The Atlas Mountains: A Backbone Of North Africa
The Atlas Mountains: A Backbone of North Africa
Related Articles: The Atlas Mountains: A Backbone of North Africa
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Atlas Mountains: A Backbone of North Africa. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Atlas Mountains: A Backbone of North Africa

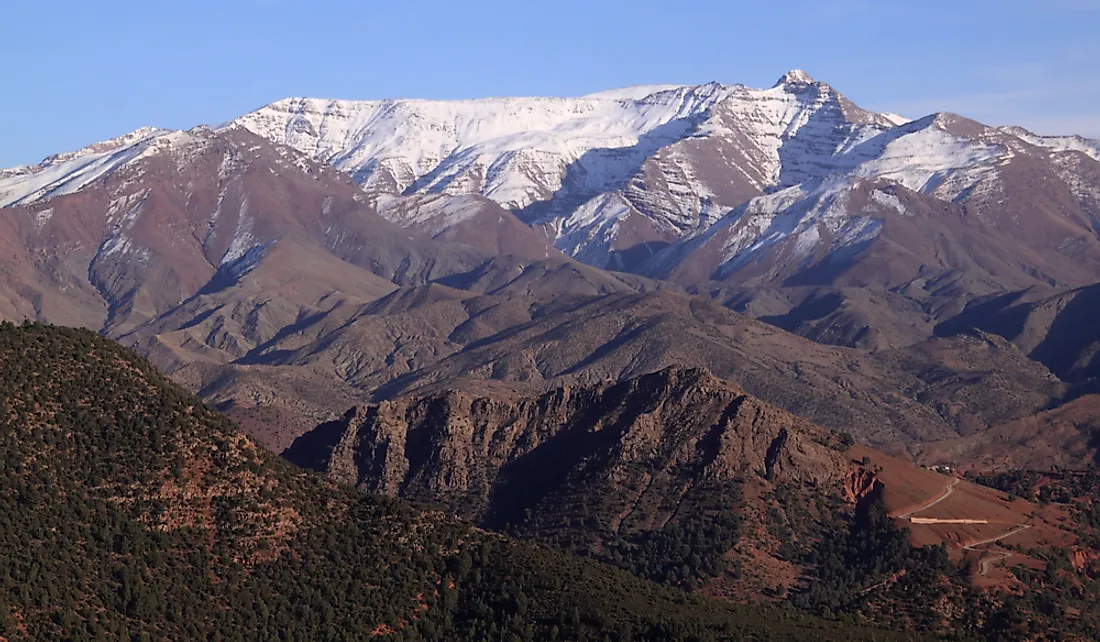
The Atlas Mountains, a majestic range that stretches across northwest Africa, are a defining feature of the continent’s geography. Their imposing presence shapes the climate, influences biodiversity, and plays a crucial role in the lives of millions of people. Understanding their location, characteristics, and significance on a map is essential for grasping the complexities of this region.
A Geographic Tapestry:
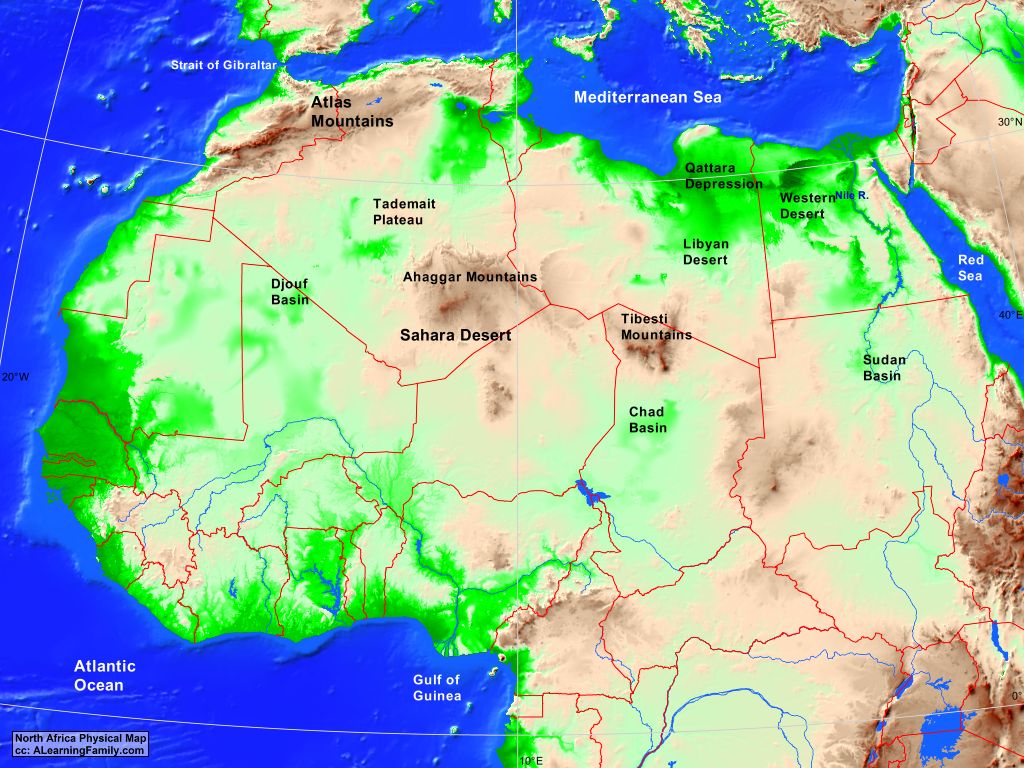
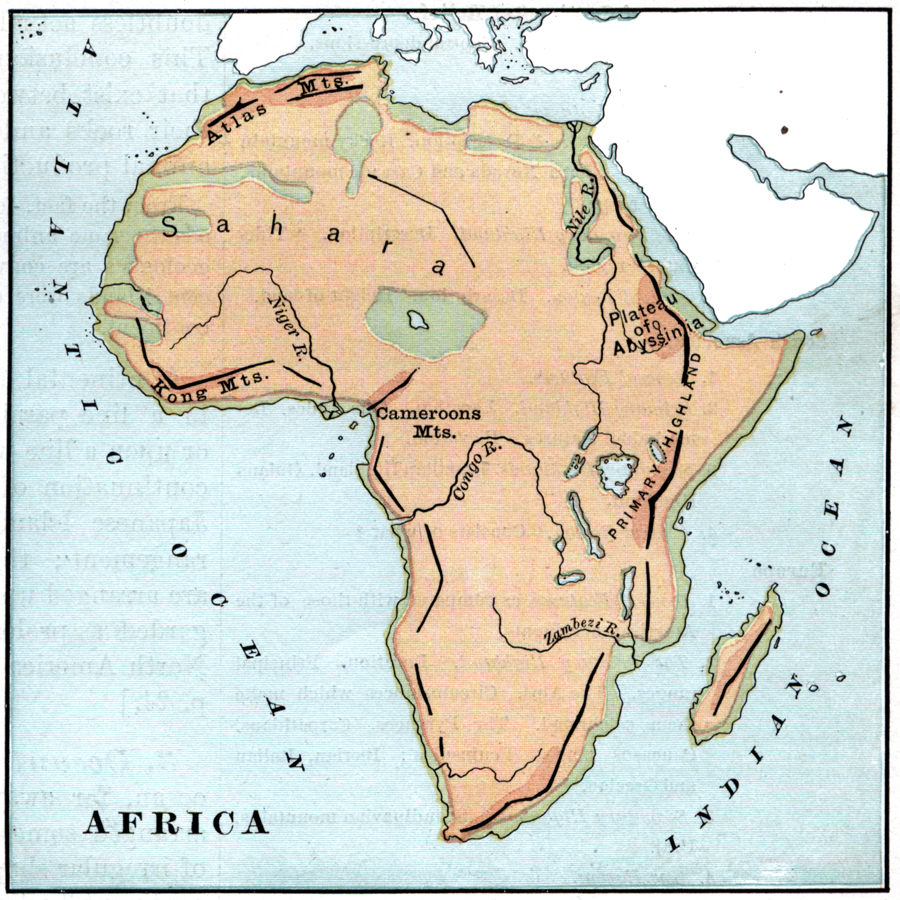
The Atlas Mountains are not a single, monolithic range, but rather a series of interconnected mountain chains that form a vast arc. They extend for over 2,000 kilometers, running from the Atlantic coast of Morocco in the west, through Algeria and Tunisia, and ending near the Mediterranean Sea in the east. This impressive length encompasses a diverse range of landscapes, from snow-capped peaks to arid deserts, from fertile valleys to rugged canyons.
Mapping the Atlas:
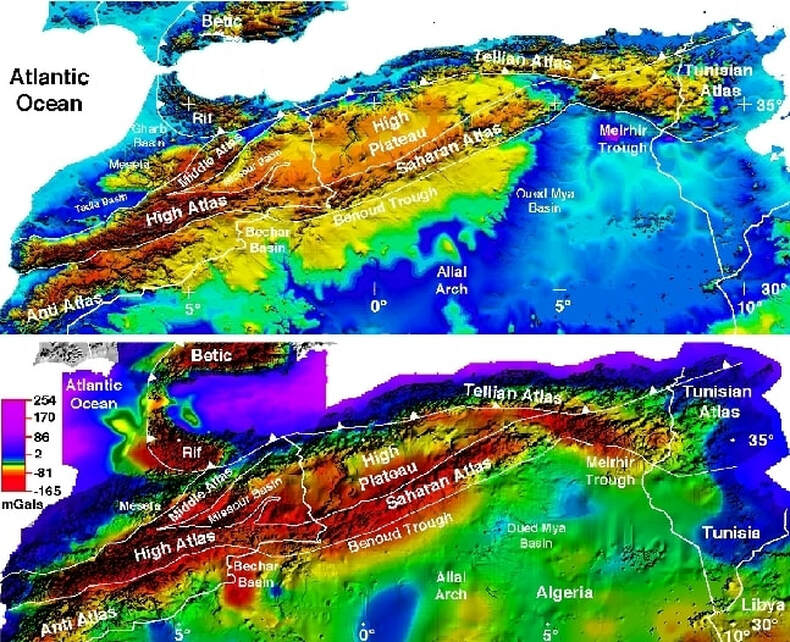
To understand the Atlas Mountains’ significance, it’s crucial to examine their placement on a map. The most prominent range, the High Atlas, forms a formidable barrier in Morocco, reaching heights of over 4,000 meters. Mount Toubkal, the highest peak in North Africa, stands proudly within this range. The Middle Atlas, situated to the north, is less elevated but still a significant geographical feature. Further east, the Anti-Atlas, characterized by its rugged and arid terrain, stretches along the border of Morocco and Western Sahara.
Moving eastward, the Atlas Mountains continue into Algeria as the Tell Atlas, a range that runs parallel to the Mediterranean coast. South of this, the Saharan Atlas, a less prominent but still important chain, marks the transition zone between the Tell Atlas and the vast Sahara Desert. Finally, in Tunisia, the Aurès Mountains, a rugged and isolated range, mark the easternmost extension of the Atlas system.
Beyond the Mountains: Significance and Impact:
The Atlas Mountains are far more than just a geographical feature; they are a vital force shaping the environment and the lives of the surrounding communities.
1. Climate and Water:
The Atlas Mountains act as a crucial barrier, influencing rainfall patterns and creating distinct microclimates. The northern slopes receive ample rainfall, fostering lush forests and fertile valleys. In contrast, the southern slopes are much drier, giving rise to semi-arid and desert landscapes. The mountains also serve as a source of freshwater, with numerous rivers and streams originating from their slopes, providing water for irrigation, drinking, and hydropower.
2. Biodiversity Hotspot:
The Atlas Mountains are a haven for a diverse array of flora and fauna. The varied elevations and microclimates support a wide range of plant communities, from cedar and juniper forests to alpine meadows and desert scrubland. The mountains are also home to numerous endemic species, including the Barbary macaque, the Atlas cedar, and the Atlas bear, highlighting the unique biodiversity of this region.
3. Cultural and Historical Significance:
The Atlas Mountains have played a significant role in the history and culture of North Africa. Ancient civilizations, such as the Berbers, have lived in these mountains for centuries, adapting to their unique environment and developing distinctive traditions and languages. The mountains have also served as a natural barrier, influencing trade routes and political boundaries.
4. Economic Importance:
The Atlas Mountains provide a range of economic opportunities, from agriculture and forestry to tourism and mining. The fertile valleys support agriculture, while the forests provide timber and other resources. The stunning landscapes attract tourists, while mineral deposits provide valuable resources. However, these economic activities must be managed sustainably to preserve the delicate balance of the ecosystem.
FAQs about the Atlas Mountains:
Q: What are the highest peaks in the Atlas Mountains?
A: The highest peak is Mount Toubkal, located in the High Atlas of Morocco, reaching an elevation of 4,167 meters. Other notable peaks include Mount Djebel Ayachi (3,737 meters) and Mount M’Goun (4,071 meters), also in the High Atlas.
Q: What are the main cultural groups living in the Atlas Mountains?
A: The Berbers, a diverse group of indigenous peoples, have inhabited the Atlas Mountains for centuries. They are known for their unique traditions, languages, and cultural practices.
Q: What are the major threats to the Atlas Mountains ecosystem?
A: The Atlas Mountains face several threats, including deforestation, overgrazing, climate change, and unsustainable tourism. These factors can lead to habitat loss, biodiversity decline, and soil erosion.
Q: What are some of the most popular tourist destinations in the Atlas Mountains?
A: Popular tourist destinations include the High Atlas National Park in Morocco, which encompasses Mount Toubkal and offers stunning views and hiking opportunities. The Dades Valley and Todra Gorge are also renowned for their natural beauty.
Tips for Exploring the Atlas Mountains:
- Plan your trip in advance: Research the best time to visit, consider the weather conditions, and book accommodation and transportation in advance.
- Respect local customs: Be mindful of local traditions and customs, dress appropriately, and avoid taking photos of people without their permission.
- Pack for all conditions: The weather in the Atlas Mountains can be unpredictable, so pack layers of clothing, appropriate footwear, and a waterproof jacket.
- Choose a reputable guide: Hiring a local guide can enhance your experience and provide valuable insights into the culture and history of the region.
- Leave no trace: Pack out all trash, stay on designated trails, and avoid disturbing wildlife or plant life.
Conclusion:
The Atlas Mountains stand as a testament to the power and beauty of nature. Their location on a map reveals their strategic importance, shaping the landscape, climate, and cultural identity of North Africa. Understanding their significance and the challenges they face is crucial for preserving this unique and valuable ecosystem for future generations. By appreciating the Atlas Mountains’ role in the region’s history, culture, and environment, we can foster a deeper connection to this remarkable part of the world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Atlas Mountains: A Backbone of North Africa. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!