The Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline For The United States
The Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline for the United States
Related Articles: The Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline for the United States
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline for the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline for the United States

The Atlantic Ocean, a vast expanse of water stretching from the Arctic to the Antarctic, plays a pivotal role in the life of the United States. Its shores cradle a diverse array of coastal states, its waters support a vibrant maritime industry, and its currents influence the climate of the entire eastern seaboard. Understanding the relationship between the United States and the Atlantic Ocean is crucial for comprehending the nation’s history, economy, and environmental outlook.
The Geography of the Atlantic Ocean and its Relationship with the United States:
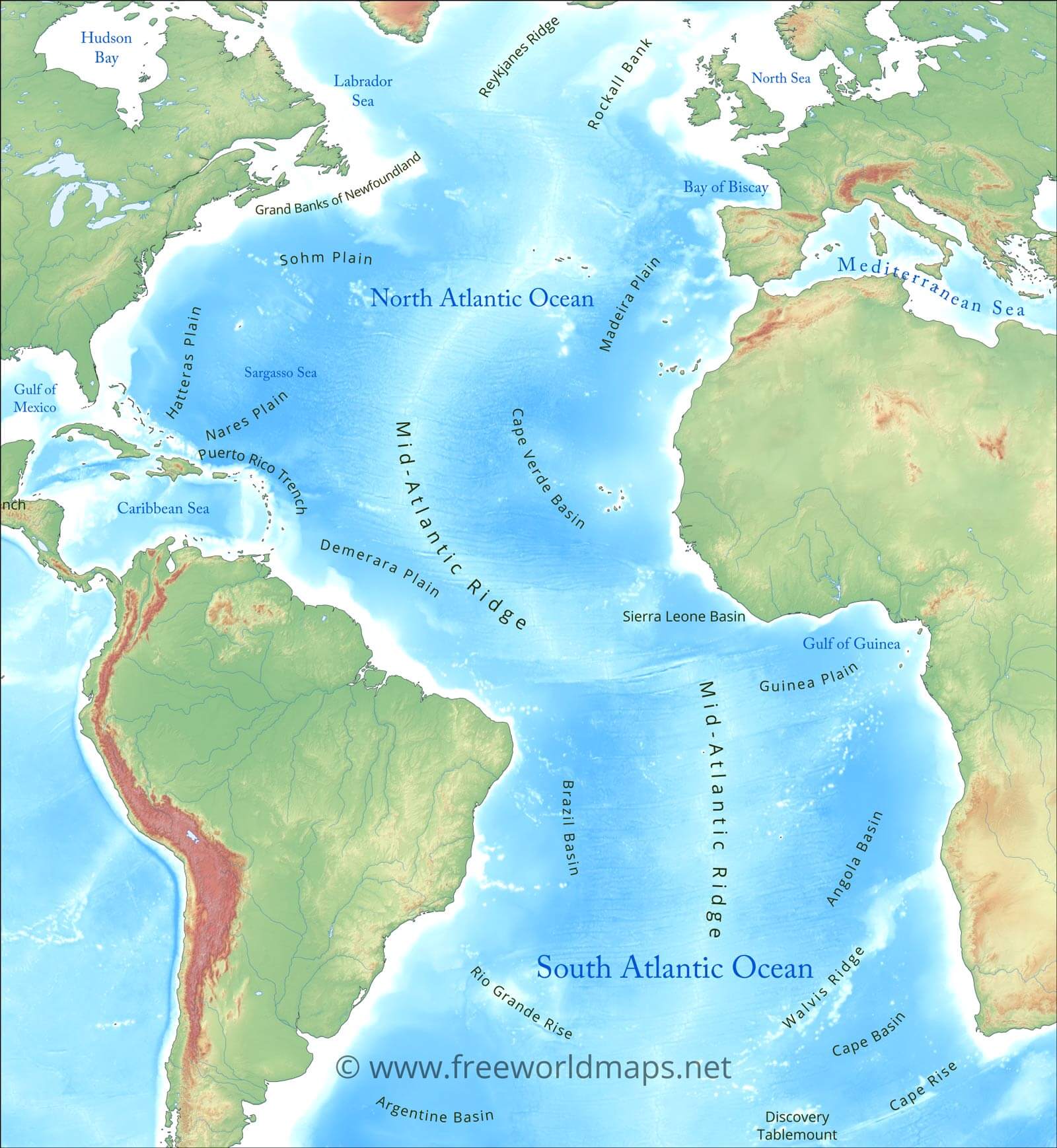
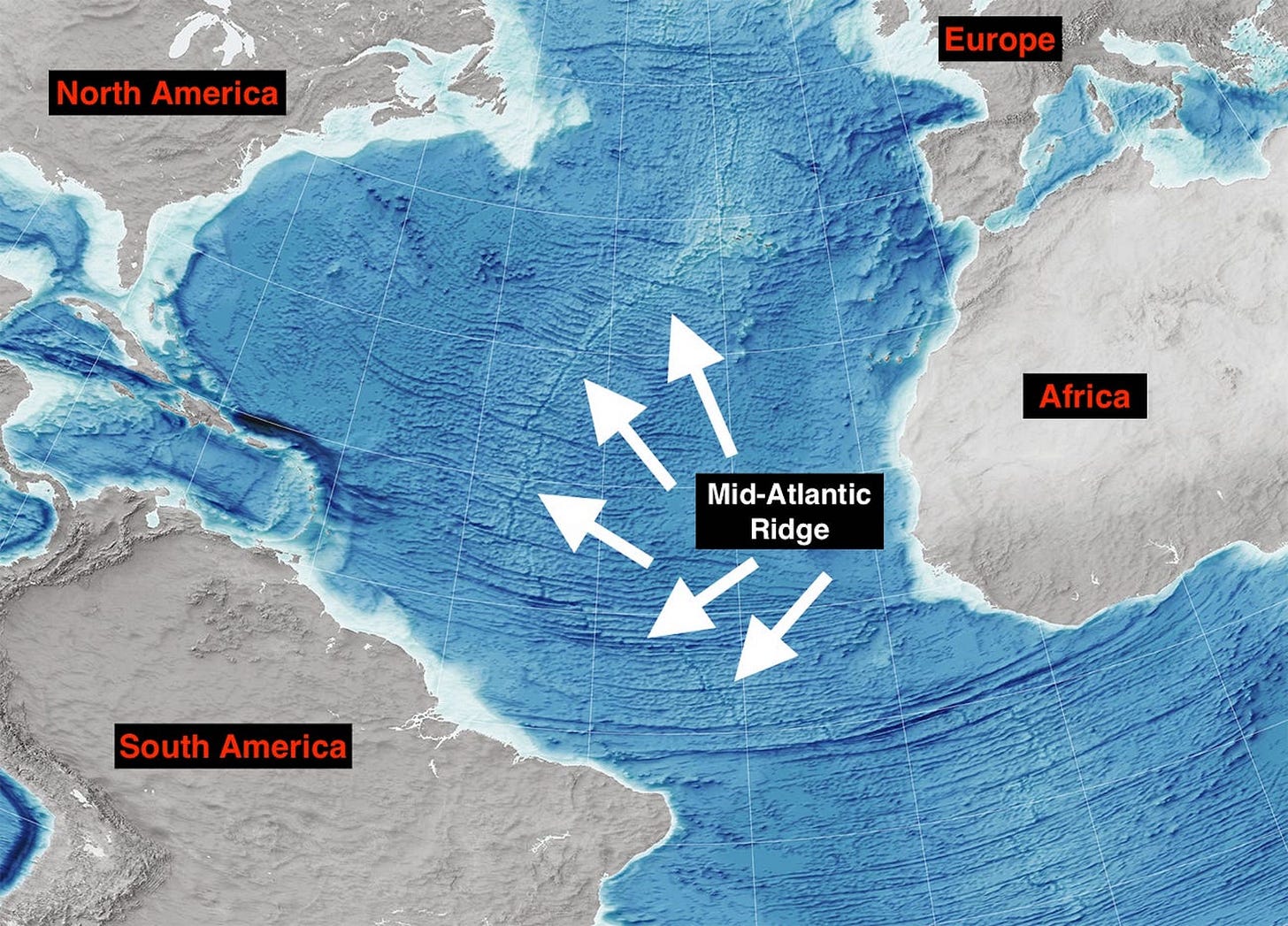
The Atlantic Ocean, the second largest of the world’s oceans, covers approximately 20% of the Earth’s surface. It borders North and South America to the west, Europe and Africa to the east, and the Arctic Ocean to the north. The United States, with its extensive coastline along the Atlantic, shares a unique connection with this vast body of water.
The Eastern Seaboard: A Tapestry of Coastal States:
From Maine in the north to Florida in the south, the Atlantic coastline of the United States encompasses a diverse range of states, each with its own distinct character and relationship with the ocean.
-
New England: Characterized by rocky shores, quaint fishing villages, and bustling port cities, New England has a long history of maritime activity. The region’s economy is deeply intertwined with the Atlantic, relying heavily on fishing, shipping, and tourism.
-
The Mid-Atlantic: This region, with its iconic cities like New York and Philadelphia, is a hub of commerce and industry. The Atlantic provides access to global markets, facilitating trade and economic growth.
-
The South: From the sandy beaches of the Carolinas to the subtropical climate of Florida, the southern Atlantic coast offers a blend of tourism, agriculture, and fishing. The Gulf Stream, a powerful warm current originating in the Gulf of Mexico, significantly influences the region’s climate.
Maritime Industry: A Backbone of the American Economy:
The Atlantic Ocean has long been a vital artery for the United States, facilitating trade, transportation, and resource extraction.
-
Shipping: The Atlantic plays a central role in international trade, connecting the United States to Europe, Africa, and South America. Major ports like New York, Boston, and Miami handle massive volumes of cargo, driving economic growth and supporting countless jobs.
-
Fishing: The Atlantic is a rich fishing ground, providing livelihoods for generations of American fishermen. From cod and lobster in the north to tuna and shrimp in the south, the ocean yields a bounty of seafood, contributing to both domestic consumption and international markets.
-
Energy Resources: The Atlantic holds significant energy reserves, both traditional and renewable. Offshore oil and gas drilling, while controversial, contribute to the nation’s energy supply. Additionally, the ocean’s vast potential for wind power is being increasingly explored, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
The Atlantic’s Influence on Climate and Environment:
The Atlantic Ocean plays a critical role in shaping the climate of the eastern United States.
-
Gulf Stream: This powerful warm current, originating in the Gulf of Mexico, transports warm water northward along the eastern seaboard, moderating winter temperatures and influencing precipitation patterns.
-
Hurricanes: The Atlantic is a breeding ground for hurricanes, which can cause significant damage to coastal communities. Understanding the dynamics of hurricane formation and forecasting their paths is crucial for disaster preparedness.
-
Marine Ecosystems: The Atlantic is home to a diverse array of marine life, from microscopic plankton to giant whales. Maintaining the health of these ecosystems is essential for the long-term well-being of both the ocean and the human communities that depend on it.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The relationship between the United States and the Atlantic Ocean is not without its challenges.
-
Climate Change: Rising sea levels, ocean acidification, and warming waters pose significant threats to coastal communities, marine ecosystems, and the maritime industry. Adapting to these changes and mitigating their impact is crucial for the future of the Atlantic.
-
Pollution: Runoff from agriculture, industry, and urban areas contaminates the ocean with harmful pollutants. Reducing these inputs and protecting marine ecosystems is essential for the health of the Atlantic and its inhabitants.
-
Overfishing: Unsustainable fishing practices can deplete fish populations, jeopardizing the livelihoods of fishermen and the integrity of marine ecosystems. Implementing sustainable fishing practices and managing fish stocks is crucial for ensuring the long-term health of the Atlantic.
The Atlantic Ocean: A Source of Inspiration and Exploration:
Beyond its economic and environmental significance, the Atlantic Ocean holds a deep cultural and historical significance for the United States.
-
Exploration and Discovery: From the voyages of Christopher Columbus to the explorations of the early American settlers, the Atlantic has been a stage for human ambition and discovery.
-
Literature and Art: The ocean has inspired generations of artists, writers, and musicians, capturing the imagination and evoking a sense of wonder.
-
Recreation and Tourism: The Atlantic coast offers countless opportunities for recreation and tourism, from swimming and sunbathing to sailing and fishing. The ocean provides a source of relaxation and enjoyment for millions of Americans.
FAQs:
1. What are the major ports on the Atlantic coast of the United States?
The Atlantic coast of the United States is home to several major ports, including:
- New York City: The largest port on the East Coast, handling a vast volume of containerized goods, bulk cargo, and cruise ships.
- Boston: A major port for containerized goods, automobiles, and seafood.
- Baltimore: A significant port for containerized goods, bulk cargo, and automobiles.
- Philadelphia: A major port for containerized goods, bulk cargo, and petroleum products.
- Charleston: A growing port for containerized goods, automobiles, and agricultural products.
- Miami: A major port for cruise ships, containerized goods, and automobiles.
2. What are the main currents in the Atlantic Ocean that affect the United States?
The Atlantic Ocean has several major currents that influence the climate and environment of the United States, including:
- Gulf Stream: A warm current originating in the Gulf of Mexico, bringing warm water northward along the eastern seaboard, moderating winter temperatures and influencing precipitation patterns.
- North Atlantic Current: An extension of the Gulf Stream, carrying warm water across the North Atlantic, influencing the climate of Western Europe.
- Labrador Current: A cold current flowing southward along the eastern coast of Canada, bringing cold water and fog to the region.
- Canary Current: A cold current flowing southward along the western coast of Africa, influencing the climate of the Canary Islands.
3. What are the major environmental challenges facing the Atlantic Ocean?
The Atlantic Ocean faces several major environmental challenges, including:
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels, ocean acidification, and warming waters pose significant threats to coastal communities, marine ecosystems, and the maritime industry.
- Pollution: Runoff from agriculture, industry, and urban areas contaminates the ocean with harmful pollutants.
- Overfishing: Unsustainable fishing practices can deplete fish populations, jeopardizing the livelihoods of fishermen and the integrity of marine ecosystems.
- Habitat Loss: Coastal development, dredging, and other human activities can destroy or degrade marine habitats.
4. How can we protect the Atlantic Ocean?
Protecting the Atlantic Ocean requires a multi-faceted approach, including:
- Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Combating climate change is essential to mitigating its impact on the ocean.
- Improving Waste Management: Reducing pollution from land-based sources is crucial for protecting marine ecosystems.
- Implementing Sustainable Fishing Practices: Managing fish stocks and ensuring the long-term health of marine ecosystems.
- Protecting Marine Habitats: Preserving and restoring marine habitats is essential for the biodiversity of the Atlantic.
Tips for Understanding the Atlantic Ocean:
- Use Online Maps and Resources: Interactive maps and online resources can provide valuable insights into the geography, currents, and ecosystems of the Atlantic Ocean.
- Explore Coastal Communities: Visiting coastal communities and observing their relationship with the ocean can provide a firsthand understanding of the importance of the Atlantic.
- Learn about Marine Life: Educate yourself about the diverse species of marine life that inhabit the Atlantic, and the threats they face.
- Support Sustainable Practices: Make informed choices as a consumer and advocate for policies that protect the ocean.
Conclusion:
The Atlantic Ocean is more than just a vast body of water; it is a vital lifeline for the United States, shaping its history, economy, and environment. Understanding the complex relationship between the nation and the ocean is crucial for navigating the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. By embracing a responsible stewardship of this precious resource, we can ensure its health and prosperity for generations to come.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Atlantic Ocean: A Vital Lifeline for the United States. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!