The Atlas Mountains: A Backbone Of North Africa
The Atlas Mountains: A Backbone of North Africa
Related Articles: The Atlas Mountains: A Backbone of North Africa
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Atlas Mountains: A Backbone of North Africa. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Atlas Mountains: A Backbone of North Africa

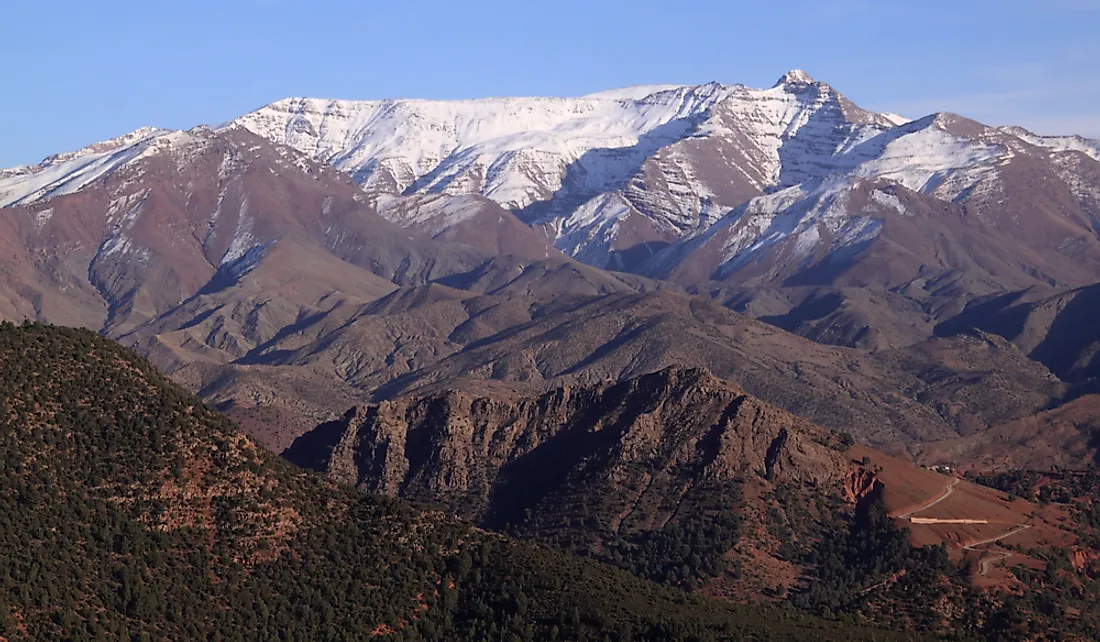
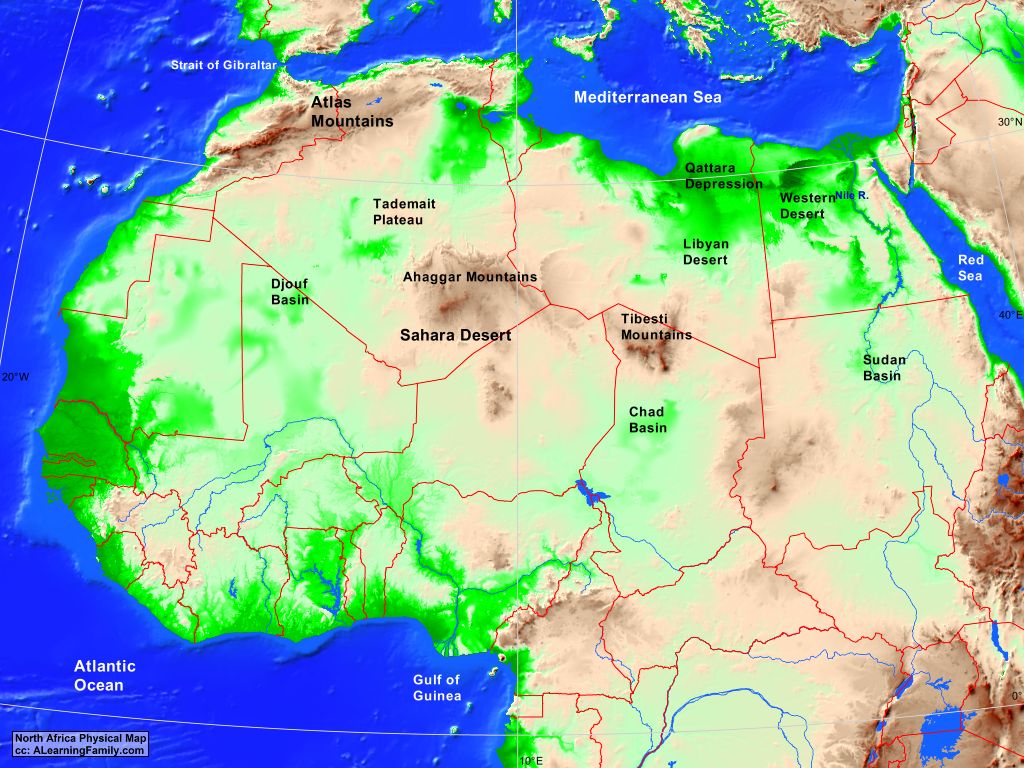
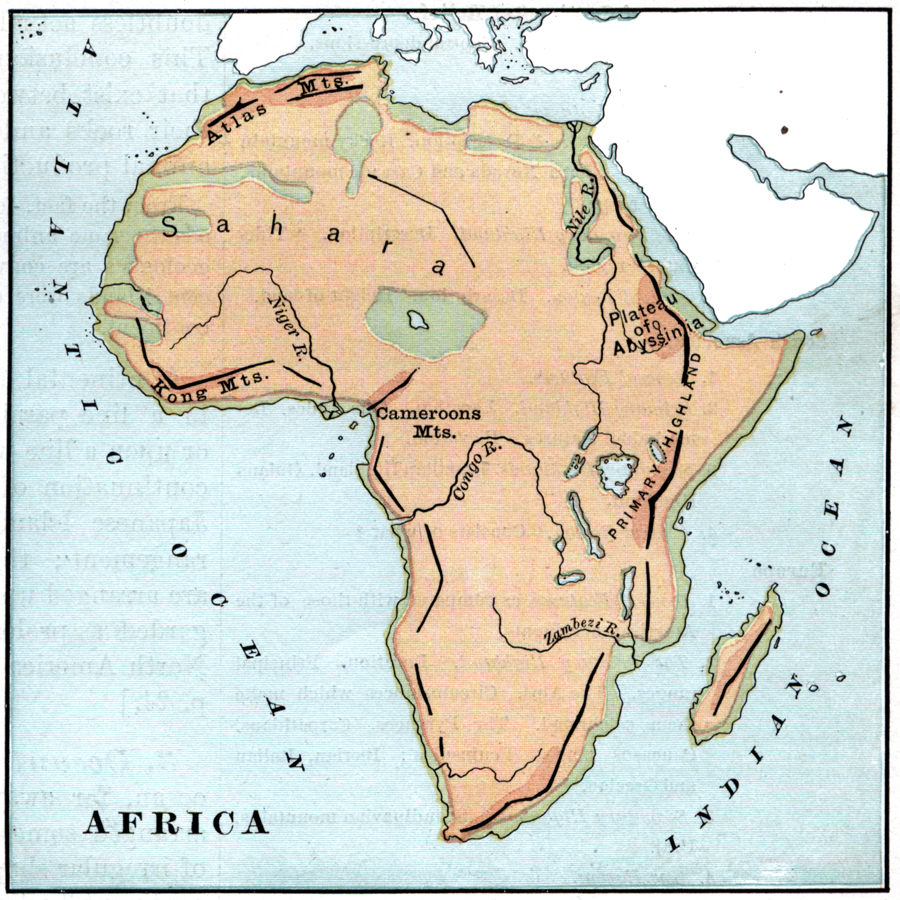
The Atlas Mountains, a majestic chain stretching across North Africa, are more than just a geographical feature. They are a testament to the continent’s geological history, a haven for diverse ecosystems, and a vital resource for the surrounding communities. Understanding the Atlas Mountains’ position on the African map reveals their profound impact on the region’s environment, culture, and economy.
A Geological Tapestry:
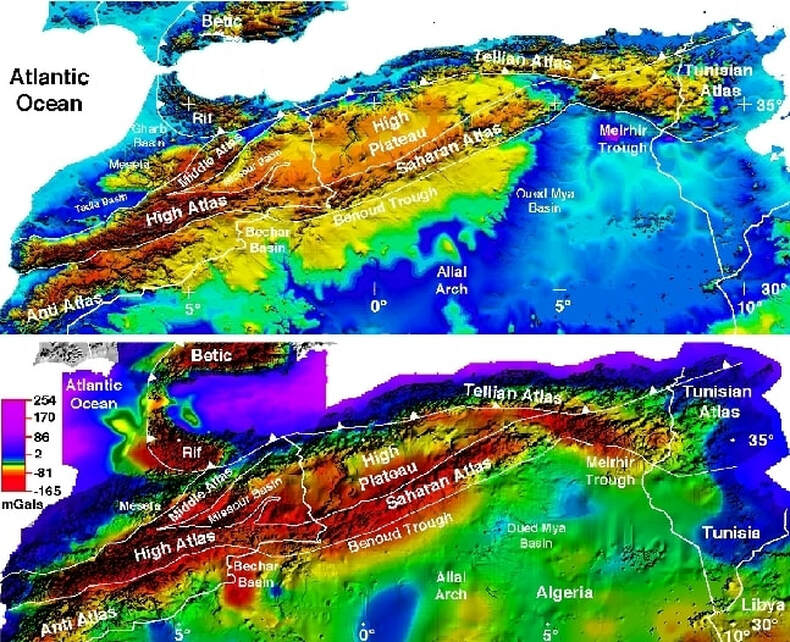
The Atlas Mountains are a young mountain range, formed relatively recently in geological terms, during the late Tertiary period. The tectonic collision between the African and Eurasian plates caused the Earth’s crust to buckle and fold, creating the dramatic peaks and valleys that characterize the Atlas. This geological process continues today, evidenced by occasional earthquakes and volcanic activity.
The Atlas range is divided into three main sections: the High Atlas, the Middle Atlas, and the Anti-Atlas. The High Atlas, the most prominent, boasts the highest peak in North Africa, Mount Toubkal, reaching a height of 4,167 meters. The Middle Atlas, characterized by rolling hills and forested slopes, offers a gentler landscape. The Anti-Atlas, located in the southwest, is a rugged and arid region, with ancient rock formations and dramatic canyons.
A Biodiversity Hotspot:
The Atlas Mountains are a haven for a remarkable diversity of life. Their varied altitudes and microclimates support a wide range of plant and animal species, many of which are endemic, found nowhere else in the world.
The lower slopes are covered in forests of cork oak, cedar, and juniper, while higher elevations transition to alpine meadows and rocky plateaus. The mountains are home to a variety of mammals, including Barbary macaques, Barbary sheep, and the endangered Atlas lion. The region’s diverse birdlife includes eagles, vultures, and migratory birds that use the mountains as a vital stopover point during their journeys.
A Source of Life:
The Atlas Mountains play a crucial role in the water cycle of North Africa. Their slopes capture rainfall and snowmelt, feeding a network of rivers and streams that provide water for agriculture, drinking, and hydropower generation. The mountains also act as a natural barrier, influencing weather patterns and creating distinct microclimates on either side.
Cultural Heritage and Economic Significance:
The Atlas Mountains have been inhabited for centuries, and their landscapes have shaped the culture and livelihoods of the local Berber communities. Traditional villages, built with local materials like stone and mud, dot the mountain slopes. Nomadic tribes have long herded livestock across the high plains, and their unique way of life continues to thrive.
The mountains also offer a wealth of natural resources. Mining, particularly for phosphates, is a significant economic activity in the region. The Atlas Mountains are also a popular destination for tourism, attracting adventurers seeking challenging treks and breathtaking views. The region’s rich cultural heritage is also a major draw, with traditional crafts, music, and cuisine attracting visitors from around the world.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite their immense value, the Atlas Mountains face a number of challenges. Climate change is impacting the region’s water resources, threatening the livelihoods of local communities. Deforestation and overgrazing are leading to soil erosion and desertification. Tourism, while beneficial, can also have negative impacts if not managed sustainably.
Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from governments, local communities, and international organizations. Sustainable development strategies are crucial to ensure the long-term prosperity of the Atlas Mountains and the people who depend on them. This includes promoting sustainable agriculture practices, conserving biodiversity, and developing responsible tourism initiatives.
FAQs:
- What is the highest peak in the Atlas Mountains? Mount Toubkal, located in the High Atlas, is the highest peak, reaching 4,167 meters.
- What are the main geographical features of the Atlas Mountains? The Atlas Mountains are divided into three main sections: the High Atlas, the Middle Atlas, and the Anti-Atlas. Each section has distinct geographical features, including high peaks, valleys, plateaus, and canyons.
- What are the main threats to the Atlas Mountains? Climate change, deforestation, overgrazing, and unsustainable tourism are the main threats to the Atlas Mountains and their ecosystems.
- How are the Atlas Mountains important for the surrounding communities? The Atlas Mountains provide water resources, fertile land for agriculture, and opportunities for mining and tourism. They also hold cultural and historical significance for the local Berber communities.
- What are some ways to protect the Atlas Mountains? Sustainable development strategies, including promoting sustainable agriculture practices, conserving biodiversity, and developing responsible tourism initiatives, are crucial for protecting the Atlas Mountains.
Tips for Exploring the Atlas Mountains:
- Plan your trip in advance: The Atlas Mountains offer a variety of experiences, from trekking to cultural immersion. Research different regions and choose activities that suit your interests and fitness level.
- Respect local customs: The Atlas Mountains are home to Berber communities with their own traditions and values. Dress modestly and be mindful of local customs, particularly when visiting villages or sacred sites.
- Hire a local guide: A knowledgeable guide can enhance your experience, providing insights into the region’s history, culture, and natural wonders.
- Be prepared for varied weather conditions: The Atlas Mountains experience a range of weather conditions, from scorching summers to snowy winters. Pack appropriate clothing and gear.
- Support local communities: Choose accommodations and activities that benefit local communities, such as homestays or tours run by local operators.
Conclusion:
The Atlas Mountains stand as a vital part of North Africa’s landscape and culture. Their geological significance, biodiversity, and role in the water cycle make them a vital resource for the region. Recognizing the challenges facing the Atlas Mountains and implementing sustainable development strategies is essential for preserving their natural beauty and cultural heritage for future generations. By understanding the importance of this majestic range, we can work towards ensuring its continued prosperity for the benefit of both people and nature.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Atlas Mountains: A Backbone of North Africa. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!