The Atlantic Ocean During The Ice Age: A Landscape Transformed
The Atlantic Ocean During the Ice Age: A Landscape Transformed
Related Articles: The Atlantic Ocean During the Ice Age: A Landscape Transformed
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Atlantic Ocean During the Ice Age: A Landscape Transformed. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Atlantic Ocean During the Ice Age: A Landscape Transformed
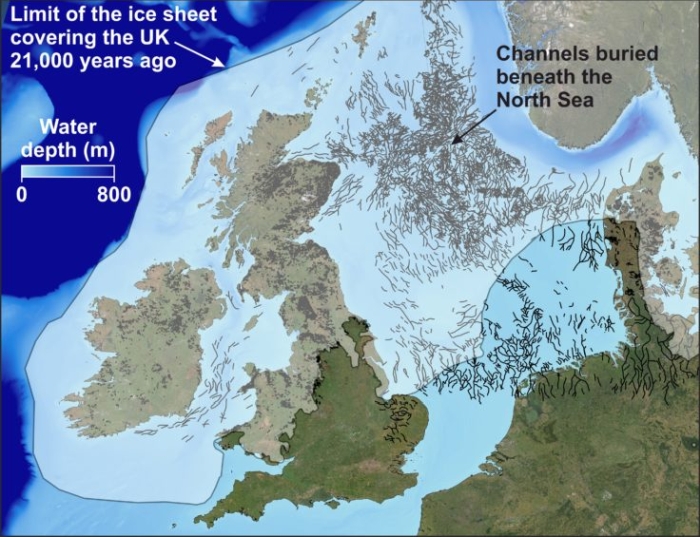
The Atlantic Ocean, a vast expanse of water spanning the globe, is a dynamic entity constantly shaped by geological forces and climatic shifts. During the Pleistocene epoch, which encompassed the last ice age, the Atlantic experienced profound transformations, impacting both its physical geography and the ecosystems it supported. Understanding these changes offers valuable insights into the complex interplay between climate, oceanography, and life on Earth.
A World of Ice and Lower Sea Levels
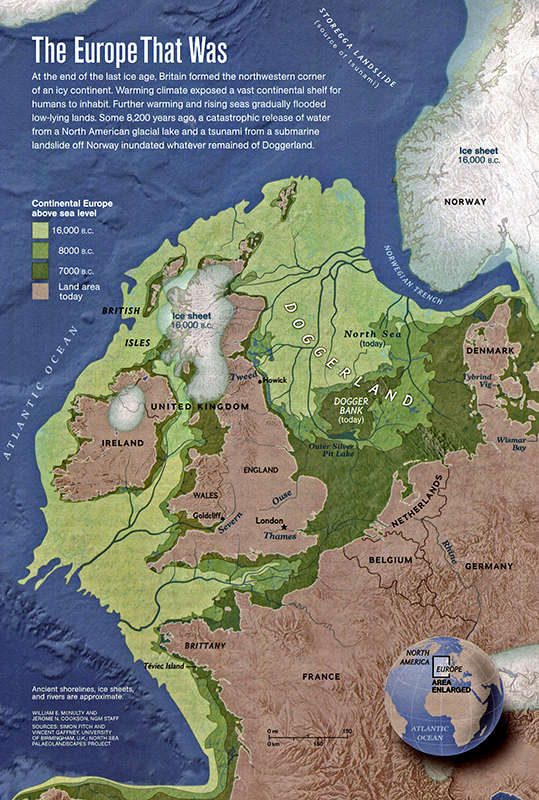
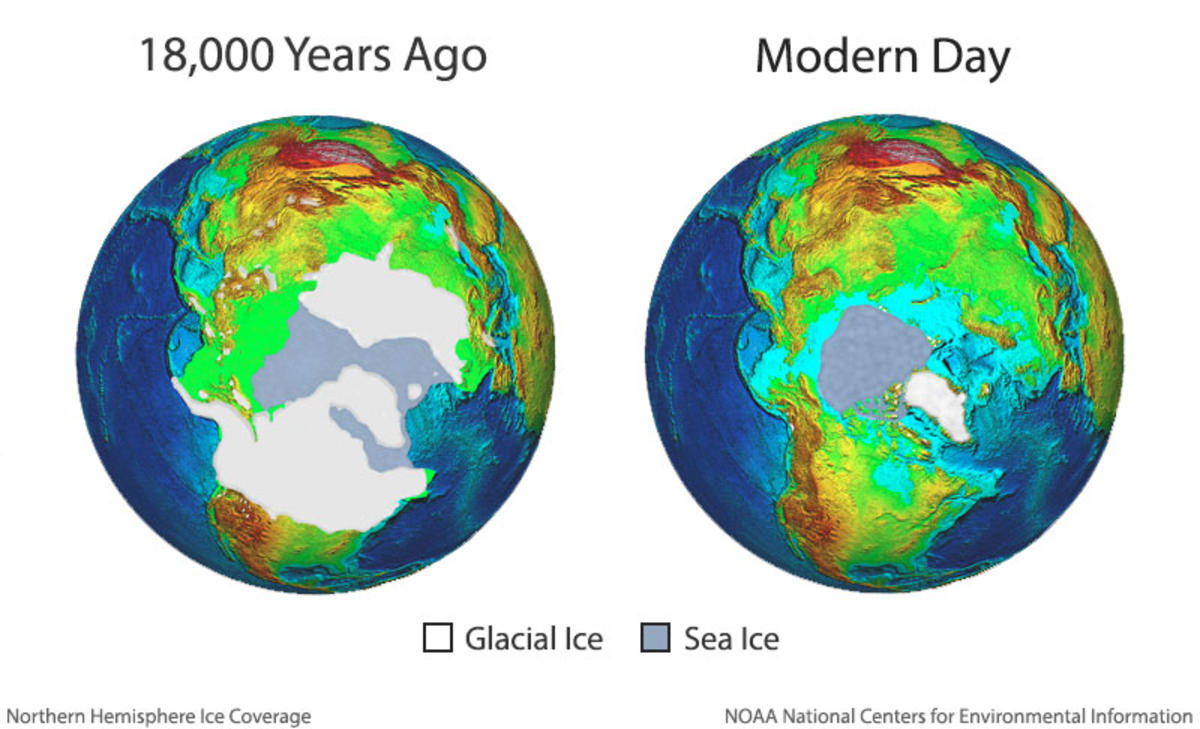
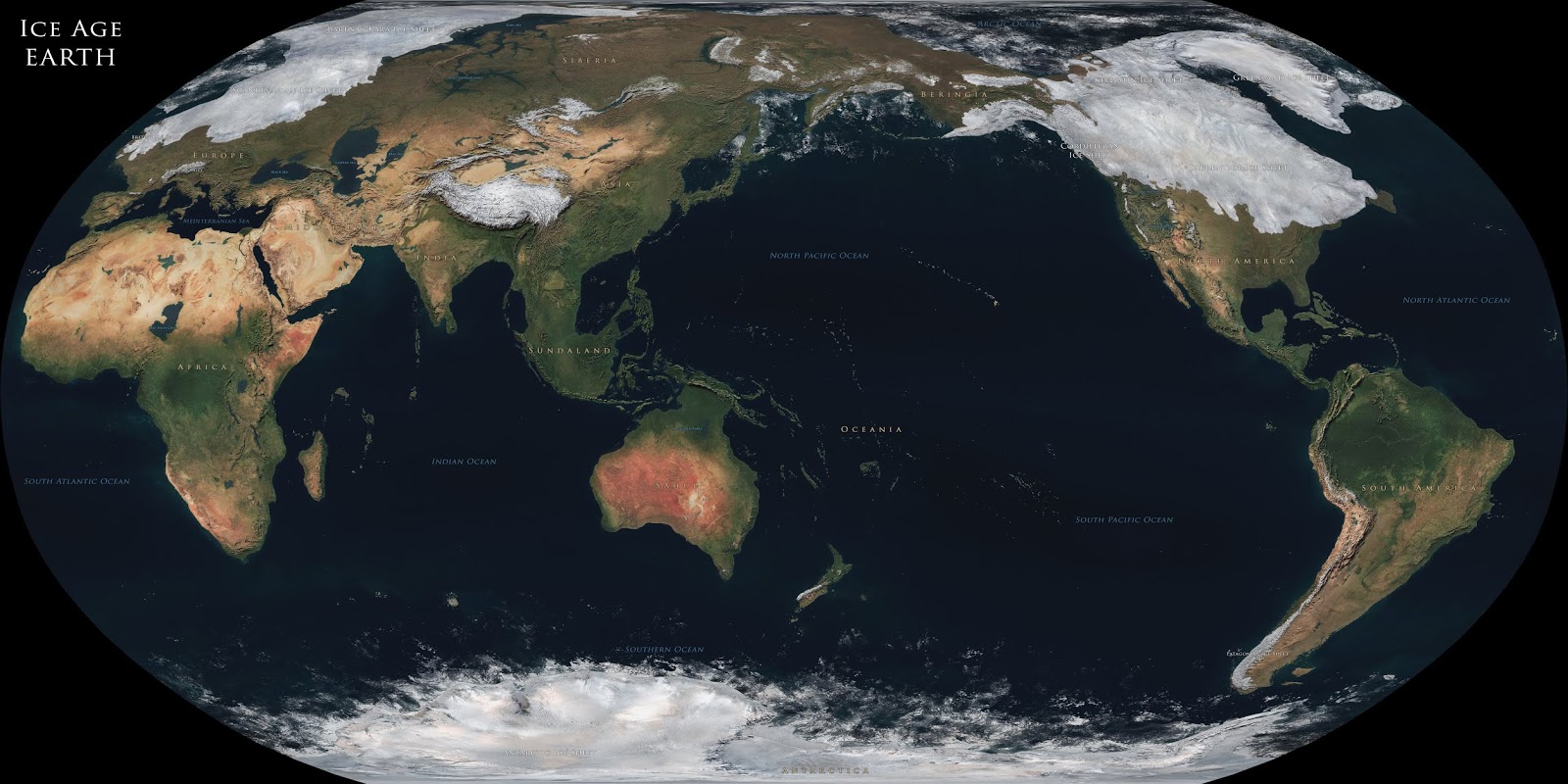
The defining characteristic of the Pleistocene ice age was the presence of massive ice sheets, particularly in the Northern Hemisphere. These colossal sheets of ice, covering vast swathes of North America and Eurasia, exerted a significant influence on global sea levels. As water was locked up in these glaciers, global sea levels plummeted, exposing vast areas of the continental shelf that are now submerged.
The Atlantic’s Shifting Coastlines
The lowered sea levels dramatically altered the Atlantic’s coastline. The continental shelf, now dry land, provided new pathways for migration and expanded the territories of various species. For instance, the Bering Land Bridge, a landmass connecting Siberia and Alaska, emerged due to the lowered sea levels, facilitating the migration of humans and animals between continents.
The North Atlantic Deep Water: A Vital Current
During the ice age, the North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW), a significant ocean current, played a crucial role in regulating global climate. The NADW, formed in the high latitudes of the North Atlantic, is a dense, cold current that sinks and flows southward. This current transports heat from the tropics towards the poles, influencing global climate patterns.
The Impact on Ocean Circulation
The presence of massive ice sheets and the associated lower sea levels significantly impacted ocean circulation. The reduced salinity of the North Atlantic due to glacial meltwater likely hindered the formation of NADW, potentially altering global climate patterns. This alteration in ocean circulation likely had far-reaching consequences for marine ecosystems and global climate.
The Role of the Atlantic in Shaping the Ice Age
The Atlantic Ocean played a crucial role in shaping the ice age. The ocean’s circulation patterns, influenced by the formation of NADW, played a key role in regulating global climate. The lowered sea levels during the ice age exposed vast areas of the continental shelf, creating new landscapes and impacting the distribution of marine life.
Exploring the Past Through Sediments and Fossils
Scientists study the past by analyzing sediment cores extracted from the ocean floor. These cores contain a wealth of information about past climates, oceanographic conditions, and the evolution of marine life. Fossils found in these sediments provide evidence of the species that inhabited the Atlantic during the ice age, offering insights into the ecosystems that thrived under these unique conditions.
Understanding the Past to Predict the Future
Understanding the Atlantic Ocean’s response to past climate changes, particularly during the ice age, provides valuable insights into how the ocean might respond to future climate change. Studying the impact of ice sheets on ocean circulation, sea levels, and marine ecosystems helps scientists predict how similar events might affect our planet in the future.
FAQs on the Atlantic Ocean During the Ice Age
1. How did the ice age affect sea levels?
The massive ice sheets that formed during the ice age locked up vast amounts of water, causing global sea levels to drop significantly. This exposed large areas of the continental shelf, which are now submerged.
2. What was the Bering Land Bridge and how did it form?
The Bering Land Bridge was a landmass connecting Siberia and Alaska that emerged due to the lowered sea levels during the ice age. This bridge facilitated the migration of humans and animals between continents.
3. How did the ice age impact ocean circulation?
The presence of ice sheets and the associated lower sea levels likely altered the formation of the North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW), a significant ocean current. This alteration in circulation potentially impacted global climate patterns.
4. What evidence do scientists use to study the Atlantic Ocean during the ice age?
Scientists analyze sediment cores extracted from the ocean floor. These cores contain fossils and other evidence that reveals past climates, oceanographic conditions, and the evolution of marine life.
5. Why is studying the Atlantic Ocean during the ice age important?
Understanding how the Atlantic Ocean responded to past climate change provides insights into how the ocean might respond to future climate change. This knowledge is essential for predicting and mitigating the impacts of climate change on our planet.
Tips for Studying the Atlantic Ocean During the Ice Age
- Focus on the role of ice sheets: Understanding the formation and impact of ice sheets on sea levels and ocean circulation is crucial.
- Explore the Bering Land Bridge: The Bering Land Bridge played a significant role in human and animal migration during the ice age.
- Investigate the North Atlantic Deep Water: The NADW is a vital ocean current that was impacted by the ice age.
- Analyze sediment cores: These cores provide a wealth of information about past climates and ecosystems.
Conclusion
The Atlantic Ocean during the ice age was a vastly different landscape than the one we see today. Lowered sea levels, altered ocean circulation, and the presence of massive ice sheets profoundly impacted the ocean’s geography, ecosystems, and global climate. Understanding these transformations provides invaluable insights into the complex relationship between climate, oceanography, and life on Earth, and helps us better understand the potential impacts of future climate change on our planet.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Atlantic Ocean During the Ice Age: A Landscape Transformed. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!