The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast Waterway Shaping The World
The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast Waterway Shaping the World
Related Articles: The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast Waterway Shaping the World
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast Waterway Shaping the World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast Waterway Shaping the World
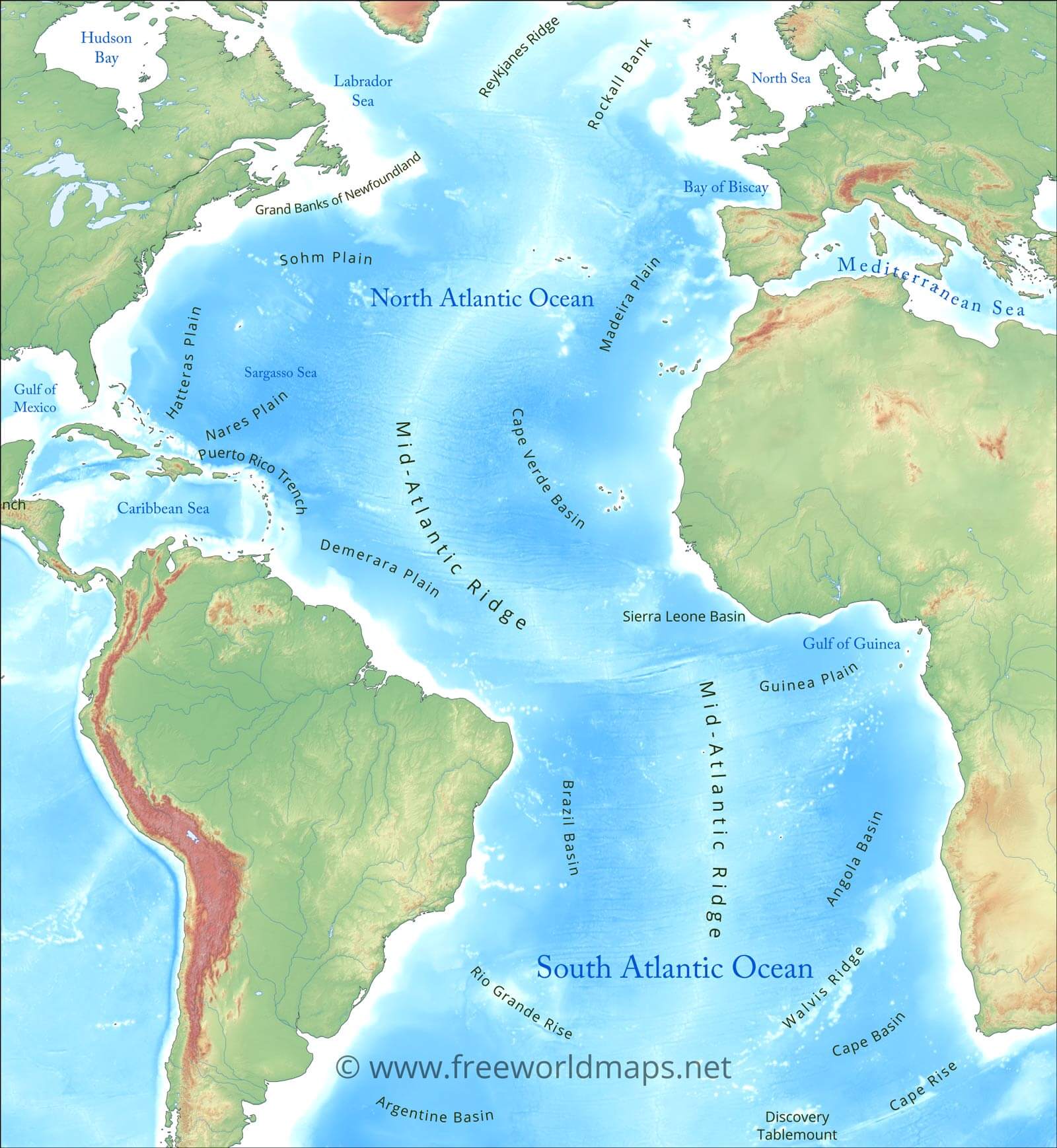
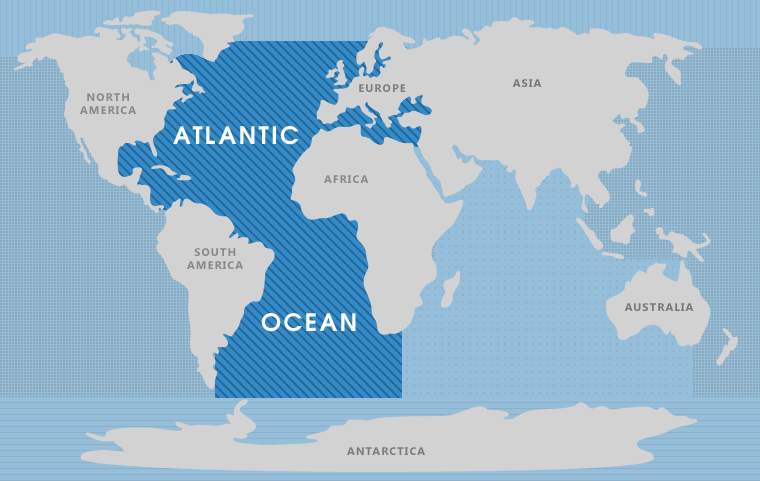
The Atlantic Ocean, a vast expanse of water covering approximately 20% of the Earth’s surface, is a prominent feature on any world map. Its presence is not merely geographical; it has profoundly shaped history, culture, and the global economy. Understanding the Atlantic’s location and its significance is crucial for comprehending the interconnectedness of our planet.
A Global Waterway:
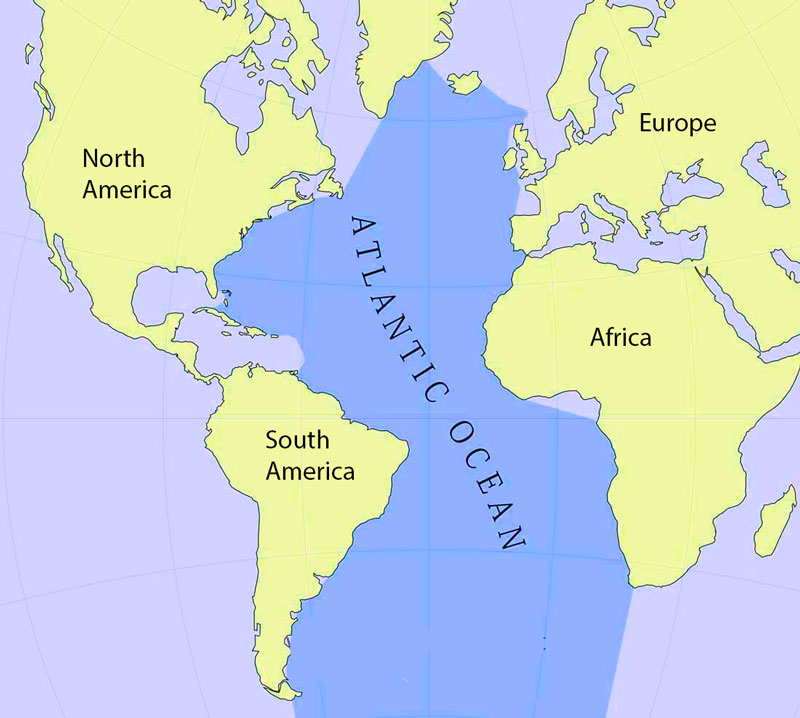
The Atlantic Ocean stretches from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, and from the Americas in the west to Europe and Africa in the east. It is the second-largest ocean on Earth, only surpassed by the Pacific Ocean. The Atlantic’s vastness is evident in its numerous marginal seas, including the Caribbean Sea, the Mediterranean Sea, the North Sea, and the Gulf of Mexico.
Mapping the Atlantic’s Boundaries:
- North: The Atlantic’s northern boundary is marked by the Arctic Circle, where it meets the Arctic Ocean.
- South: The Southern Ocean, which surrounds Antarctica, forms the southern boundary.
- West: The Atlantic’s western boundary is defined by the coasts of North and South America.
- East: The eastern boundary comprises the coasts of Europe and Africa.
Key Features and Significance:
The Atlantic Ocean is not just a vast body of water; it is a dynamic system with numerous features that contribute to its importance:
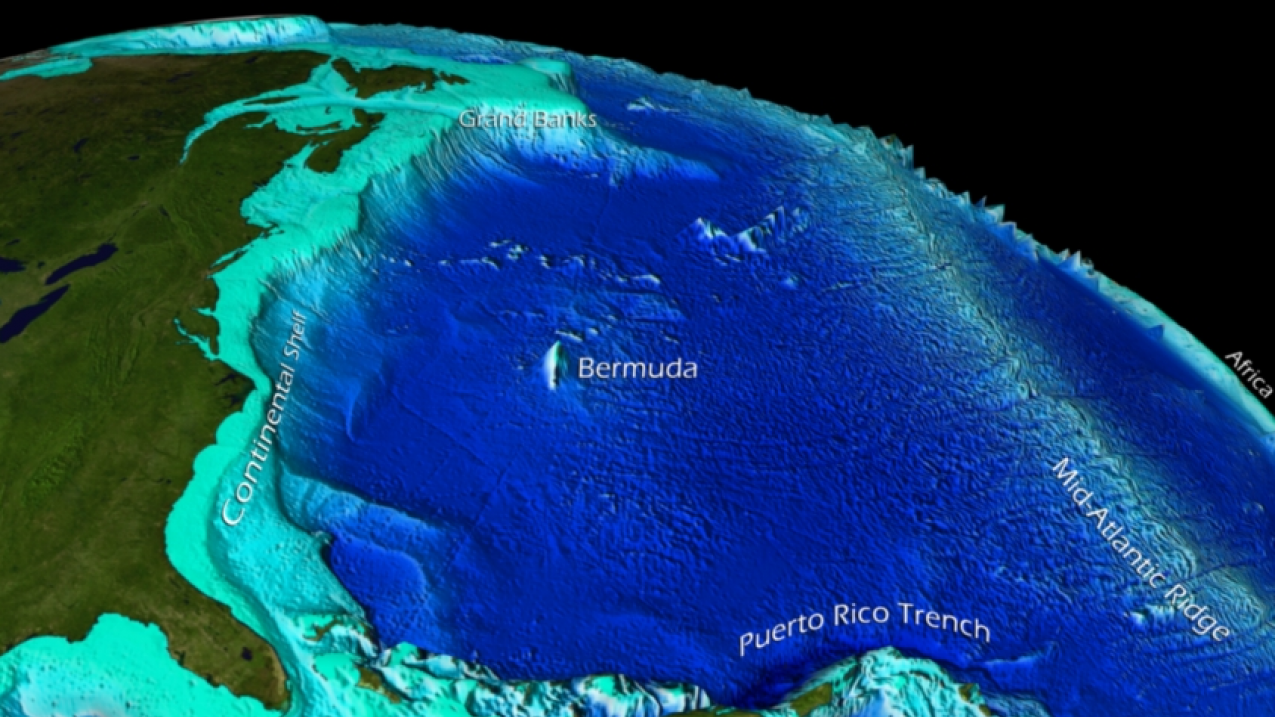
- The Mid-Atlantic Ridge: This underwater mountain range, formed by tectonic plate movement, runs down the center of the Atlantic. It is a site of intense volcanic activity and plays a crucial role in the ocean’s circulation patterns.
- The Gulf Stream: This warm current, originating in the Gulf of Mexico, flows northward along the eastern coast of North America and then across the Atlantic towards Europe. It significantly moderates the climate of Western Europe, making it warmer than it would otherwise be.
- The North Atlantic Deep Water: This cold, dense water mass forms in the North Atlantic and sinks to the ocean floor, playing a key role in global ocean circulation.
- Biodiversity: The Atlantic Ocean is home to a vast array of marine life, including whales, dolphins, sharks, fish, and coral reefs. Its diverse ecosystems contribute to global biodiversity and provide valuable resources.
- Trade and Transportation: The Atlantic has served as a vital trade route for centuries, facilitating the exchange of goods, people, and ideas between continents. Major shipping lanes crisscross the ocean, connecting ports around the world.
- Energy Resources: The Atlantic holds significant energy resources, including oil and gas deposits found on the ocean floor. These resources are important for global energy production.
Understanding the Atlantic’s Influence:
The Atlantic Ocean’s location and features have profound impacts on the world:
- Climate Regulation: The Atlantic’s currents play a crucial role in regulating global climate patterns. The Gulf Stream, for instance, transports warm water northward, moderating the climate of Western Europe.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: The Atlantic’s diverse ecosystems support a rich array of marine life, contributing to global biodiversity and providing valuable resources for research and conservation.
- Global Connectivity: The Atlantic has facilitated trade and cultural exchange between continents for centuries, connecting people and economies across the world.
- Resource Management: The Atlantic’s resources, including fisheries, energy deposits, and shipping lanes, require careful management to ensure sustainability and responsible utilization.
FAQs:
Q: What is the Atlantic Ocean’s deepest point?
A: The deepest point in the Atlantic Ocean is the Puerto Rico Trench, reaching a depth of approximately 8,605 meters (28,232 feet).
Q: What are some of the major islands located in the Atlantic Ocean?
A: The Atlantic Ocean is home to numerous islands, including the British Isles, Iceland, Greenland, the Canary Islands, the Azores, the Caribbean Islands, and the Falkland Islands.
Q: What are the main currents in the Atlantic Ocean?
A: The Atlantic Ocean is characterized by several major currents, including the Gulf Stream, the North Atlantic Drift, the Canary Current, and the Benguela Current.
Q: What are the main environmental threats facing the Atlantic Ocean?
A: The Atlantic Ocean faces various environmental threats, including overfishing, pollution, climate change, and habitat destruction.
Tips for Locating the Atlantic Ocean on a Map:
- Identify the Continents: Start by identifying the continents of North America, South America, Europe, and Africa.
- Look for the Ocean’s Boundaries: The Atlantic Ocean is bordered by the Arctic Ocean in the north, the Southern Ocean in the south, and the continents mentioned above.
- Recognize Key Features: Look for the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, the Gulf Stream, and other prominent features that distinguish the Atlantic Ocean.
Conclusion:
The Atlantic Ocean is a vast and dynamic body of water that plays a crucial role in shaping the world. Its location and features influence global climate patterns, support diverse ecosystems, facilitate trade and transportation, and provide valuable resources. Understanding the Atlantic’s importance is essential for appreciating the interconnectedness of our planet and for promoting responsible stewardship of its resources.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast Waterway Shaping the World. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!