The Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline In The Global Tapestry
The Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline in the Global Tapestry
Related Articles: The Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline in the Global Tapestry
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline in the Global Tapestry. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline in the Global Tapestry
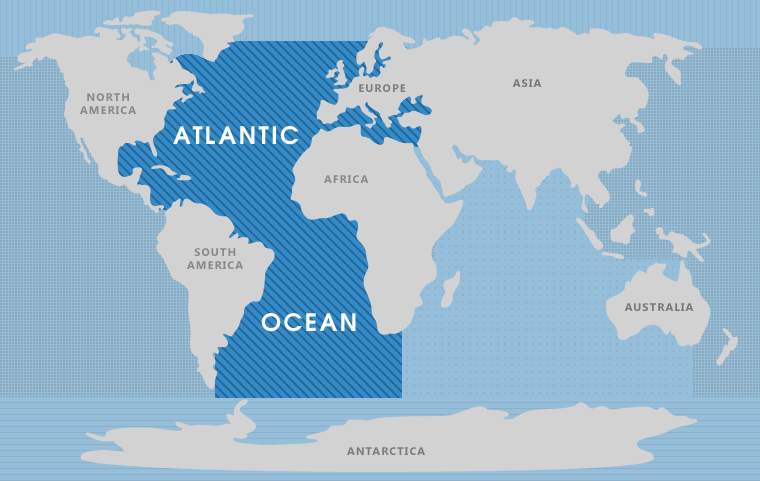
The Atlantic Ocean, a vast expanse of water covering approximately 20% of the Earth’s surface, plays a pivotal role in the global ecosystem and human civilization. It is a dynamic force, shaping coastlines, influencing weather patterns, and serving as a crucial artery for trade and transportation. This article delves into the Atlantic Ocean’s geographical features, its impact on the world, and its significance in the context of global interconnectedness.
Geographical Significance:
The Atlantic Ocean, the second-largest ocean on Earth, separates the continents of North and South America from Europe and Africa. It stretches from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, encompassing a diverse range of environments. Its vastness is underscored by its impressive dimensions:
- Surface Area: Approximately 106,400,000 square kilometers (41,100,000 square miles)
- Maximum Width: Approximately 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles)
- Average Depth: Approximately 3,900 meters (12,800 feet)
The Atlantic Ocean is characterized by its distinct features, including:
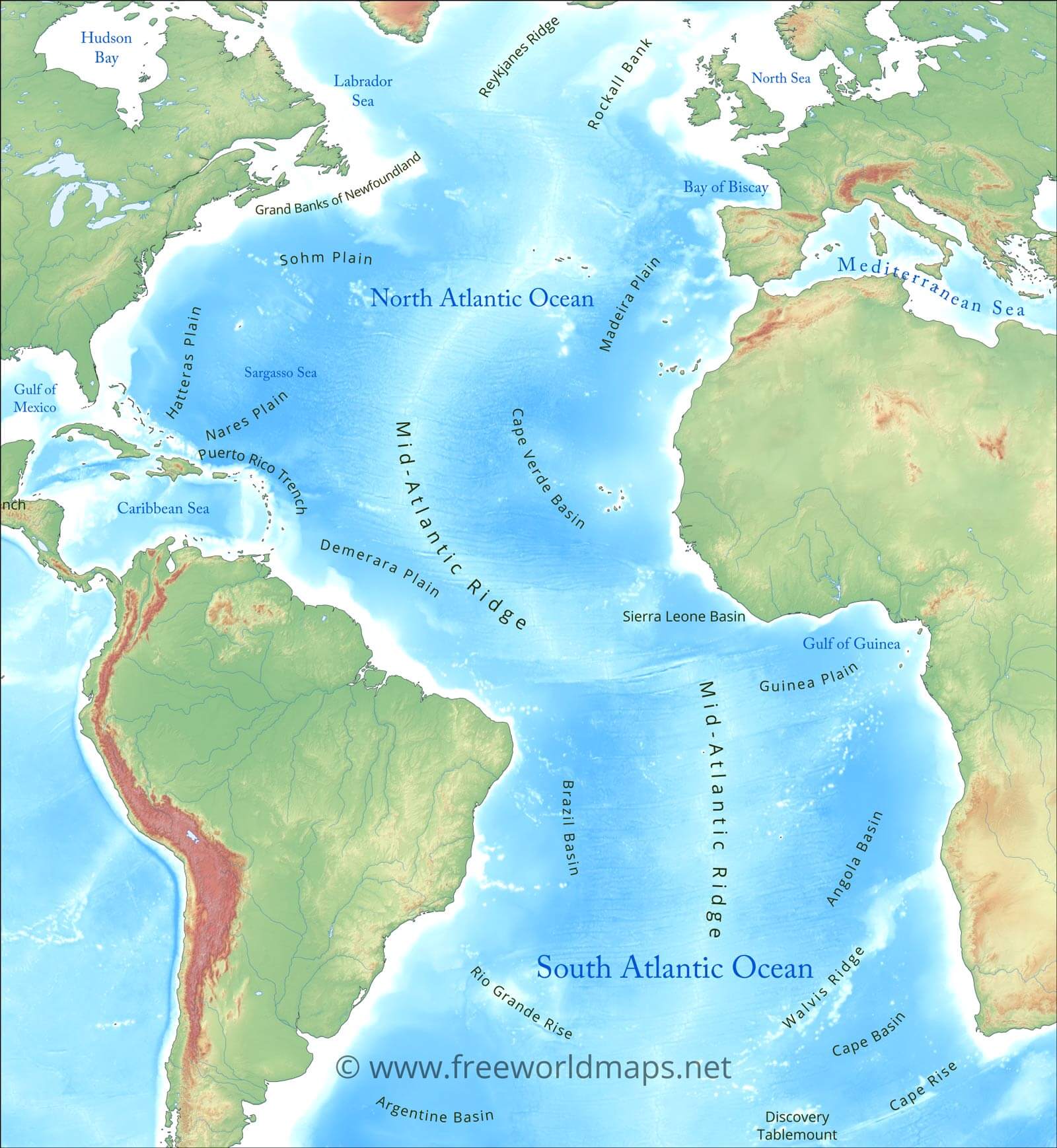
- Mid-Atlantic Ridge: A massive underwater mountain range running down the center of the ocean, formed by tectonic plate movements.
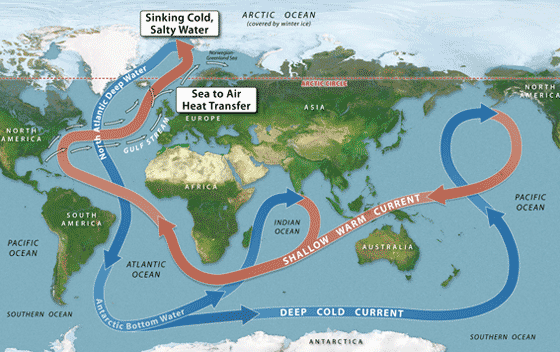
- Gulf Stream: A powerful warm current flowing northward along the eastern coast of North America, influencing the climate of Western Europe.
- North Atlantic Drift: A continuation of the Gulf Stream, bringing warm water to the coasts of northwestern Europe.
- Canary Current: A cold current flowing southward along the western coast of Africa, influencing the climate of the region.
- Benguela Current: A cold current flowing northward along the western coast of southern Africa, supporting a rich ecosystem.
Geological and Ecological Importance:
The Atlantic Ocean is a dynamic force in the Earth’s geological and ecological systems. Its formation, driven by tectonic plate movements, continues to shape the surrounding continents and influence global climate patterns.
- Tectonic Activity: The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a site of intense tectonic activity, where new ocean floor is being created through volcanic eruptions and seafloor spreading. This process plays a vital role in the Earth’s geological cycle.
- Climate Regulation: The Atlantic Ocean’s currents play a crucial role in regulating global climate. The Gulf Stream, for instance, transports warm water from the tropics to higher latitudes, moderating the climate of Western Europe.
- Marine Biodiversity: The Atlantic Ocean is home to a vast array of marine life, including whales, dolphins, sharks, fish, and coral reefs. Its diverse ecosystems provide essential habitat for numerous species, contributing to the global biodiversity.
Economic and Social Significance:
The Atlantic Ocean has been a vital artery for trade and transportation since ancient times. It remains a crucial link for global commerce, connecting continents and facilitating the movement of goods, people, and ideas.
- Trade Routes: The Atlantic Ocean has historically been a major trade route, connecting Europe, Africa, and the Americas. It continues to be a vital waterway for international trade, transporting goods across continents.
- Fishing Industry: The Atlantic Ocean is a major source of seafood, supporting a thriving fishing industry in many countries. However, overfishing and habitat degradation pose significant challenges to the sustainability of this industry.
- Tourism and Recreation: The Atlantic Ocean’s coastline offers numerous opportunities for tourism and recreation, including beaches, resorts, and marine parks. These activities contribute significantly to the economies of coastal communities.
Environmental Challenges:
Despite its vastness and importance, the Atlantic Ocean faces a range of environmental challenges, including:
- Pollution: Industrial and agricultural runoff, oil spills, and plastic waste contaminate the ocean, harming marine life and ecosystems.
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels, ocean acidification, and warming waters are impacting the Atlantic Ocean’s ecosystems and posing threats to coastal communities.
- Overfishing: Unsustainable fishing practices are depleting fish stocks and disrupting marine food webs, threatening the long-term health of the ocean.
FAQs:
Q: What are the major currents in the Atlantic Ocean?
A: The major currents in the Atlantic Ocean include the Gulf Stream, North Atlantic Drift, Canary Current, Benguela Current, and the Brazil Current. These currents play a crucial role in regulating global climate and supporting marine ecosystems.
Q: What are the main threats to the Atlantic Ocean’s environment?
A: The Atlantic Ocean faces significant threats from pollution, climate change, and overfishing. These factors are impacting marine life, ecosystems, and coastal communities.
Q: What measures are being taken to protect the Atlantic Ocean?
A: Various measures are being taken to protect the Atlantic Ocean, including international agreements to reduce pollution, sustainable fishing practices, and conservation efforts to protect marine ecosystems.
Tips:
- Reduce your plastic consumption: Single-use plastics are a major source of pollution in the ocean. Reduce your reliance on these products and choose reusable alternatives.
- Support sustainable seafood: Choose seafood from sustainable sources to help protect fish stocks and marine ecosystems.
- Advocate for environmental policies: Support policies that address climate change, pollution, and overfishing to protect the Atlantic Ocean.
Conclusion:
The Atlantic Ocean is a vast and dynamic body of water that plays a vital role in the global ecosystem and human civilization. Its geographical features, geological processes, and rich biodiversity make it a critical resource for the world. However, the Atlantic Ocean faces significant environmental challenges, requiring concerted efforts to protect its health and ensure its sustainability for future generations. By understanding its importance and taking responsible actions, we can contribute to the preservation of this vital lifeline in the global tapestry.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline in the Global Tapestry. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!