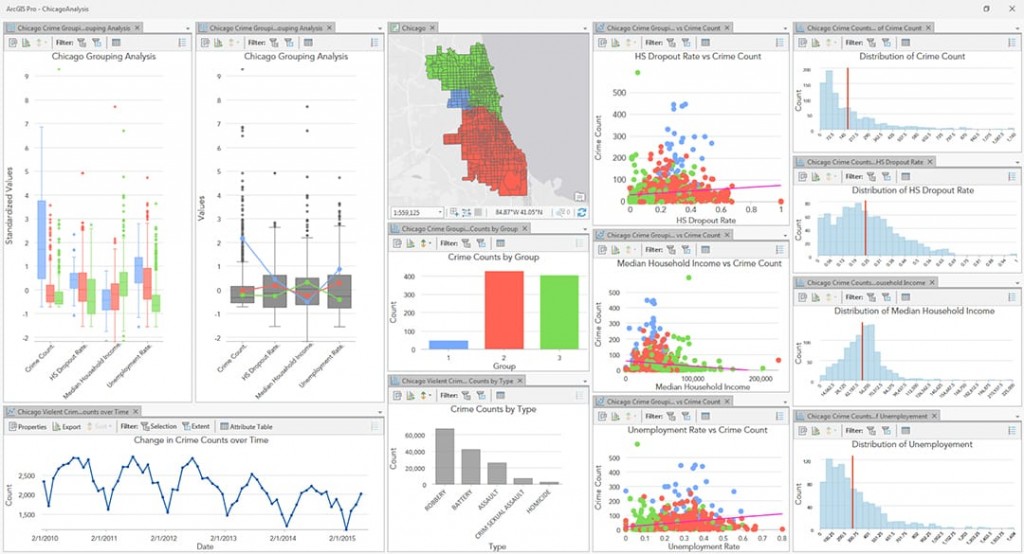
Map calculators, often integrated within Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software, are powerful tools that enable users to perform complex calculations and transformations on spatial data. These calculations are not limited to basic arithmetic operations; they encompass a wide range of functionalities, empowering users to analyze, manipulate, and derive valuable insights from geographic information.
The Core of Spatial Analysis: Map Calculator Functions
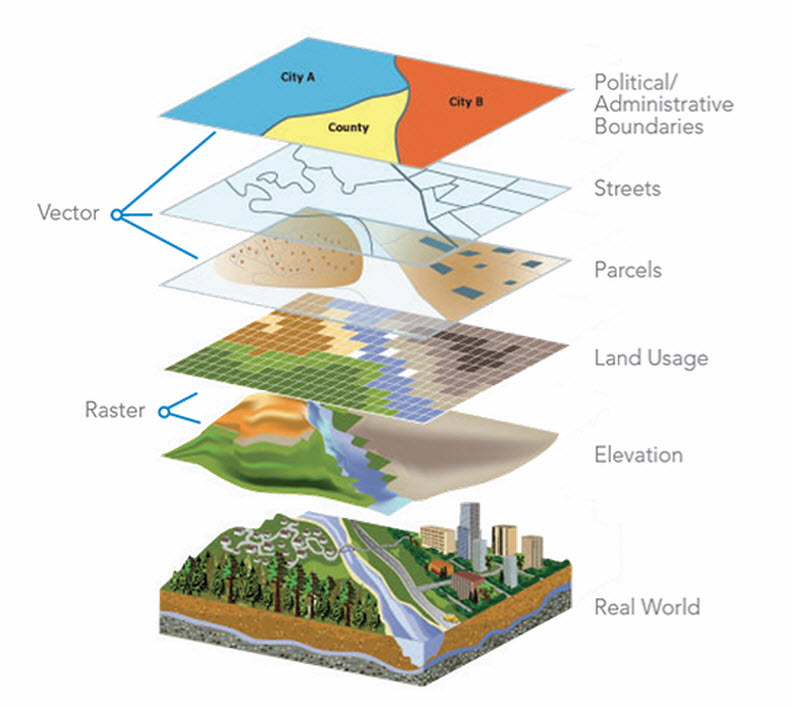
At its core, a map calculator operates on the values of individual cells or features within a raster or vector layer, respectively. This allows for the application of mathematical operations, logical comparisons, and various spatial functions, enabling the creation of new data layers or the modification of existing ones.
Key Functions of a Map Calculator:
- Mathematical Operations: Basic arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division can be applied to individual cells or feature attributes. This allows for the calculation of new values based on existing data.
- Logical Comparisons: Using logical operators like "greater than," "less than," "equal to," or "not equal to," users can create conditions to filter data, identify specific areas, or classify features based on predefined criteria.
- Spatial Functions: Map calculators often incorporate a suite of spatial functions, enabling users to analyze spatial relationships between features or cells. These functions include distance calculations, proximity analysis, neighborhood analysis, and overlay operations.
Applications of Map Calculator in Diverse Fields
The versatility of map calculators extends across a wide range of disciplines, making them essential tools for analyzing spatial data. Here are some examples:
1. Environmental Sciences:
- Calculating Vegetation Indices: By combining spectral bands from satellite imagery, vegetation indices like NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) can be calculated to assess plant health, monitor vegetation growth, and track deforestation patterns.
- Estimating Soil Erosion: Map calculators can be used to analyze topographic data and rainfall patterns to predict areas prone to soil erosion, aiding in the development of conservation strategies.
- Modeling Climate Change Impacts: Combining climate models with spatial data, map calculators can project future changes in temperature, precipitation, and sea levels, providing valuable insights for adaptation and mitigation planning.
2. Urban Planning and Development:
- Assessing Accessibility: Map calculators can calculate travel times and distances from specific locations to points of interest, helping urban planners evaluate the accessibility of public services, transportation networks, and amenities.
- Analyzing Land Use Patterns: Combining land use data with population density, map calculators can identify areas with high population density and limited green spaces, informing urban planning decisions for improved quality of life.
- Simulating Urban Growth: By incorporating factors like population growth, economic development, and infrastructure availability, map calculators can simulate urban growth patterns, providing valuable insights for infrastructure planning and development strategies.
3. Public Health and Disaster Management:
- Mapping Disease Outbreaks: By combining population density, environmental factors, and disease incidence data, map calculators can create maps that identify areas at risk of disease outbreaks, enabling targeted interventions and resource allocation.
- Assessing Flood Risk: Using elevation data, rainfall patterns, and river flow models, map calculators can identify areas vulnerable to flooding, informing flood preparedness plans and evacuation strategies.
- Evaluating Healthcare Access: Map calculators can analyze the distribution of healthcare facilities and population density to assess healthcare access and identify underserved areas, guiding the development of healthcare infrastructure and resource allocation.
4. Agriculture and Forestry:
- Optimizing Crop Yields: By analyzing soil properties, climate data, and crop growth models, map calculators can identify optimal locations for specific crops, maximizing yields and improving agricultural efficiency.
- Managing Forest Resources: Map calculators can analyze forest cover, identify areas at risk of deforestation, and evaluate the impact of logging activities, supporting sustainable forest management practices.
- Assessing Soil Health: By combining soil analysis data with environmental factors, map calculators can create maps showing soil health indicators, aiding in the development of soil conservation and management strategies.
5. Transportation and Logistics:
- Optimizing Delivery Routes: Map calculators can analyze road networks, traffic data, and delivery locations to calculate the most efficient delivery routes, reducing transportation costs and improving delivery times.
- Analyzing Traffic Flow: By analyzing traffic patterns and road network data, map calculators can identify traffic congestion hotspots and evaluate the impact of infrastructure projects, informing traffic management strategies.
- Planning Transportation Infrastructure: Map calculators can analyze population density, land use patterns, and transportation demand to inform the planning and development of efficient transportation networks.
Understanding the Importance of Map Calculator Range
The range of functions available within a map calculator is crucial for its effectiveness and versatility. A comprehensive range of functions enables users to tackle complex spatial analysis tasks, extract meaningful insights, and make data-driven decisions.
FAQs on Map Calculator Range:
1. What are the limitations of map calculator range?
While map calculators offer a wide range of functionalities, they may not be suitable for every spatial analysis task. Certain complex operations or advanced statistical analyses might require specialized tools or programming languages.
2. How can I expand the map calculator range?
Many GIS software packages offer scripting capabilities, allowing users to write custom functions and extend the functionality of the map calculator. Additionally, third-party libraries and extensions can provide access to advanced spatial analysis tools.
3. How do I choose the right map calculator for my needs?
Consider the type of spatial data you are working with, the specific analysis you need to perform, and the level of complexity required. Choose a map calculator that offers the necessary functions and capabilities to meet your specific requirements.
Tips for Utilizing Map Calculator Effectively:
- Understand your data: Before using a map calculator, familiarize yourself with the data structure, units of measurement, and any potential errors or inconsistencies.
- Start with simple operations: Begin with basic calculations and gradually increase the complexity as you gain familiarity with the tool.
- Test your results: Verify the accuracy of your calculations by comparing the output to known values or using independent methods.
- Document your process: Keep a record of the functions used, parameters applied, and any assumptions made during the analysis to ensure reproducibility and transparency.
- Explore advanced features: Many map calculators offer advanced functionalities like scripting, custom functions, and integration with external tools, enabling more complex and customized analyses.
Conclusion: The Power of Spatial Analysis at Your Fingertips
Map calculators are indispensable tools for analyzing spatial data, enabling users to extract valuable insights, make data-driven decisions, and solve complex problems in diverse fields. Their ability to perform a wide range of calculations and spatial functions empowers users to understand spatial relationships, quantify spatial patterns, and gain a deeper understanding of the world around us. By mastering the use of map calculators, users can unlock the power of spatial analysis and contribute to informed decision-making across various disciplines.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Spatial Analysis: Understanding and Utilizing Map Calculator. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!