The North Atlantic Ocean Currents: A Symphony Of Motion
The North Atlantic Ocean Currents: A Symphony of Motion
Related Articles: The North Atlantic Ocean Currents: A Symphony of Motion
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The North Atlantic Ocean Currents: A Symphony of Motion. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The North Atlantic Ocean Currents: A Symphony of Motion
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The North Atlantic Ocean Currents: A Symphony of Motion
- 3.1 A Glimpse into the North Atlantic’s Circulation:
- 3.2 The Importance of the North Atlantic Ocean Currents:
- 3.3 Frequently Asked Questions about North Atlantic Ocean Currents:
- 3.4 Tips for Understanding North Atlantic Ocean Currents:
- 3.5 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
The North Atlantic Ocean Currents: A Symphony of Motion

The North Atlantic Ocean, a vast expanse of water covering over 20 million square miles, is far from static. It is a dynamic system, its waters constantly in motion, driven by a complex interplay of forces like wind, solar radiation, and the Earth’s rotation. This intricate dance of currents shapes the climate of the surrounding continents, influences marine life, and even impacts global weather patterns. Understanding the North Atlantic Ocean currents, therefore, is crucial for comprehending the Earth’s climate system and its various manifestations.
A Glimpse into the North Atlantic’s Circulation:
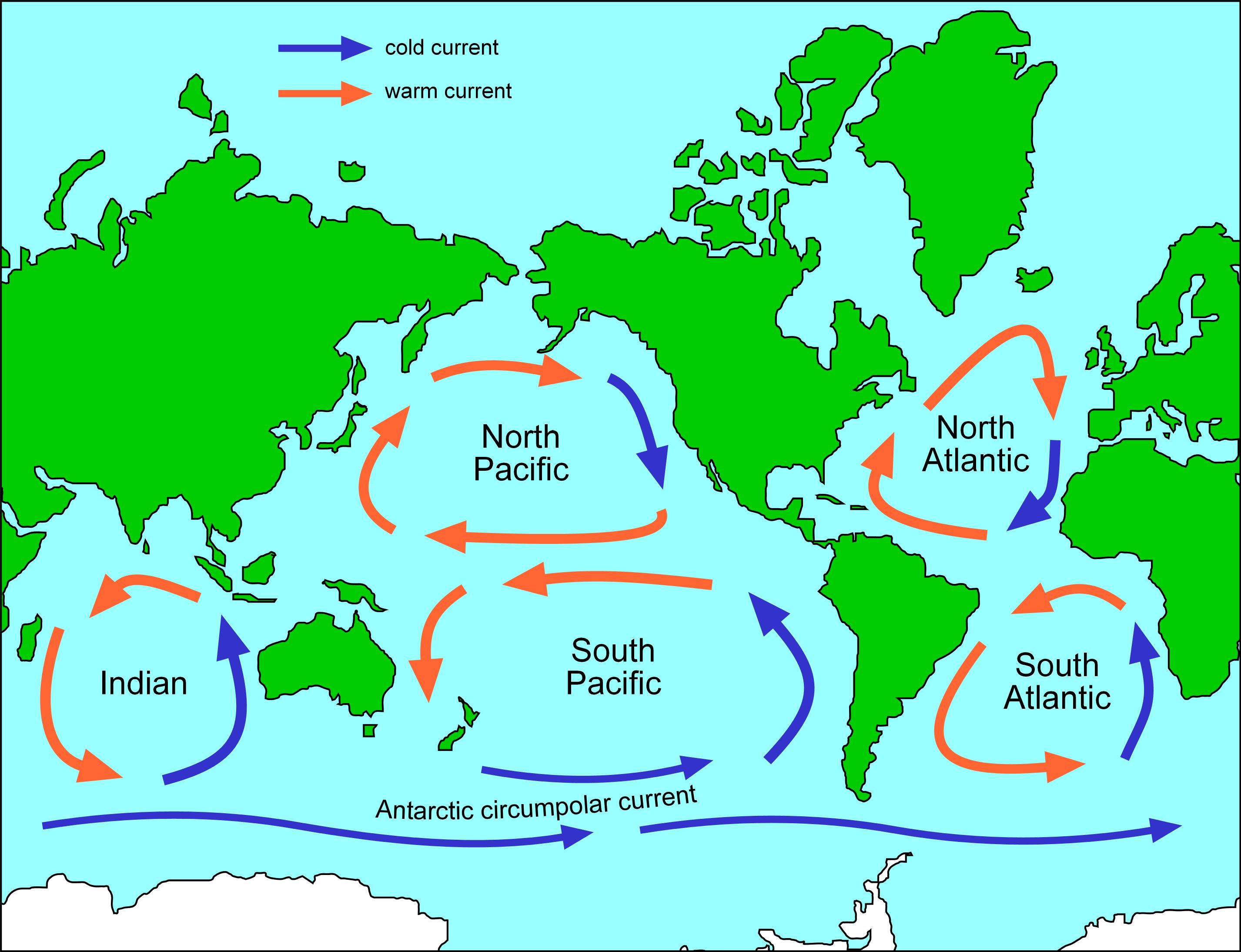
The North Atlantic Ocean currents can be broadly categorized into two main systems: the North Atlantic Gyre and the North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW) circulation.
1. The North Atlantic Gyre:
This vast, clockwise circulation pattern encompasses the North Atlantic basin, fueled by prevailing winds and the Earth’s rotation. It is composed of four major currents:
- The Gulf Stream: This warm, swift current originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows northward along the eastern coast of North America. It then turns eastward, crossing the Atlantic towards Europe, where it branches into the North Atlantic Current and the Canary Current.
- The North Atlantic Current: This current, an extension of the Gulf Stream, carries warm water across the Atlantic, influencing the climate of Western Europe. It is responsible for the relatively mild winters experienced in countries like Ireland and the United Kingdom, compared to their counterparts at similar latitudes in North America.
- The Canary Current: This cold current flows southward along the western coast of Africa, bringing cooler temperatures to the region.
- The North Atlantic Equatorial Current: This westward-flowing current, driven by the trade winds, transports warm water from the eastern Atlantic towards the Caribbean.
2. The North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW) Circulation:
This deep-ocean circulation, driven by density differences, plays a crucial role in the global ocean circulation system. Cold, salty water from the Arctic and North Atlantic sinks in the North Atlantic, forming the NADW. This dense water then flows southward, eventually joining the global thermohaline circulation, a vast system of interconnected currents that transports heat and nutrients around the globe.
The Importance of the North Atlantic Ocean Currents:
The North Atlantic Ocean currents exert a profound influence on the planet, shaping climate, marine ecosystems, and even human activities:
1. Climate Regulation:
The North Atlantic currents are instrumental in regulating the climate of the Northern Hemisphere. The Gulf Stream, for instance, transports immense quantities of heat from the tropics to higher latitudes, moderating the climate of Western Europe and making it significantly warmer than other regions at similar latitudes. This influence is evident in the milder winters experienced in countries like Ireland and the United Kingdom compared to regions in North America at similar latitudes.
2. Marine Ecosystems:
The currents transport nutrients, plankton, and other marine organisms, creating a dynamic environment that supports a rich diversity of life. The Gulf Stream, for example, plays a vital role in the migration patterns of many fish species, including cod, herring, and tuna. The upwelling zones, where cold, nutrient-rich water rises from the depths, are particularly productive, supporting a rich abundance of marine life.
3. Navigation and Transportation:
The currents have historically influenced maritime navigation, aiding sailors in their journeys across the Atlantic. The Gulf Stream, in particular, has been a valuable aid for transatlantic voyages, reducing travel times and offering a favorable route. Today, the currents continue to be important for shipping, influencing shipping routes and the efficiency of maritime transportation.
4. Climate Change Impacts:
The North Atlantic currents are sensitive to climate change, and their behavior is evolving in response to rising global temperatures. Changes in the strength and patterns of these currents can have significant implications for regional climate, marine ecosystems, and even human societies. For instance, a slowdown of the Gulf Stream could lead to colder winters in Western Europe, disrupting agriculture and other industries.
Frequently Asked Questions about North Atlantic Ocean Currents:
1. How do the North Atlantic currents affect the climate of Western Europe?
The Gulf Stream, a major component of the North Atlantic Gyre, transports warm water from the tropics to higher latitudes, moderating the climate of Western Europe. This results in relatively mild winters compared to regions at similar latitudes in North America.
2. What is the role of the North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW) circulation in the global ocean circulation system?
The NADW circulation plays a crucial role in the global thermohaline circulation, a vast system of interconnected currents that transports heat and nutrients around the globe. Cold, salty water from the Arctic and North Atlantic sinks, forming the NADW, which then flows southward, contributing to the global ocean circulation.
3. How do the North Atlantic currents impact marine ecosystems?
The currents transport nutrients, plankton, and other marine organisms, creating a dynamic environment that supports a rich diversity of life. Upwelling zones, where cold, nutrient-rich water rises from the depths, are particularly productive, supporting a rich abundance of marine life.
4. How are the North Atlantic currents affected by climate change?
The North Atlantic currents are sensitive to climate change, and their behavior is evolving in response to rising global temperatures. Changes in the strength and patterns of these currents can have significant implications for regional climate, marine ecosystems, and even human societies.
5. What are the potential consequences of a slowdown in the Gulf Stream?
A slowdown of the Gulf Stream could lead to colder winters in Western Europe, disrupting agriculture and other industries. It could also impact marine ecosystems, potentially leading to changes in fish populations and distribution.
Tips for Understanding North Atlantic Ocean Currents:
1. Visualize the circulation: Utilize maps and animations to visualize the complex patterns of the North Atlantic currents. This will help you understand the direction and flow of the different currents and their interconnectedness.
2. Explore the driving forces: Learn about the forces that drive the currents, such as wind, solar radiation, and the Earth’s rotation. This will provide a deeper understanding of how these currents are generated and sustained.
3. Consider the impacts: Explore the various impacts of the currents, including their influence on climate, marine ecosystems, and human activities. This will highlight the importance of understanding these dynamic systems.
4. Stay informed about climate change: Learn about the potential impacts of climate change on the North Atlantic currents and the implications for the surrounding regions.
5. Engage in discussions: Participate in discussions and forums related to oceanography and climate change to gain further insights and perspectives on the North Atlantic currents and their significance.
Conclusion:
The North Atlantic Ocean currents are a testament to the dynamic nature of our planet. They play a vital role in regulating climate, shaping marine ecosystems, and influencing human activities. Understanding these currents is essential for comprehending the Earth’s climate system and its intricate workings. As we navigate the challenges of a changing climate, it is crucial to continue researching and monitoring these vital currents, ensuring their continued role in supporting life on Earth.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The North Atlantic Ocean Currents: A Symphony of Motion. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!