The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast Body Of Water Shaping The World
The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast Body of Water Shaping the World
Related Articles: The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast Body of Water Shaping the World
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast Body of Water Shaping the World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast Body of Water Shaping the World

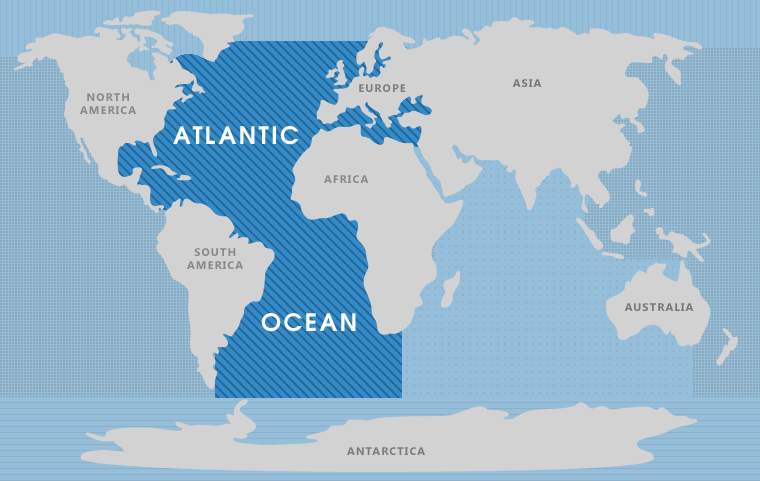
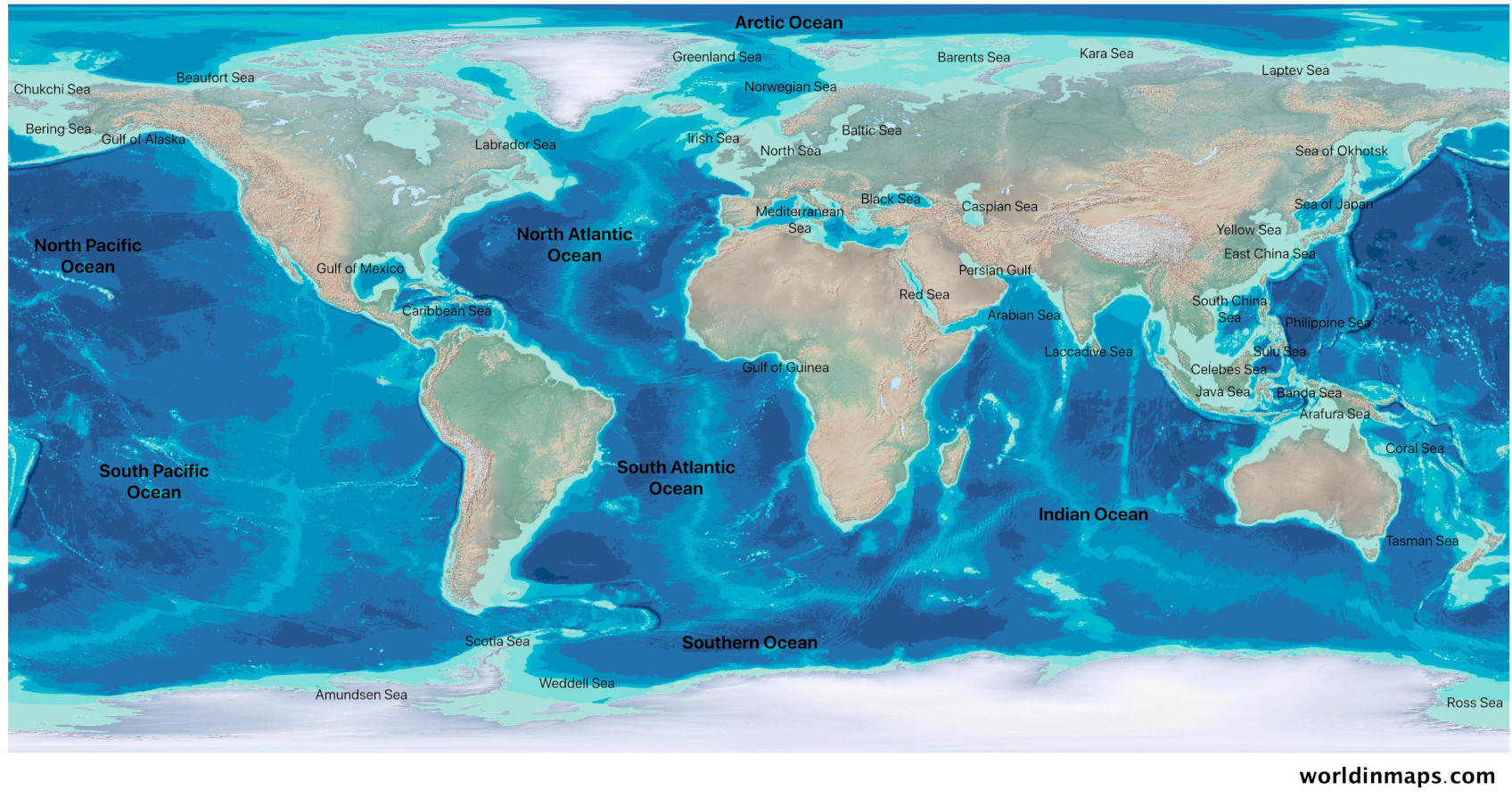
The Atlantic Ocean, the second-largest of Earth’s five oceans, is a colossal body of water that stretches across the globe, connecting continents and shaping global climates. Understanding its location on a map is essential to grasping its profound influence on human history, trade, and the very fabric of life on Earth.
A Global Divide:
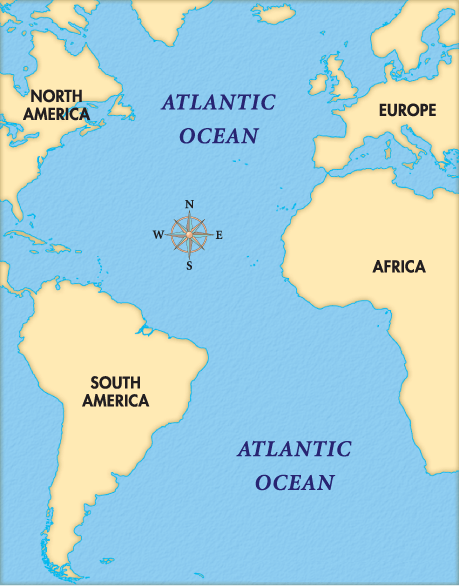
The Atlantic Ocean occupies a unique position on the world map, effectively dividing the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. It forms a wedge between North and South America to the west and Europe and Africa to the east. The ocean’s northernmost point reaches the Arctic Ocean, while its southern boundary merges with the Southern Ocean.
Navigating the Atlantic:
To visualize the Atlantic’s location on a map, imagine a vast, S-shaped body of water. Its northern portion, known as the North Atlantic, is relatively narrow, separating North America from Europe and Africa. The South Atlantic, in contrast, broadens significantly, stretching between South America and Africa.
Landmarks and Boundaries:
Several prominent landmasses and geographical features define the Atlantic Ocean’s boundaries:
- North America: The eastern coast of North America, from Greenland to Argentina, forms the western boundary of the Atlantic.
- South America: The eastern coast of South America, from Argentina to Venezuela, marks the western edge of the South Atlantic.
- Europe: The western coast of Europe, from Norway to Portugal, defines the eastern boundary of the North Atlantic.
- Africa: The western coast of Africa, from Morocco to South Africa, forms the eastern boundary of the Atlantic.
- The Arctic Ocean: The Atlantic merges with the Arctic Ocean in the north, forming a complex, dynamic boundary.
- The Southern Ocean: The Atlantic flows into the Southern Ocean in the south, where the three major oceans (Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific) converge.
Beyond the Map:
Understanding the Atlantic’s position on a map is only the first step in appreciating its significance. This vast body of water is a dynamic entity, constantly in motion, influenced by currents, tides, and weather patterns.
The Importance of the Atlantic:
- Global Trade and Commerce: The Atlantic has long been a vital artery for global trade and commerce. Its vast expanse has facilitated the movement of goods, people, and ideas across continents.
- Climate Regulation: The Atlantic plays a crucial role in regulating global climate. Its currents distribute heat and moisture around the world, influencing weather patterns and temperature variations.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: The Atlantic is home to a diverse array of marine life, from microscopic plankton to colossal whales. Its diverse ecosystems support a vast network of interconnected species.
- Natural Resources: The Atlantic holds vast reserves of natural resources, including oil and gas, minerals, and fish stocks, contributing significantly to global economies.
- Cultural and Historical Significance: The Atlantic has been a stage for countless historical events, from voyages of exploration to the transatlantic slave trade. Its waters have witnessed the rise and fall of empires and the development of global cultures.
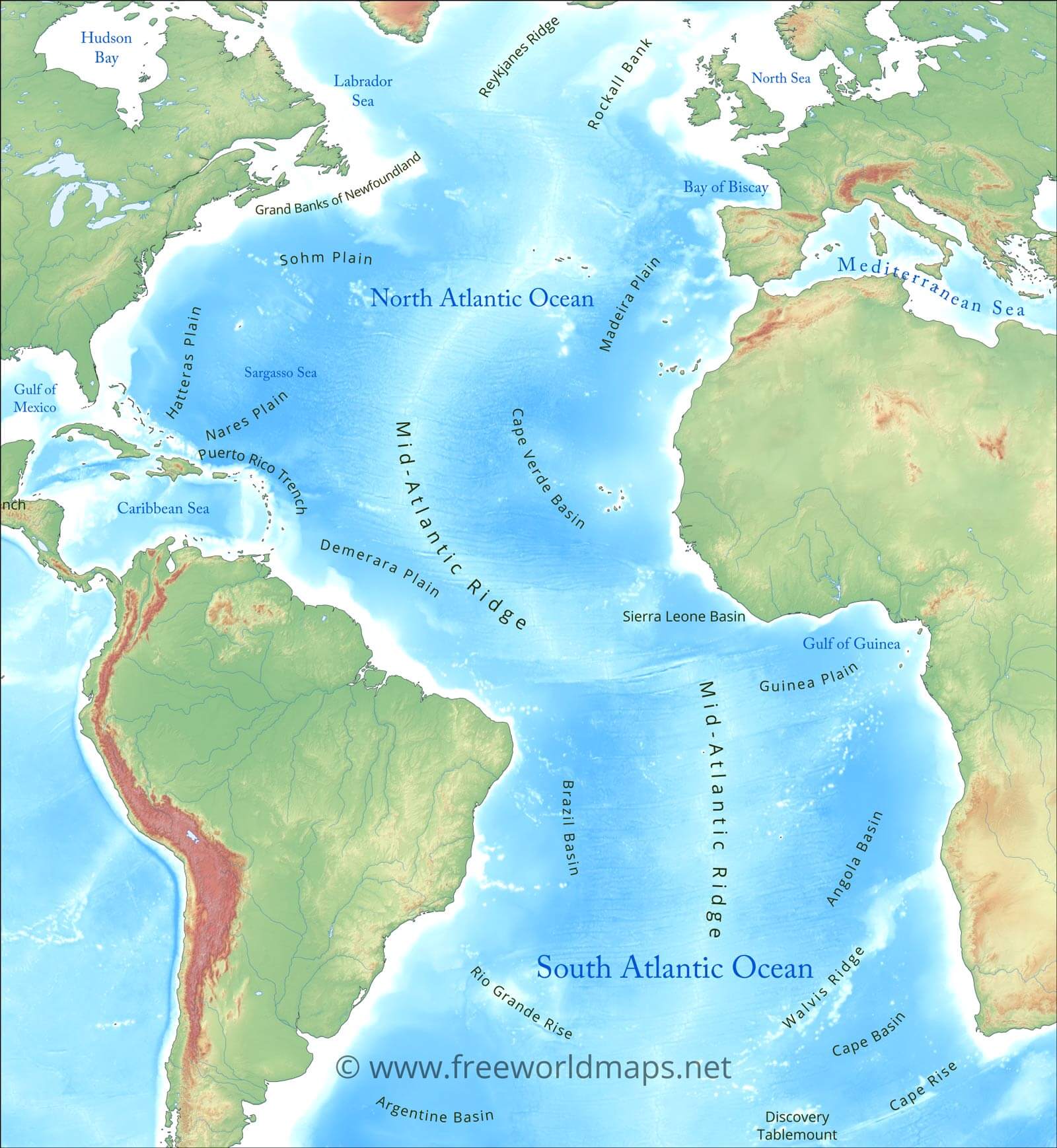
Exploring the Depths:
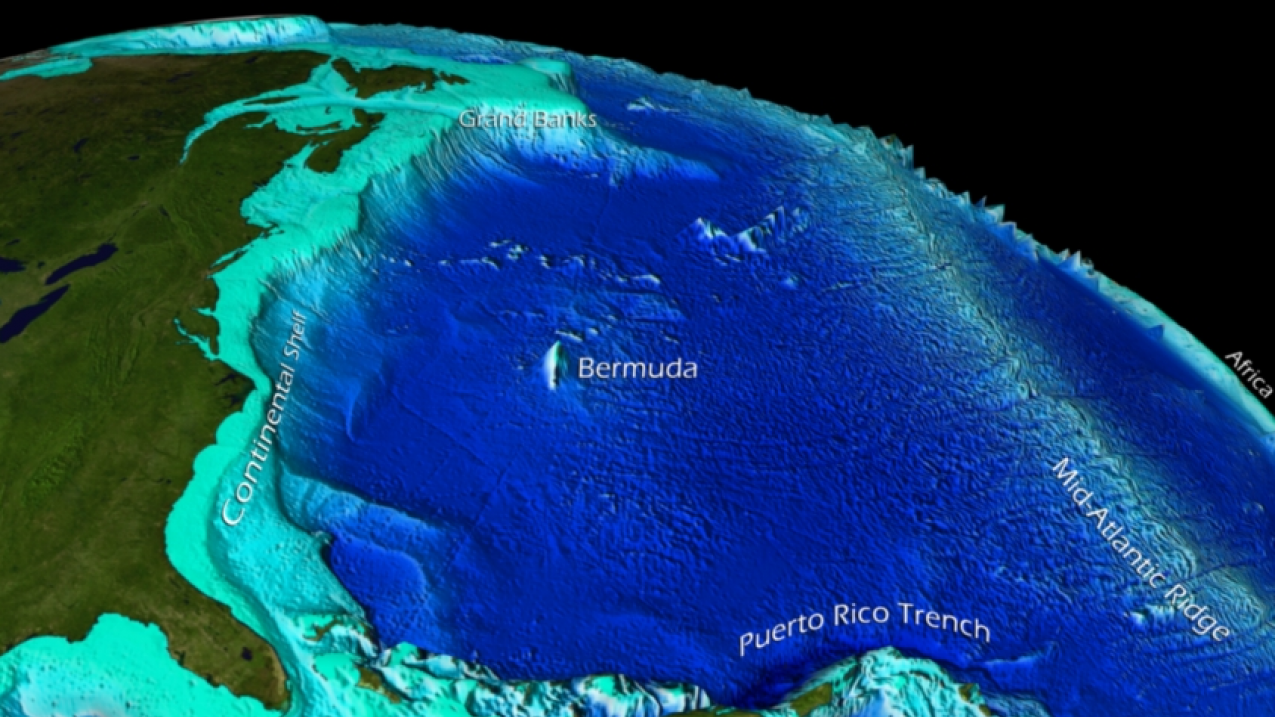
The Atlantic’s depths hold secrets waiting to be unveiled. Its seabed features a diverse topography, including underwater mountain ranges, deep trenches, and volcanic vents. Exploring these underwater landscapes provides valuable insights into Earth’s history and the evolution of life.
FAQs:
Q: What is the deepest point in the Atlantic Ocean?
A: The deepest point in the Atlantic Ocean is the Puerto Rico Trench, reaching a depth of approximately 8,605 meters (28,232 feet).
Q: What are some of the major currents in the Atlantic Ocean?
A: The Atlantic Ocean is home to several significant currents, including the Gulf Stream, the North Atlantic Current, the South Atlantic Current, and the Benguela Current.
Q: How does the Atlantic Ocean influence the climate of Europe?
A: The Gulf Stream, a warm current originating in the Gulf of Mexico, transports warm water across the Atlantic, moderating the climate of Western Europe and making it warmer than it would otherwise be.
Q: What are some of the environmental threats facing the Atlantic Ocean?
A: The Atlantic Ocean faces numerous environmental threats, including overfishing, pollution, climate change, and habitat destruction.
Tips:
- Use online maps: Interactive online maps provide a dynamic and detailed view of the Atlantic Ocean’s location and features.
- Study atlases and globes: Traditional atlases and globes offer a comprehensive overview of the Atlantic’s position within the global context.
- Explore documentaries and books: Educational documentaries and books provide valuable insights into the Atlantic’s geography, history, and ecology.
Conclusion:
The Atlantic Ocean, a vast expanse of water shaping continents and influencing global climates, holds a place of profound importance in human history and the natural world. Understanding its location on a map is only the beginning of appreciating its immense scale, dynamic nature, and enduring impact on life on Earth.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Atlantic Ocean: A Vast Body of Water Shaping the World. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!