The Convergence Of Titans: Where The Atlantic And Pacific Oceans Meet
The Convergence of Titans: Where the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans Meet
Related Articles: The Convergence of Titans: Where the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans Meet
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Convergence of Titans: Where the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans Meet. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Convergence of Titans: Where the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans Meet
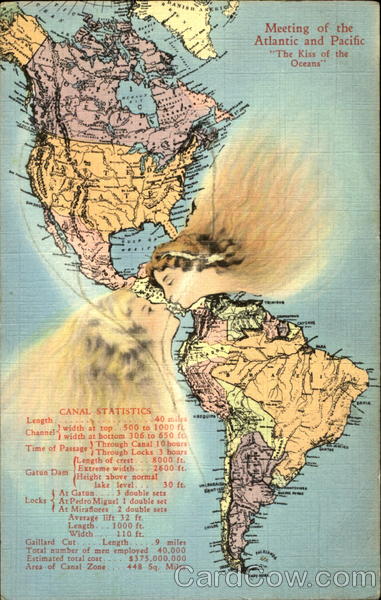
The Earth’s oceans, vast and interconnected, are often perceived as singular entities. However, the reality is far more nuanced. The world’s oceans are distinct bodies of water, each with unique characteristics and boundaries. One of the most striking examples of this distinction is the meeting point of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, a phenomenon that has captivated explorers and scientists alike for centuries.
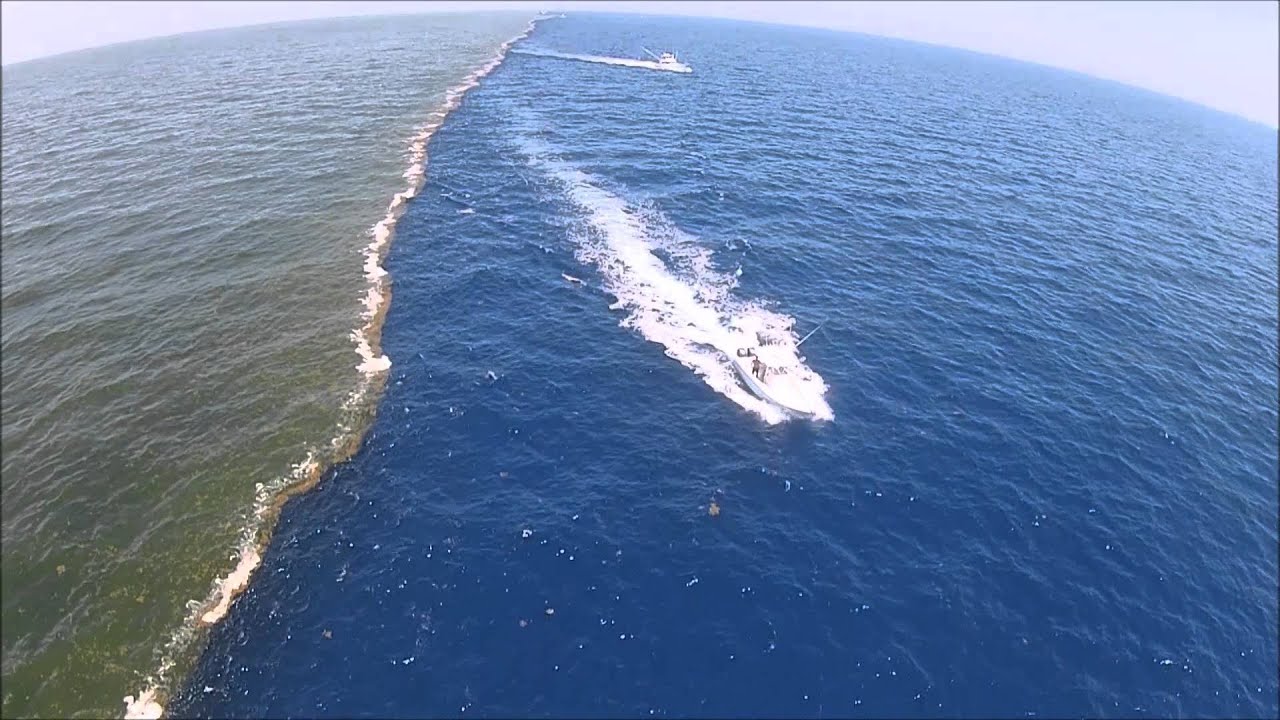
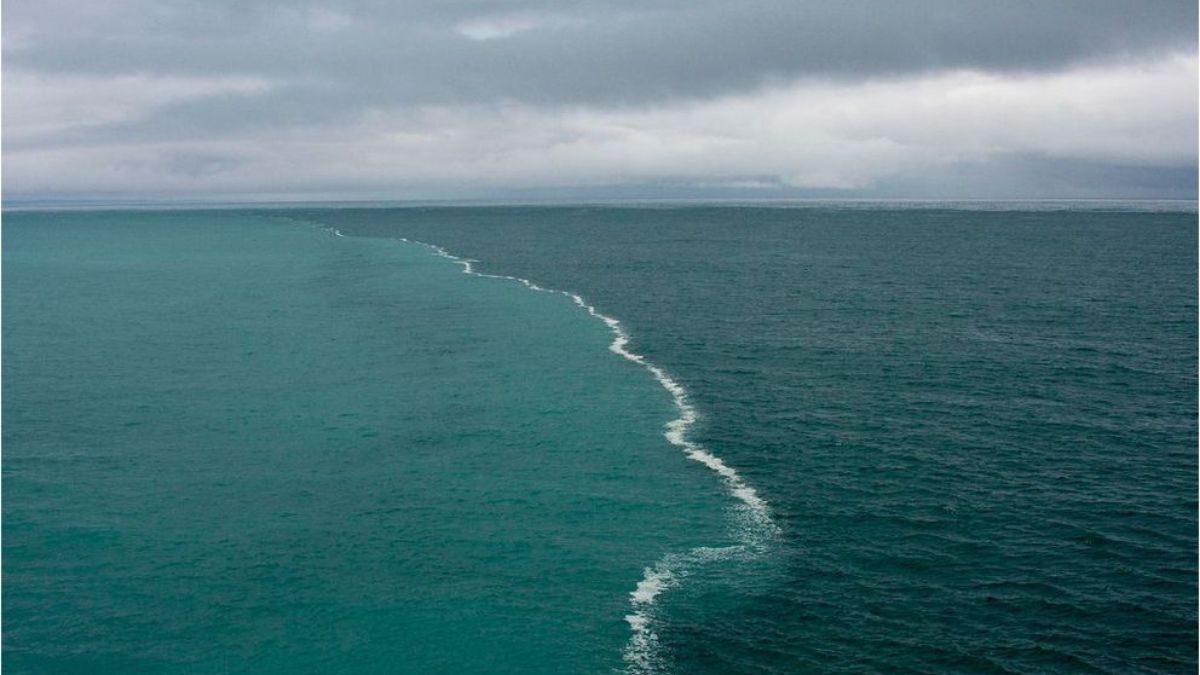
While the idea of two oceans colliding and creating a dramatic boundary might evoke images of a clashing, turbulent landscape, the reality is far more subtle. The Atlantic and Pacific do not truly "meet" in the traditional sense. Instead, they converge in a zone known as the Drake Passage, located between the southern tip of South America and the Antarctic Peninsula. This passage, roughly 600 miles wide and 800 miles long, represents a dynamic boundary where the waters of the two oceans mix and interact.
A Symphony of Currents and Water Masses:
The convergence of the Atlantic and Pacific in the Drake Passage is not a static line but a dynamic zone where water masses from both oceans interact. The interplay of currents, temperature differences, and salinity levels creates a unique environment, influencing the distribution of marine life, weather patterns, and global climate.
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC): This powerful current, flowing eastward around Antarctica, plays a pivotal role in the Drake Passage. It acts as a conduit for water exchange between the Atlantic and Pacific, transporting heat, nutrients, and marine organisms between the two ocean basins.
The Cold Waters of the Pacific: The Pacific Ocean, particularly in the south, is characterized by cold, nutrient-rich waters. These waters, driven by the ACC, flow eastward into the Drake Passage, contributing to the unique ecosystem of the region.
The Warm Waters of the Atlantic: The Atlantic Ocean, in contrast, carries warmer, saltier waters. These waters, influenced by the Gulf Stream and other currents, flow westward into the Drake Passage, creating a thermal gradient and influencing the mixing process.
The Convergence Zone: The Drake Passage represents a zone of intense mixing where the cold, nutrient-rich waters of the Pacific meet the warmer, saltier waters of the Atlantic. This mixing process results in a complex interplay of currents, temperature variations, and salinity gradients, creating a unique environment for marine life.
Ecological Significance:
The convergence of the Atlantic and Pacific in the Drake Passage has significant ecological implications. The mixing of water masses creates a zone of high productivity, supporting a diverse array of marine life, including whales, seals, penguins, and numerous fish species. The region is also a crucial breeding ground for many migratory species, making it a vital habitat for marine biodiversity.
The Influence on Global Climate:
The Drake Passage plays a crucial role in regulating global climate. The exchange of heat and water between the Atlantic and Pacific through the ACC influences the distribution of heat and salinity around the globe. This dynamic process helps regulate ocean currents, weather patterns, and global climate stability.
A Window into the Past:
The Drake Passage also provides a valuable window into the Earth’s past. Sediments deposited on the seabed offer insights into past climate changes, oceanographic conditions, and the evolution of marine life. By studying these sediments, scientists can reconstruct the history of the region and gain a deeper understanding of the Earth’s climate system.
Navigational Challenges:
The Drake Passage is notorious for its challenging navigational conditions. Strong winds, large waves, and unpredictable weather patterns make it a treacherous route for ships. Despite these challenges, the Drake Passage remains a vital shipping route connecting the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
The Importance of Research:
The Drake Passage is a region of immense scientific interest, offering a unique opportunity to study the interaction of two major ocean basins. Continued research is essential to understand the complex processes at play in this dynamic zone and its implications for global climate, marine life, and human activities.
FAQs:
Q: What is the exact location where the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans meet?
A: The Atlantic and Pacific Oceans do not meet in a defined line. They converge in a zone known as the Drake Passage, located between the southern tip of South America and the Antarctic Peninsula.
Q: Is there a visible boundary between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans?
A: While there is a distinct change in water characteristics, there is no clearly defined visible boundary. The convergence is a gradual mixing zone, not a sharp divide.
Q: What is the significance of the Drake Passage?
A: The Drake Passage is a crucial point of interaction between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, influencing global climate, marine life, and oceanographic processes.
Q: Why is the Drake Passage considered challenging for navigation?
A: The Drake Passage is known for its strong winds, large waves, and unpredictable weather patterns, making it a treacherous route for ships.
Q: What are the major currents involved in the Drake Passage?
A: The Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) plays a pivotal role, transporting water masses between the Atlantic and Pacific.
Q: How does the Drake Passage influence global climate?
A: The exchange of heat and water through the ACC influences the distribution of heat and salinity around the globe, contributing to global climate regulation.
Tips:
- Study maps and charts: Understanding the geography of the Drake Passage is crucial for appreciating its significance.
- Explore documentaries and videos: Visual representations of the Drake Passage can provide a better understanding of its dynamic nature.
- Follow research updates: Stay informed about the latest scientific findings on the Drake Passage and its implications.
- Consider visiting the region: If possible, experiencing the Drake Passage firsthand can offer a profound appreciation for its unique beauty and ecological importance.
Conclusion:
The convergence of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans in the Drake Passage is a testament to the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems. This dynamic zone, characterized by the mixing of water masses, currents, and temperature gradients, plays a vital role in regulating global climate, supporting marine biodiversity, and providing a valuable window into the Earth’s past. Continued research and exploration are essential to understand the complex processes at play in this remarkable region and its implications for the future of our planet.

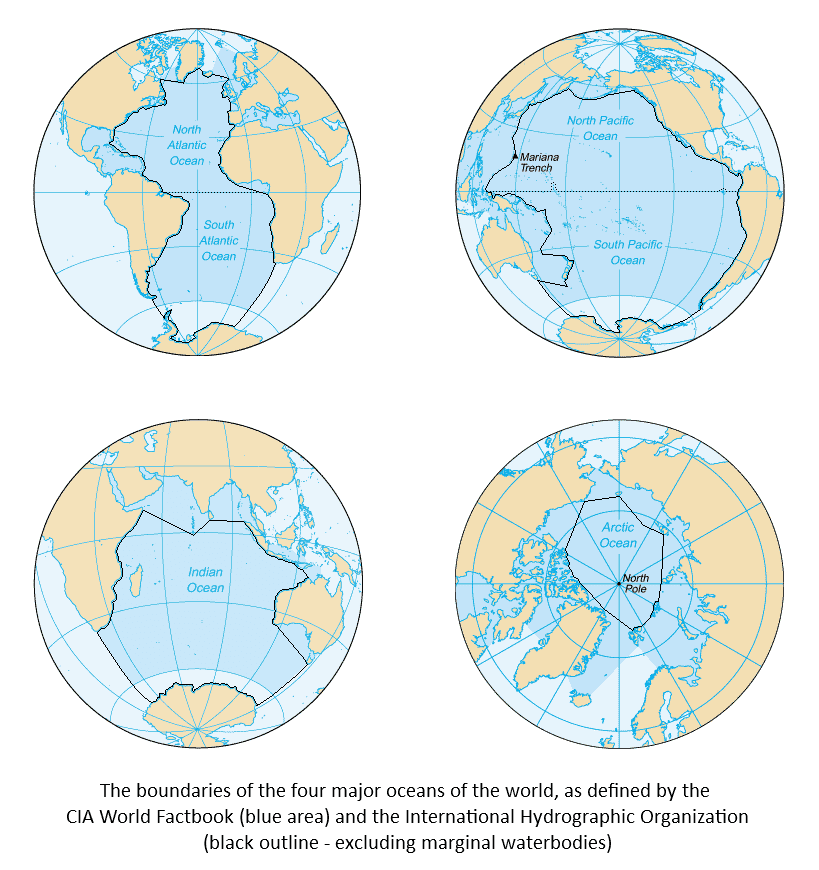



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Convergence of Titans: Where the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans Meet. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!