The North Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline
The North Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline
Related Articles: The North Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The North Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The North Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline
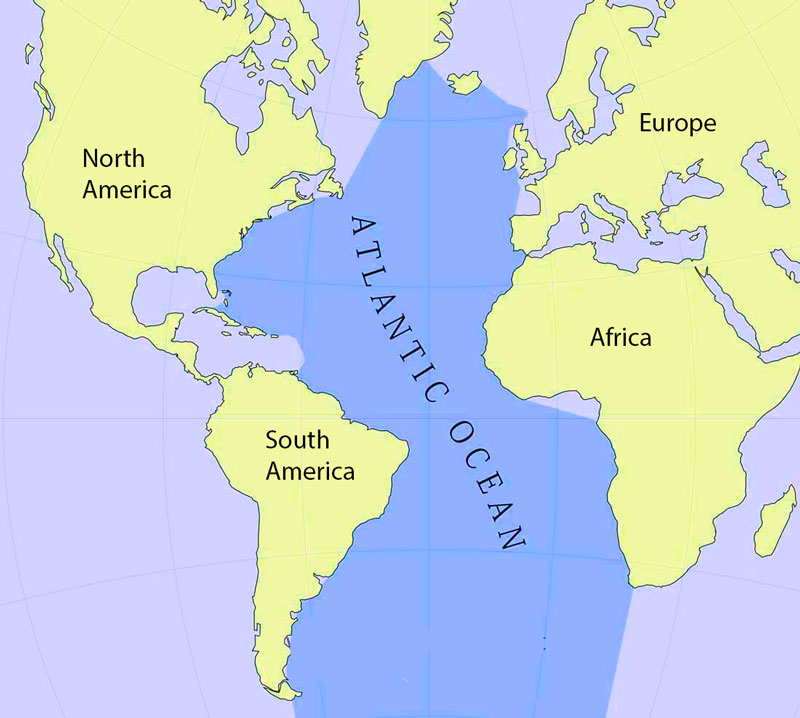
The North Atlantic Ocean, a vast expanse of water encompassing approximately 18.1 million square miles, plays a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s climate, supporting diverse ecosystems, and facilitating global trade and communication. Its significance transcends its physical boundaries, impacting human civilization and the natural world in profound ways.
A Dynamic and Complex Ecosystem
The North Atlantic is a dynamic and complex ecosystem teeming with life. Its waters support a wide variety of marine organisms, from microscopic plankton to colossal whales. The ocean’s currents, influenced by factors such as wind patterns, Earth’s rotation, and temperature differences, drive the distribution of nutrients and organisms, creating unique habitats and fostering biodiversity.
The Importance of Currents
The North Atlantic’s currents, including the Gulf Stream, the North Atlantic Current, and the Labrador Current, are vital for regulating global climate. The Gulf Stream, a powerful warm current originating in the Gulf of Mexico, transports heat northward, moderating the climate of Western Europe and making it significantly warmer than other regions at similar latitudes. The Labrador Current, a cold current flowing southward from the Arctic, brings cold water and icebergs to the eastern coast of North America, influencing the region’s weather and coastal ecosystems.
A Hub of Biodiversity
The North Atlantic is home to a rich tapestry of marine life, including fish, whales, dolphins, sea turtles, sharks, and a multitude of invertebrates. The ocean’s diverse habitats, from shallow coastal waters to deep-sea trenches, provide niches for a wide range of species, contributing to the global biodiversity pool.
Navigating the Waters
Historically, the North Atlantic has served as a vital waterway for exploration, trade, and communication. From the voyages of the Vikings to the transatlantic crossings of modern ships, the ocean has connected continents and cultures, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and people. Its strategic location has also made it a significant arena for naval power and geopolitical influence.
A Vital Resource for Humanity
The North Atlantic is a vital resource for humanity, providing food, energy, and transportation. Fisheries in the region contribute significantly to global food security, while offshore oil and gas reserves offer energy resources. The ocean’s vast expanse also supports international shipping and transportation, connecting economies and facilitating global trade.
The Impact of Climate Change
The North Atlantic is facing significant challenges from climate change. Rising sea levels, ocean acidification, and warming waters are altering the ocean’s physical and chemical properties, impacting marine ecosystems and human communities. The Gulf Stream, a key driver of Europe’s climate, is showing signs of weakening, potentially leading to significant changes in weather patterns.
Understanding the North Atlantic: A Critical Need
Understanding the North Atlantic’s complex dynamics is crucial for managing its resources sustainably, mitigating the impacts of climate change, and ensuring the long-term health of the ocean and its ecosystems. Scientific research, monitoring, and international collaboration are essential for addressing the challenges facing this vital body of water.
FAQs
Q: What are the major currents in the North Atlantic Ocean?
A: The North Atlantic Ocean is characterized by several significant currents, including:
- The Gulf Stream: A warm current originating in the Gulf of Mexico, transporting heat northward and influencing the climate of Western Europe.
- The North Atlantic Current: An extension of the Gulf Stream, flowing eastward across the Atlantic and carrying warm water towards Europe.
- The Labrador Current: A cold current flowing southward from the Arctic, bringing cold water and icebergs to the eastern coast of North America.
Q: What are some of the major threats to the North Atlantic Ocean?
A: The North Atlantic Ocean faces several threats, including:
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels, ocean acidification, and warming waters are impacting marine ecosystems and human communities.
- Overfishing: Unsustainable fishing practices can deplete fish stocks and disrupt marine food webs.
- Pollution: Runoff from land-based sources, such as agricultural fertilizers and industrial waste, can contaminate the ocean and harm marine life.
- Oil and Gas Exploration: Accidents during oil and gas exploration can lead to spills, causing significant environmental damage.
Q: What are some of the ways to protect the North Atlantic Ocean?
A: Protecting the North Atlantic Ocean requires a multi-faceted approach, including:
- Sustainable Fisheries Management: Implementing regulations to prevent overfishing and ensure the long-term health of fish stocks.
- Reducing Pollution: Implementing measures to reduce pollution from land-based sources and promote responsible waste management.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the impacts of climate change on the ocean.
- International Cooperation: Fostering international collaboration to address transboundary issues and protect shared resources.
Tips
- Reduce your carbon footprint: By reducing your energy consumption and adopting sustainable practices, you can contribute to mitigating climate change and its impacts on the North Atlantic.
- Support sustainable seafood: Choose seafood from sustainable fisheries, certified by organizations like the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC).
- Reduce plastic waste: Plastic pollution poses a significant threat to marine ecosystems. Reduce your plastic consumption and dispose of it responsibly.
- Get involved in conservation efforts: Support organizations working to protect the North Atlantic Ocean and its ecosystems.
Conclusion
The North Atlantic Ocean is a vital part of the Earth’s system, playing a crucial role in regulating climate, supporting diverse ecosystems, and facilitating human activity. Understanding its complex dynamics and addressing the challenges it faces is essential for ensuring the long-term health of the ocean and the well-being of the planet. Through scientific research, responsible management, and international cooperation, we can work to protect this vital resource for present and future generations.
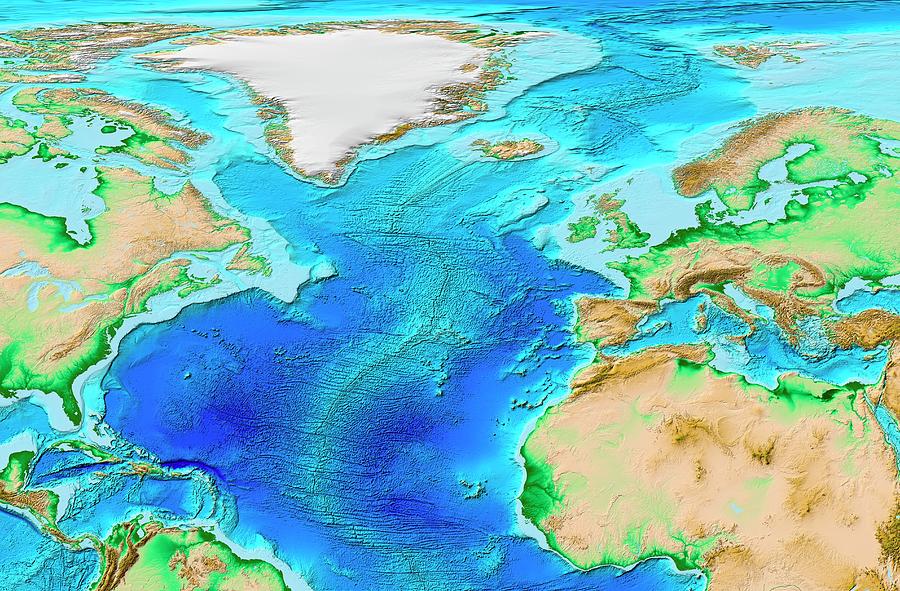





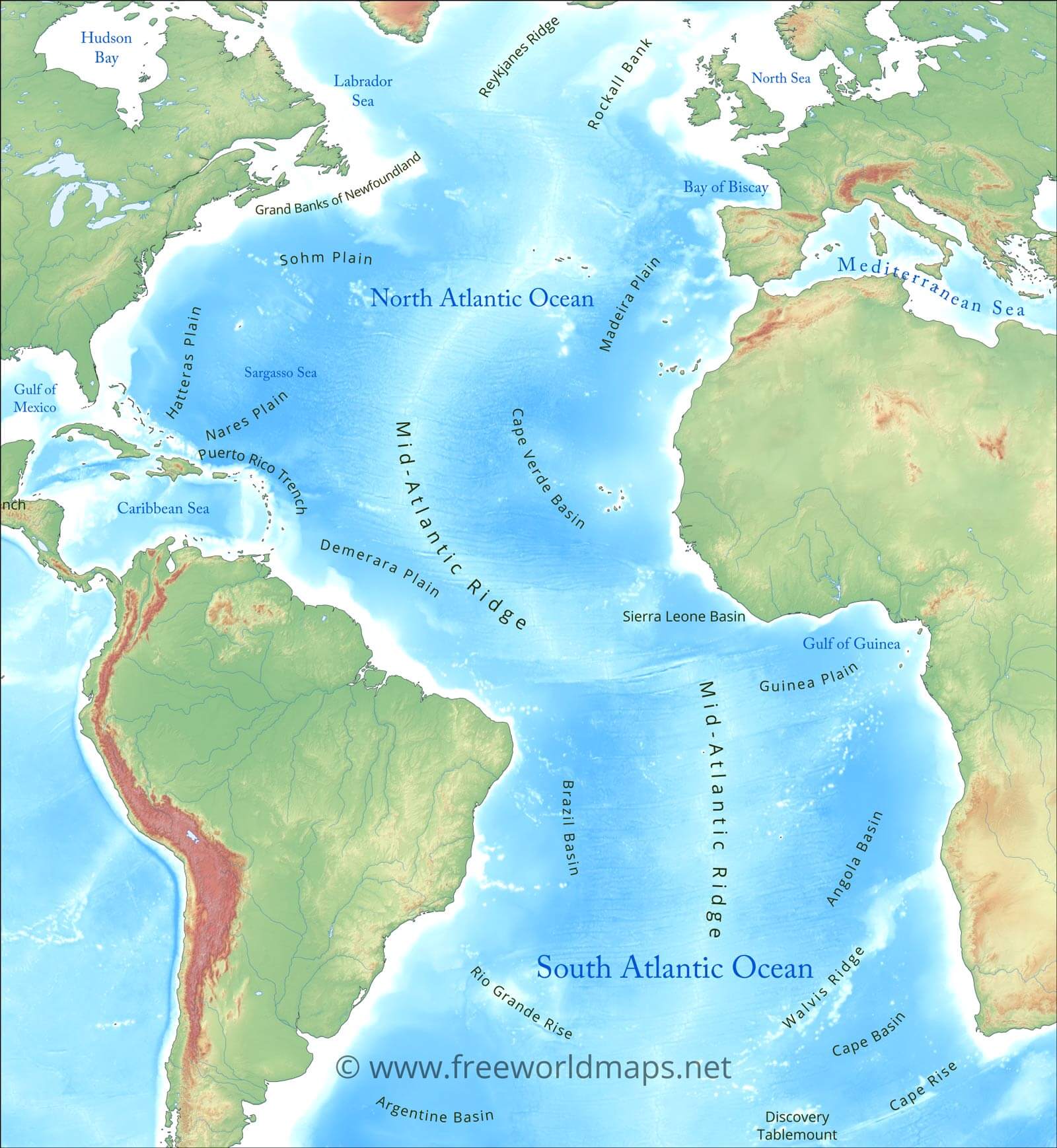
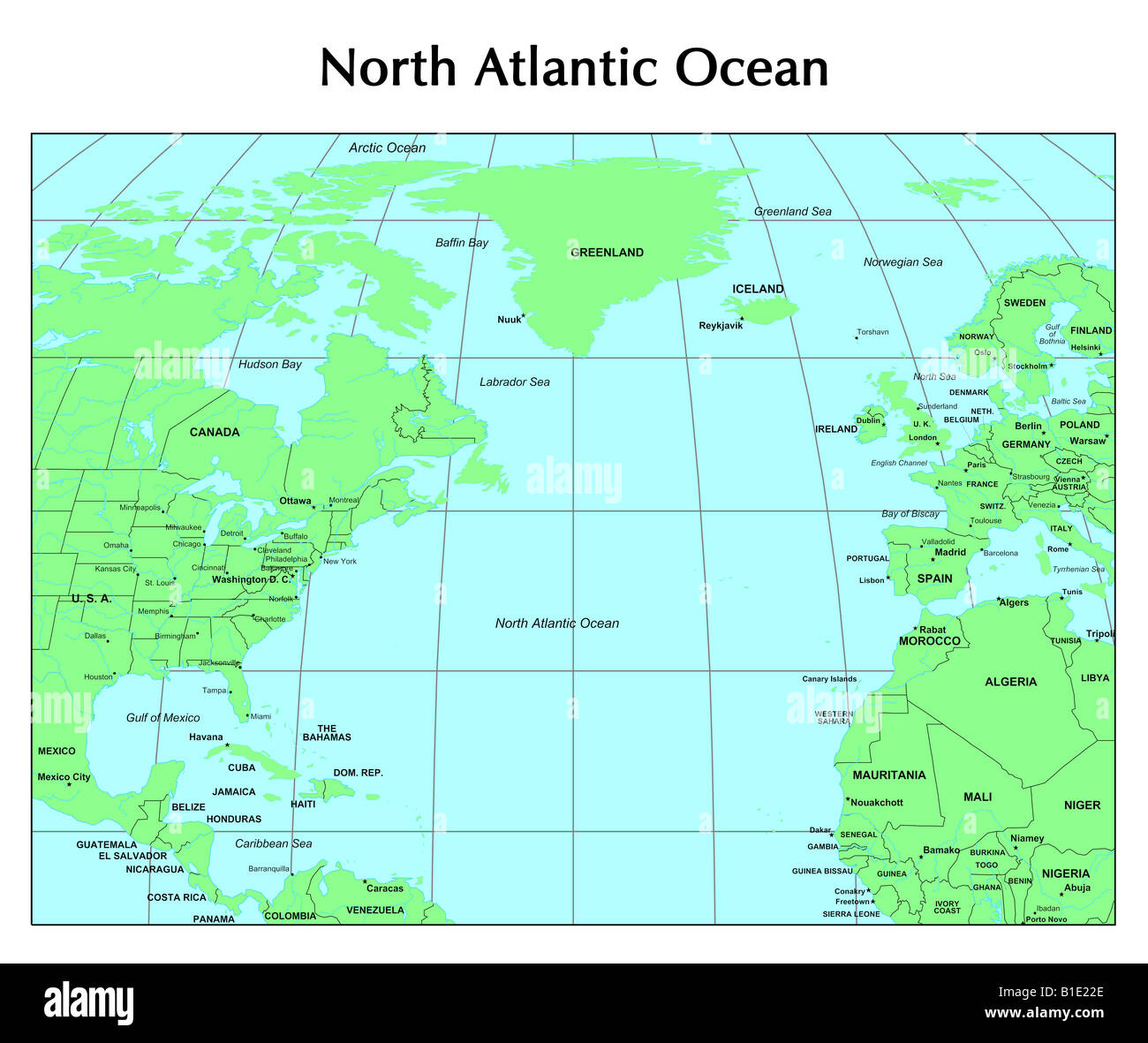
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The North Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!