The North Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline On The World Map
The North Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline on the World Map
Related Articles: The North Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline on the World Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The North Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline on the World Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The North Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline on the World Map

The North Atlantic Ocean, a vast body of water covering approximately 20 million square miles, plays a crucial role in the global ecosystem and human civilization. Its influence extends far beyond its physical boundaries, shaping weather patterns, supporting diverse marine life, and facilitating trade and transportation. Understanding the North Atlantic’s location, features, and significance on the world map is essential for comprehending its impact on our planet.
A Geographic Overview
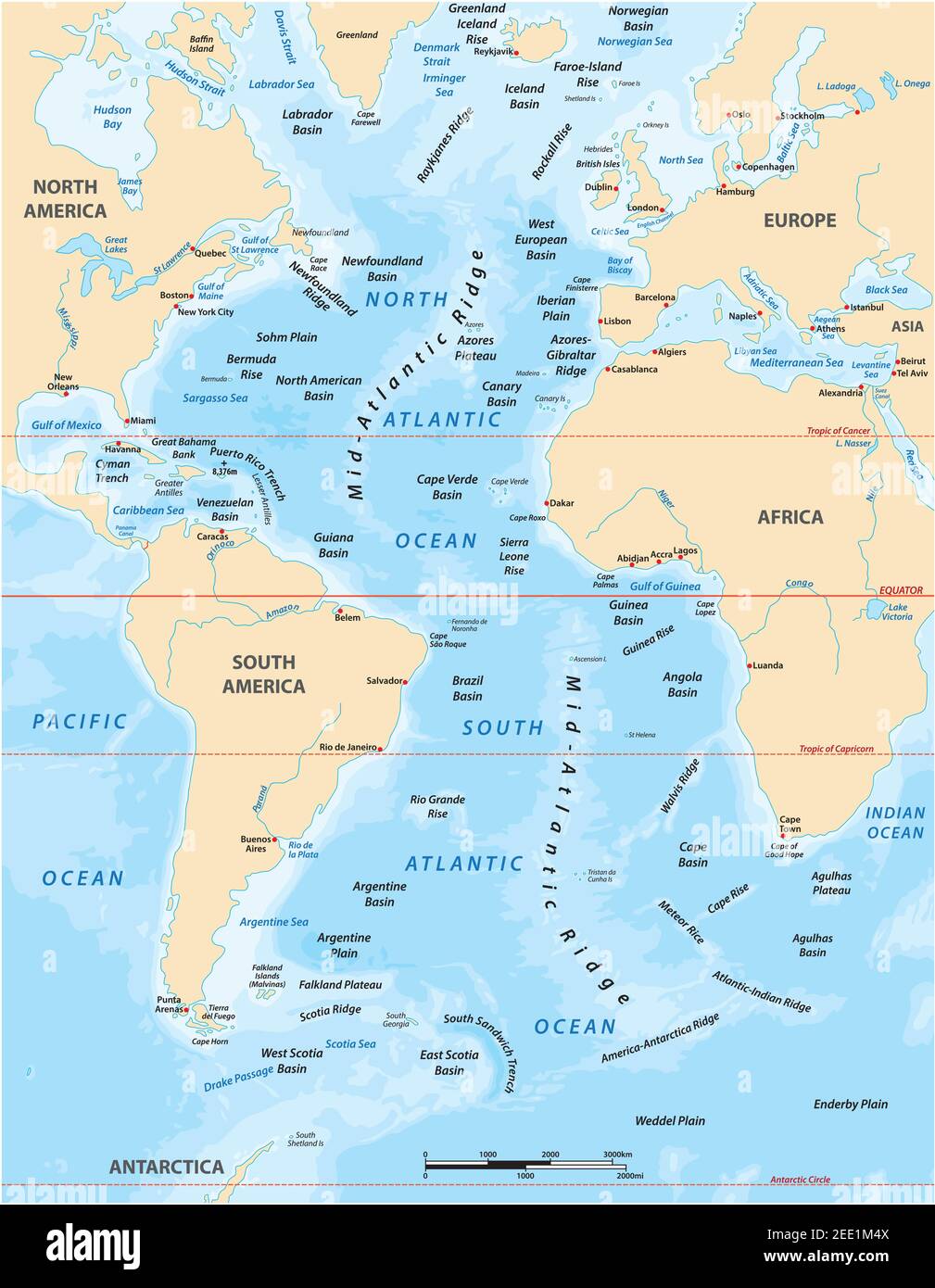
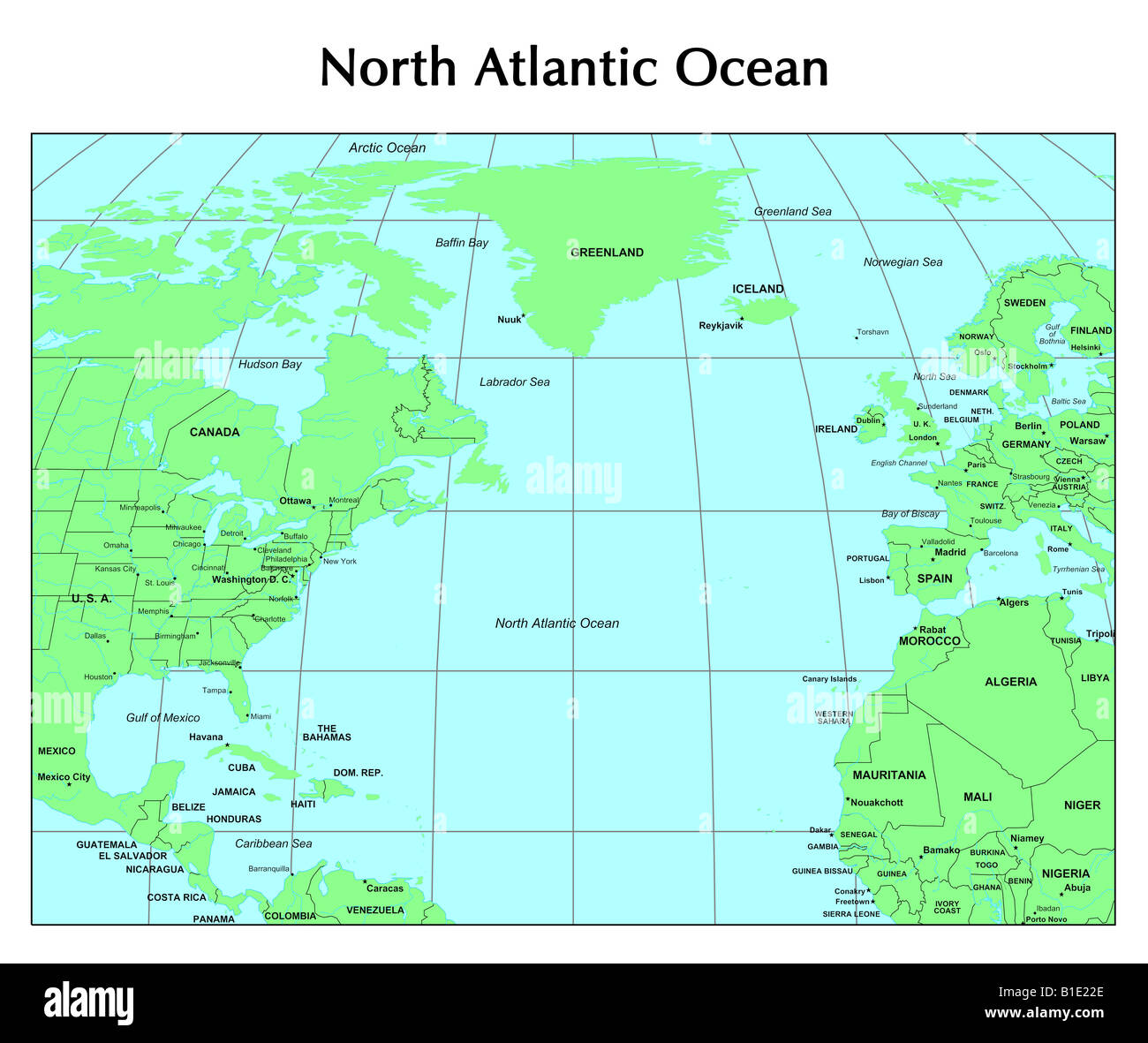
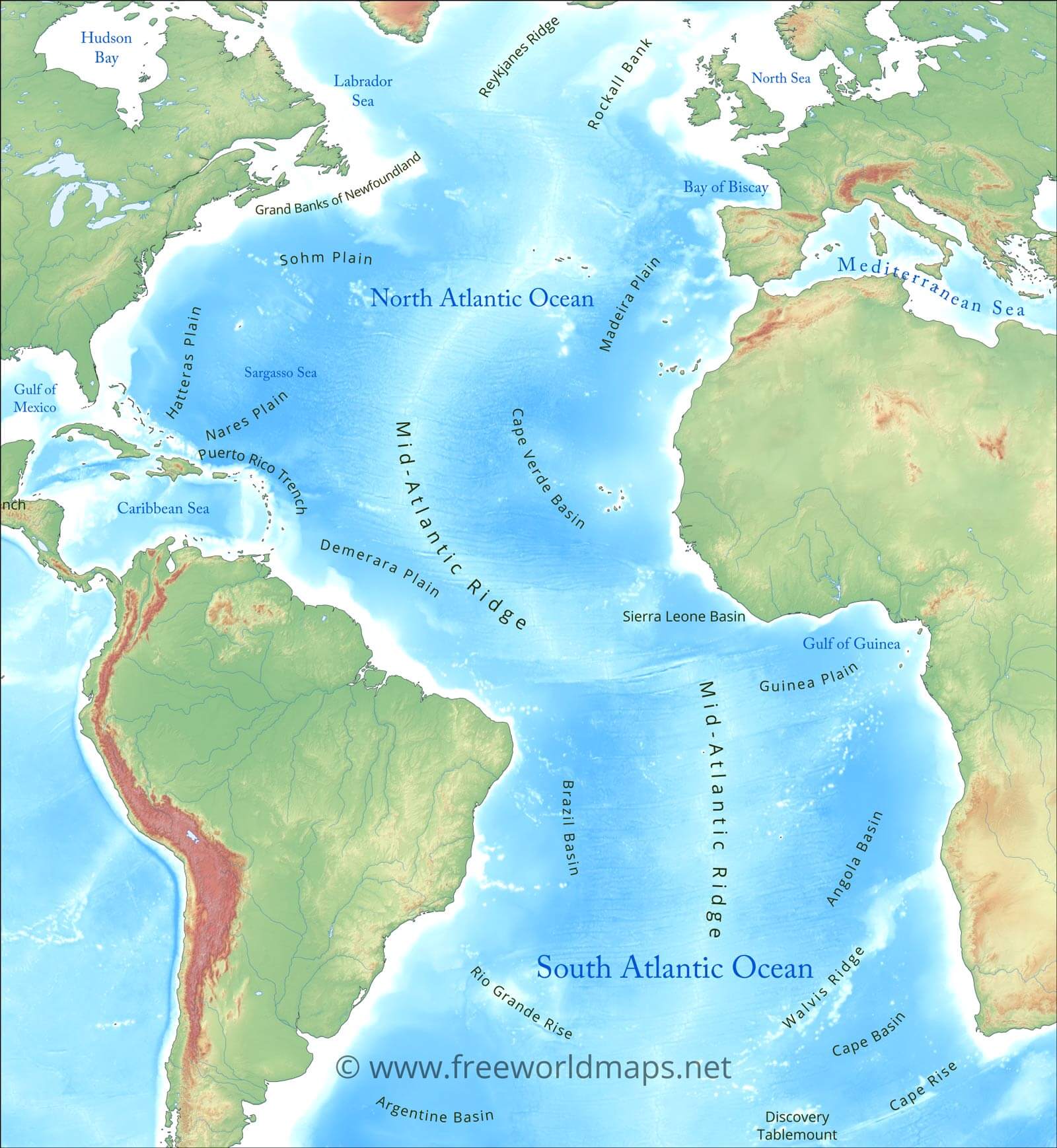
The North Atlantic Ocean occupies a prominent position on the world map, nestled between North America and Europe. It stretches from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Equator in the south, encompassing numerous prominent features:
- The Gulf Stream: This warm current, originating in the Gulf of Mexico, carries warm water northward along the eastern coast of North America, influencing the climate of Western Europe and contributing to the North Atlantic’s rich biodiversity.
- The Labrador Current: This cold current flows southward from the Arctic Ocean, bringing cold, nutrient-rich waters to the North Atlantic, supporting a diverse ecosystem and influencing the climate of northeastern North America.
- The Mid-Atlantic Ridge: This underwater mountain range, running down the center of the ocean, marks the boundary between the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates.
- The Grand Banks: These shallow waters off the coast of Newfoundland, Canada, are renowned for their abundant fisheries, historically contributing significantly to the region’s economy.
Ecological Significance
The North Atlantic Ocean is a vibrant ecosystem, teeming with diverse marine life. Its nutrient-rich waters support a complex food web, including:
- Whales: The North Atlantic is home to a variety of whale species, including humpback whales, blue whales, and fin whales, which migrate through the region for feeding and breeding.
- Fish: The North Atlantic supports a vast array of fish species, including cod, herring, and tuna, which are commercially important and contribute to the livelihoods of coastal communities.
- Seabirds: Numerous seabird species, including puffins, albatrosses, and gulls, inhabit the North Atlantic, relying on its rich marine resources for food and breeding.
- Coral Reefs: While not as extensive as in tropical waters, coral reefs exist in the North Atlantic, providing habitat for a variety of marine organisms.
Economic and Cultural Importance
The North Atlantic Ocean has played a pivotal role in human history, connecting continents and cultures, facilitating trade, and shaping economies. Its key contributions include:
- Trade and Transportation: The North Atlantic serves as a vital trade route, connecting major ports in North America, Europe, and Africa, facilitating the transportation of goods and people across the globe.
- Fishing Industry: The North Atlantic’s abundant fisheries have historically been a major source of food and income for coastal communities, contributing to the development of maritime economies.
- Tourism: The North Atlantic’s breathtaking scenery, diverse wildlife, and rich history attract millions of tourists each year, contributing to the economies of coastal regions.
- Energy Resources: The North Atlantic holds significant oil and gas reserves, contributing to the energy needs of surrounding countries.
Climate and Weather Patterns
The North Atlantic plays a crucial role in shaping global climate patterns. Its currents, particularly the Gulf Stream, influence the temperatures of surrounding landmasses, contributing to the mild climate of Western Europe and the colder climate of northeastern North America. The North Atlantic also plays a role in the development of weather systems, including hurricanes and storms.
Challenges and Threats
Despite its vital role, the North Atlantic faces numerous challenges and threats, including:
- Overfishing: The overexploitation of fish stocks has led to declines in fish populations, threatening the sustainability of the fishing industry and the marine ecosystem.
- Climate Change: Rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and changes in ocean currents due to climate change threaten the marine ecosystem and coastal communities.
- Pollution: Pollution from land-based sources, including oil spills, plastic waste, and agricultural runoff, degrades the North Atlantic’s water quality and harms marine life.
- Shipping and Maritime Activities: Increased shipping and maritime activities can lead to habitat destruction, pollution, and the introduction of invasive species.
FAQs
Q: What is the average depth of the North Atlantic Ocean?
A: The average depth of the North Atlantic Ocean is approximately 3,900 meters (12,800 feet).
Q: What are the major ports located on the North Atlantic Ocean?
A: Major ports located on the North Atlantic Ocean include New York City, Boston, Halifax, London, Rotterdam, Hamburg, and Lisbon.
Q: How does the North Atlantic Ocean influence the climate of Europe?
A: The Gulf Stream, a warm current originating in the Gulf of Mexico, carries warm water northward along the eastern coast of North America, moderating the climate of Western Europe and making it significantly warmer than other regions at similar latitudes.
Q: What are the major environmental threats to the North Atlantic Ocean?
A: The major environmental threats to the North Atlantic Ocean include overfishing, climate change, pollution, and shipping and maritime activities.
Tips
- Reduce your carbon footprint: By reducing your reliance on fossil fuels, you can contribute to mitigating climate change and its impact on the North Atlantic.
- Support sustainable fishing practices: Choose seafood from sustainable sources and avoid overfished species.
- Reduce plastic waste: Dispose of plastic properly and avoid single-use plastics.
- Educate yourself about the North Atlantic: Learn more about its importance and the threats it faces.
Conclusion
The North Atlantic Ocean is a vital component of the global ecosystem and human civilization. Its vast size, diverse marine life, and strategic location make it a critical resource for trade, transportation, and economic development. However, it faces significant challenges from overfishing, climate change, pollution, and other threats. By understanding the North Atlantic’s importance and taking action to protect it, we can ensure its continued health and vitality for future generations.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The North Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline on the World Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!