The Mediterranean Sea And Atlantic Ocean: A Tale Of Two Seas
The Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean: A Tale of Two Seas
Related Articles: The Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean: A Tale of Two Seas
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean: A Tale of Two Seas. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean: A Tale of Two Seas

The Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, though distinct bodies of water, are inextricably linked, forming a critical nexus of geography, history, and human activity. Understanding their relationship and individual characteristics is essential for comprehending the global landscape and the intricate web of interactions that shape it.
The Mediterranean Sea: A Cradle of Civilization
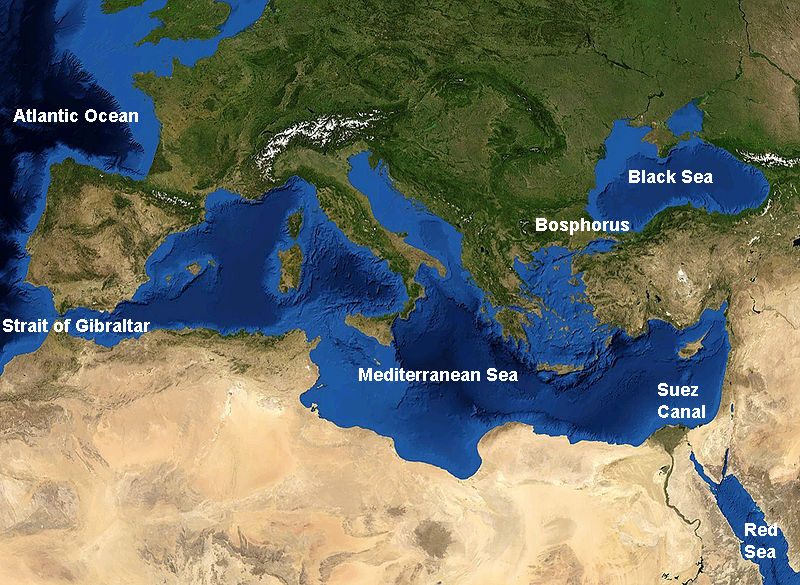
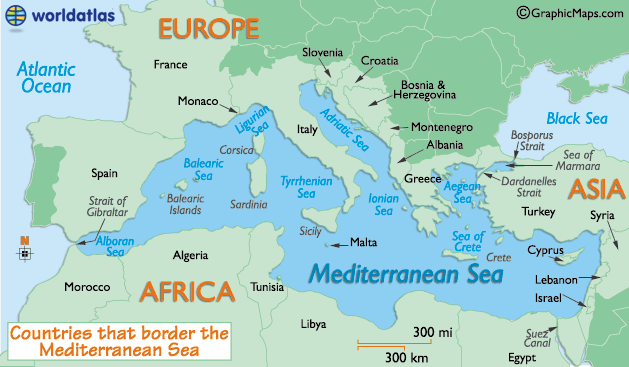
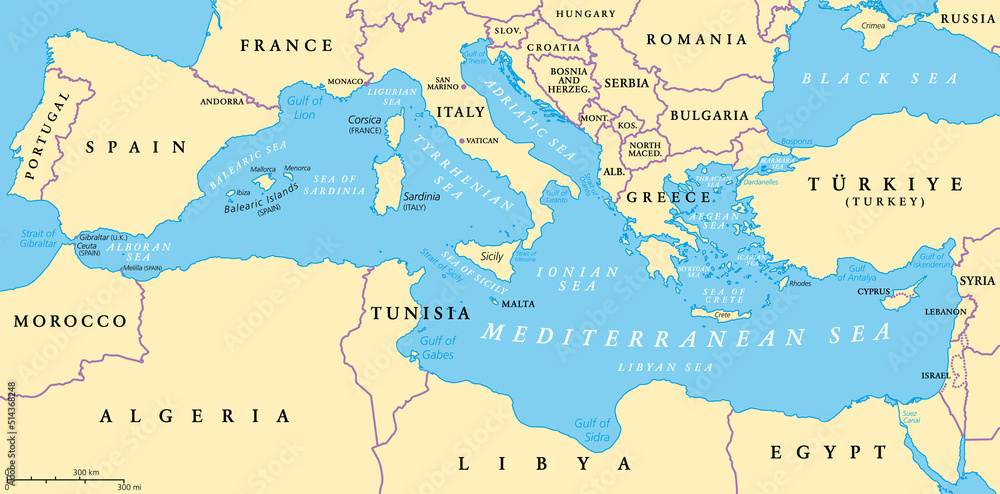
The Mediterranean Sea, a vast inland sea bordered by Europe, Asia, and Africa, has been a pivotal waterway for millennia. Its strategic location has facilitated trade, migration, and cultural exchange, shaping the course of history and leaving an indelible mark on the surrounding civilizations.
Geography and Characteristics:
- Size and Shape: The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of approximately 2.5 million square kilometers, with a maximum depth of 5,267 meters. Its shape, resembling an elongated hourglass, stretches for over 4,000 kilometers from west to east.
- Climate and Water Circulation: The Mediterranean Sea experiences a warm, dry climate with hot summers and mild winters. Its water circulation is characterized by a deep-water circulation pattern, with dense, saline water sinking in the eastern basin and flowing westward.
- Biodiversity: The Mediterranean Sea is a biodiversity hotspot, home to a rich array of marine life, including diverse fish species, marine mammals, and coral reefs. However, it faces threats from overfishing, pollution, and climate change.
Historical Significance:
- Ancient Civilizations: The Mediterranean Sea witnessed the rise and fall of ancient civilizations, including the Greeks, Romans, Phoenicians, and Egyptians. Its shores served as the cradle of Western civilization, fostering trade, cultural exchange, and the development of knowledge.
- Trade Routes: The Mediterranean Sea has been a vital trade route for centuries, connecting Europe, Asia, and Africa. It played a crucial role in the Silk Road, facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas across continents.
- Military and Political Significance: The Mediterranean Sea has been a stage for numerous historical conflicts, including the Punic Wars and the Crusades. Its strategic location has made it a focal point for military and political power throughout history.
The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast and Powerful Force
The Atlantic Ocean, the second-largest ocean in the world, is a vast expanse of water covering over 100 million square kilometers. It plays a crucial role in global climate regulation, marine biodiversity, and human activity.
Geography and Characteristics:
- Size and Depth: The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest ocean, covering over 20% of the Earth’s surface. It reaches a maximum depth of 8,605 meters in the Puerto Rico Trench.
- Climate and Water Circulation: The Atlantic Ocean experiences a wide range of climates, from tropical to polar. Its water circulation is characterized by strong currents, including the Gulf Stream and the North Atlantic Current, which influence global weather patterns.
- Biodiversity: The Atlantic Ocean is home to a vast array of marine life, including whales, dolphins, sharks, and diverse fish species. It is also home to unique ecosystems like coral reefs, seamounts, and hydrothermal vents.
Historical Significance:
- Exploration and Colonization: The Atlantic Ocean played a crucial role in European exploration and colonization, facilitating voyages to the Americas, Africa, and Asia.
- Trade Routes: The Atlantic Ocean has been a major trade route for centuries, connecting Europe, Africa, and the Americas. It facilitated the transatlantic slave trade and the exchange of goods and ideas across continents.
- Modern Transportation: The Atlantic Ocean remains a vital transportation route for shipping, fishing, and energy exploration. Its vastness and strategic location make it crucial for global trade and communication.
The Interplay of Two Seas: A Vital Connection
The Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean are connected through the Strait of Gibraltar, a narrow passage between Spain and Morocco. This connection allows for the exchange of water, nutrients, and marine life between the two seas, creating a unique ecosystem.
- Water Circulation: The Strait of Gibraltar acts as a conduit for water exchange between the Atlantic and Mediterranean. The Atlantic’s saltier water flows into the Mediterranean, while the Mediterranean’s warmer, less saline water flows out.
- Biodiversity: The Strait of Gibraltar is a biodiversity hotspot, providing a passage for migratory species and fostering a unique mix of Atlantic and Mediterranean marine life.
- Climate Influence: The Atlantic Ocean’s influence on the Mediterranean Sea is significant, moderating its climate and influencing its water circulation patterns.
Challenges and Opportunities
Both the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean face challenges from human activity and climate change.
- Pollution: Pollution from industrial activities, agriculture, and urban runoff poses a significant threat to the health of both seas.
- Overfishing: Overfishing is depleting fish stocks and disrupting marine ecosystems, impacting the livelihoods of coastal communities.
- Climate Change: Rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and sea-level rise are altering marine ecosystems and threatening coastal communities.
Conservation and Management:
Protecting the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean requires international cooperation and sustainable management practices.
- Marine Protected Areas: Establishing marine protected areas helps conserve biodiversity and protect sensitive ecosystems.
- Sustainable Fisheries: Implementing sustainable fishing practices, such as quotas and fishing gear regulations, can help protect fish stocks and ensure long-term sustainability.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and implementing adaptation strategies are crucial for mitigating the impacts of climate change on both seas.
FAQs
What is the difference between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean?
The Mediterranean Sea is a semi-enclosed sea, surrounded by landmasses, while the Atlantic Ocean is a vast open ocean. The Mediterranean Sea is warmer and saltier than the Atlantic Ocean due to its limited connection to the open ocean.
Why is the Mediterranean Sea important?
The Mediterranean Sea has been a cradle of civilization, playing a pivotal role in trade, migration, and cultural exchange. It is also a biodiversity hotspot, home to a rich array of marine life.
Why is the Atlantic Ocean important?
The Atlantic Ocean is a vast expanse of water that plays a crucial role in global climate regulation, marine biodiversity, and human activity. It is a major transportation route and a source of food and resources.
What are the threats to the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean?
Both seas face threats from pollution, overfishing, and climate change. These threats can harm marine life, disrupt ecosystems, and impact coastal communities.
What can be done to protect the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean?
Protecting these seas requires international cooperation, sustainable management practices, and a commitment to conservation. Actions include establishing marine protected areas, implementing sustainable fisheries, and mitigating climate change.
Tips
- Learn about the geography and characteristics of the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean.
- Explore the historical significance of these seas and their impact on human civilization.
- Understand the challenges and opportunities facing these seas, including pollution, overfishing, and climate change.
- Support organizations working to conserve marine ecosystems and promote sustainable practices.
- Reduce your environmental impact by minimizing plastic waste, choosing sustainable seafood, and supporting conservation efforts.
Conclusion
The Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean are interconnected bodies of water that have shaped the course of human history and continue to play a vital role in the global ecosystem. Understanding their unique characteristics, historical significance, and the challenges they face is essential for promoting their conservation and ensuring their long-term health. By embracing sustainable practices, fostering international cooperation, and mitigating the impacts of climate change, we can safeguard these vital resources for future generations.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean: A Tale of Two Seas. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!