The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast Waterway Shaping The World
The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast Waterway Shaping the World
Related Articles: The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast Waterway Shaping the World
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast Waterway Shaping the World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast Waterway Shaping the World
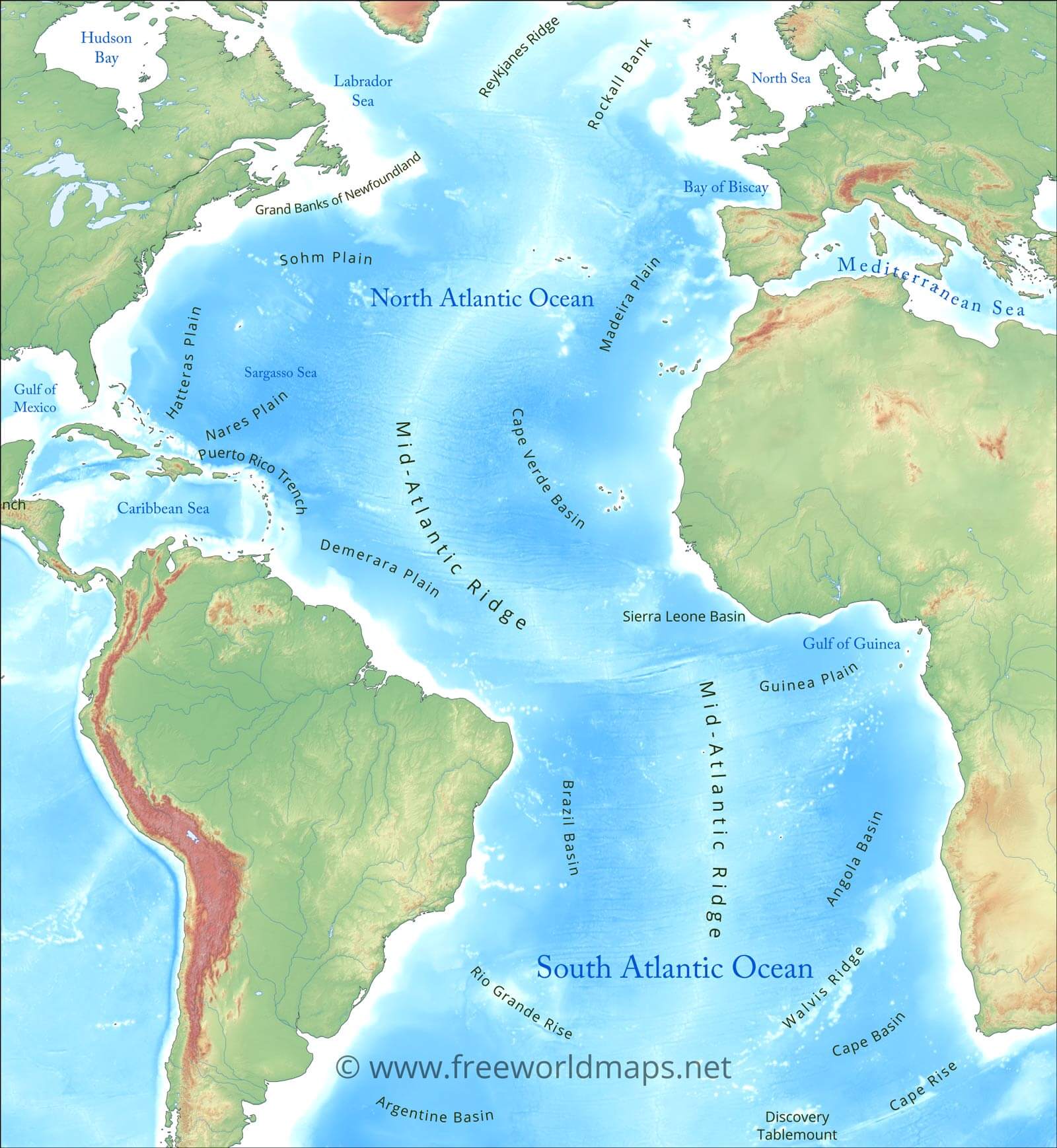
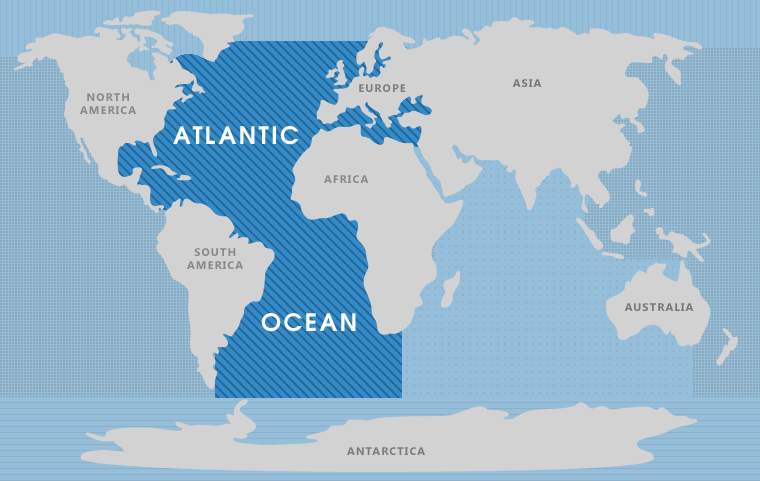
The Atlantic Ocean, the second-largest ocean on Earth, is a dynamic force shaping the planet’s geography, climate, and history. Its immense size, complex currents, and diverse ecosystems make it a fascinating subject of study for scientists, geographers, and historians alike. Understanding the Atlantic’s location and its intricate relationship with surrounding landmasses is crucial to appreciating its profound impact on the world.
A Global Waterway:
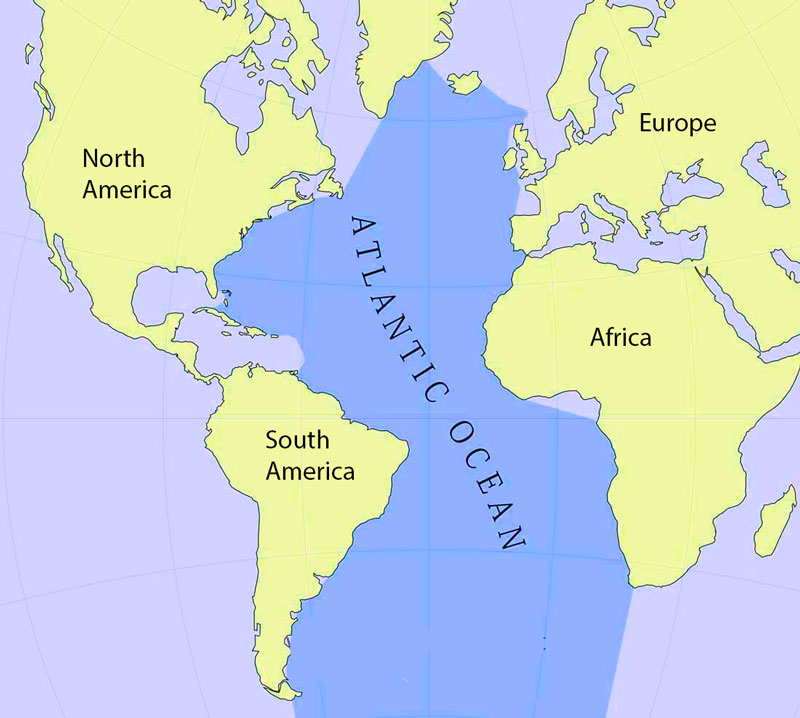
The Atlantic Ocean spans an impressive 106,400,000 square kilometers (41,100,000 square miles), covering approximately 20% of the Earth’s surface. It stretches from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bordering North and South America to the west and Europe and Africa to the east. This vast expanse connects continents, influencing their climates, economies, and cultural exchanges.
Key Features and Characteristics:
- North Atlantic: This region encompasses the North American and European continental shelves, characterized by extensive shallow waters and rich marine life. It is also home to the Gulf Stream, a warm current that significantly influences the climate of Western Europe.
- South Atlantic: This portion of the ocean features the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, an underwater mountain range that runs down its center. The South Atlantic is known for its unique ecosystems, including the Benguela Current, which supports a vibrant fishery.
- Equatorial Atlantic: This region is characterized by the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), a low-pressure zone that generates frequent thunderstorms and heavy rainfall. The Equatorial Counter Current, flowing eastwards, adds to the complex circulation patterns of the Atlantic.
Navigational Significance:
The Atlantic Ocean has been a vital waterway for centuries, facilitating trade, exploration, and migration. Its strategic location between continents allowed for the development of major shipping routes, connecting Europe to the Americas and Africa. The ocean’s currents also played a significant role in the Age of Exploration, aiding European voyages across the globe.
Impact on Climate:
The Atlantic Ocean plays a crucial role in regulating global climate patterns. The Gulf Stream, for instance, carries warm water from the tropics northward, moderating the climate of Western Europe. Conversely, cold currents from the Arctic influence the climate of the eastern United States. The Atlantic’s vast surface area also influences atmospheric circulation, affecting weather patterns worldwide.
Rich Biodiversity:
The Atlantic Ocean is home to a staggering diversity of marine life. Its diverse ecosystems, ranging from shallow coastal waters to deep-sea trenches, support a wide array of species, including whales, dolphins, sharks, fish, coral reefs, and sea turtles. The ocean’s rich biodiversity is essential for maintaining a healthy ecosystem and provides valuable resources for human populations.
Environmental Challenges:
Despite its vastness and resilience, the Atlantic Ocean faces various environmental challenges. Overfishing, pollution, climate change, and habitat destruction threaten the delicate balance of its ecosystems. Addressing these issues is critical for preserving the ocean’s health and ensuring its continued role in supporting life on Earth.
FAQs:
Q: What is the deepest point in the Atlantic Ocean?
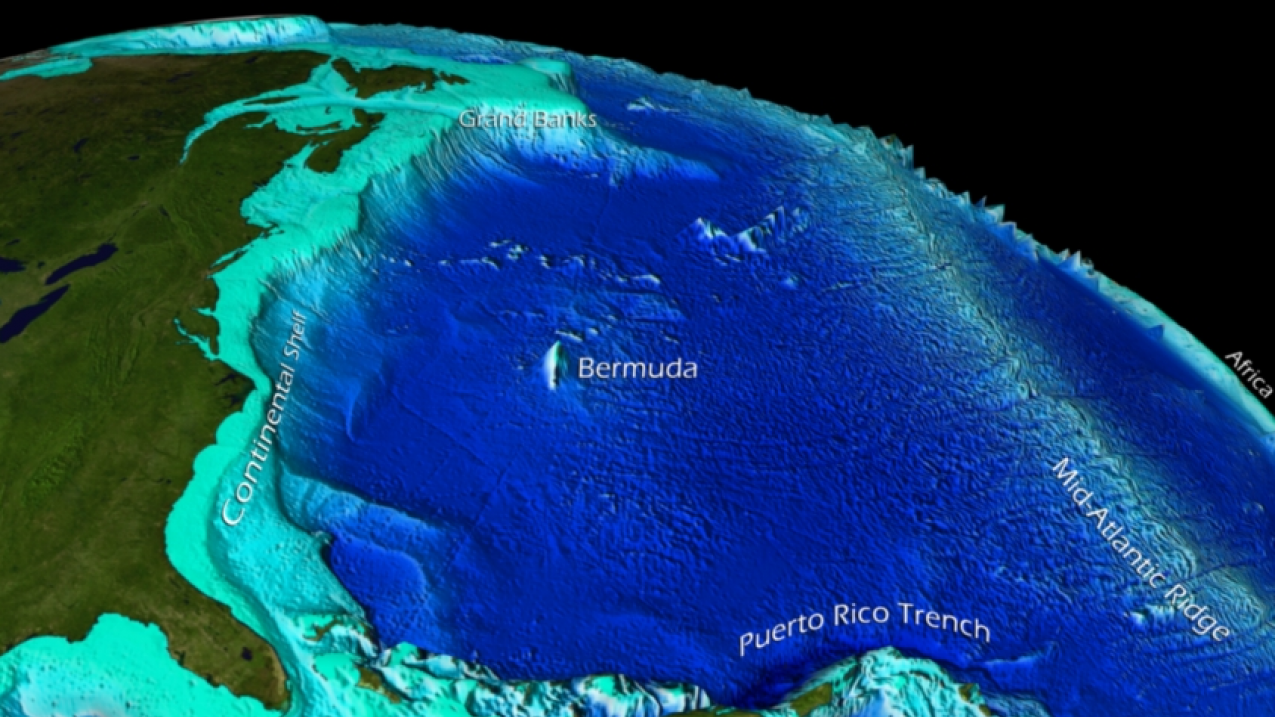
A: The deepest point in the Atlantic Ocean is the Puerto Rico Trench, reaching a depth of 8,605 meters (28,232 feet).
Q: What is the largest island in the Atlantic Ocean?
A: Greenland, located in the North Atlantic, is the largest island in the Atlantic Ocean.
Q: What are some of the major currents in the Atlantic Ocean?
A: The major currents in the Atlantic Ocean include the Gulf Stream, the North Atlantic Current, the Canary Current, the Benguela Current, and the Brazil Current.
Q: What are some of the major ports located on the Atlantic Ocean?
A: Major ports on the Atlantic Ocean include New York City, London, Rotterdam, Rio de Janeiro, and Cape Town.
Q: How does the Atlantic Ocean contribute to global climate?
A: The Atlantic Ocean plays a crucial role in regulating global climate patterns through its currents, which transport heat and moisture around the globe.
Tips for Understanding the Atlantic Ocean:
- Utilize online maps and resources: Interactive maps and websites offer detailed information about the Atlantic Ocean’s geography, currents, and ecosystems.
- Explore documentaries and educational videos: Visual resources provide a deeper understanding of the ocean’s dynamics, biodiversity, and environmental challenges.
- Engage with scientific articles and research: Academic journals and online publications offer in-depth analyses of the Atlantic Ocean’s complex processes.
- Visit museums and aquariums: These institutions offer interactive exhibits and displays showcasing the ocean’s diverse marine life and its importance to the planet.
Conclusion:
The Atlantic Ocean, with its vast expanse, complex currents, and rich biodiversity, is a vital component of the global ecosystem. Understanding its location, characteristics, and influence on the planet is crucial for appreciating its significance and addressing the environmental challenges it faces. By engaging with the wealth of information available, we can foster a deeper understanding and appreciation for this remarkable body of water.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast Waterway Shaping the World. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!