The Art And Science Of Map Editing For Atlases: Ensuring Accuracy And Clarity In A World Of Data
The Art and Science of Map Editing for Atlases: Ensuring Accuracy and Clarity in a World of Data
Related Articles: The Art and Science of Map Editing for Atlases: Ensuring Accuracy and Clarity in a World of Data
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Art and Science of Map Editing for Atlases: Ensuring Accuracy and Clarity in a World of Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Art and Science of Map Editing for Atlases: Ensuring Accuracy and Clarity in a World of Data
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Art and Science of Map Editing for Atlases: Ensuring Accuracy and Clarity in a World of Data
- 3.1 The Importance of Map Editing in Atlas Production
- 3.2 The Diverse Roles of Map Editors
- 3.3 The Evolution of Map Editing in the Digital Age
- 3.4 Challenges and Opportunities in Map Editing
- 3.5 FAQs about Map Editing for Atlases
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Map Editing
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Art and Science of Map Editing for Atlases: Ensuring Accuracy and Clarity in a World of Data
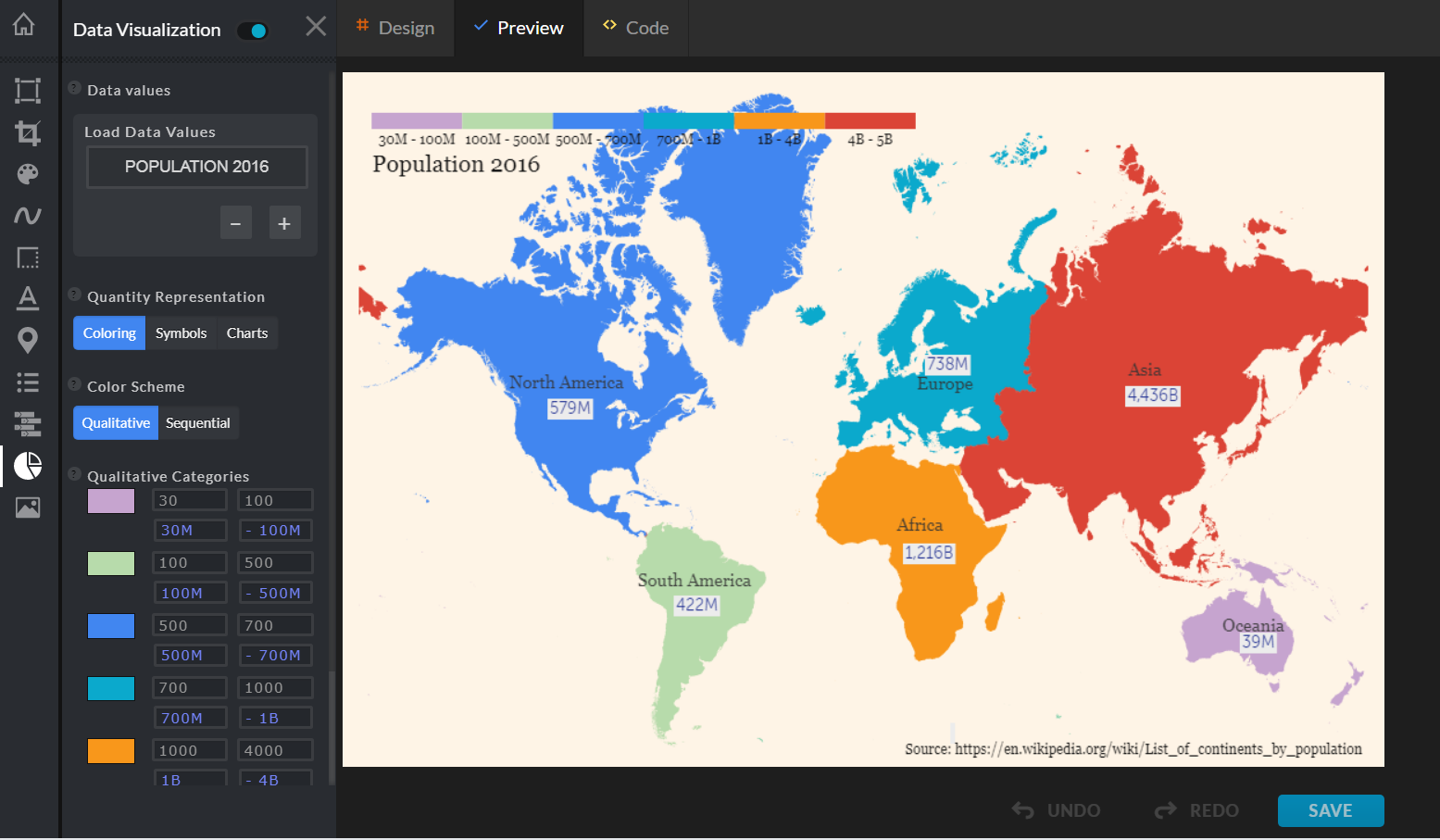
The atlas, a collection of maps, has long served as a vital tool for understanding the world. From navigating uncharted territories to exploring distant cultures, maps have been instrumental in shaping our perception of the globe. Yet, the creation of a comprehensive and accurate atlas requires meticulous attention to detail, a process that is heavily reliant on map editing. This article delves into the intricate world of map editing for atlases, exploring the diverse aspects of this crucial endeavor.
The Importance of Map Editing in Atlas Production
Map editing is not simply about aesthetics. It is a critical process that ensures the accuracy, clarity, and consistency of information presented in an atlas. This meticulous process involves a multi-layered approach, encompassing:
- Data Verification: Ensuring the accuracy of geographic data, including boundaries, names, and features, is paramount. This involves cross-referencing information from various sources, including official government databases, satellite imagery, and field surveys.
- Cartographic Design: The visual representation of data is crucial for conveying information effectively. Map editors utilize principles of cartographic design, incorporating appropriate symbology, color schemes, and scale to create maps that are both aesthetically pleasing and easily interpretable.
- Style and Consistency: Maintaining consistent style across all maps in an atlas is essential for coherence and user experience. This includes standardized fonts, symbols, and color palettes, ensuring a cohesive visual language throughout the publication.
- Content Management: Map editors are responsible for the overall organization and flow of information within the atlas. This involves selecting relevant maps, arranging them in a logical sequence, and crafting accompanying text and captions to enhance comprehension.
The Diverse Roles of Map Editors
Map editing for atlases requires a diverse skillset, encompassing technical expertise, artistic sensibility, and a deep understanding of cartographic principles. The role of a map editor often involves:
- Data Acquisition and Processing: Gathering, validating, and preparing geographic data from various sources, including databases, aerial photographs, and remote sensing data.
- Map Design and Layout: Creating cartographic representations of data, incorporating appropriate symbology, color schemes, and scale to ensure clarity and readability.
- Quality Control: Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of map content, including geographical features, names, and labels, through meticulous review and revision.
- Content Integration: Combining maps with text, captions, and other supporting materials to create a cohesive and informative narrative.
- Collaboration and Communication: Working closely with cartographers, writers, editors, and other stakeholders to ensure seamless integration of information and effective communication of content.
The Evolution of Map Editing in the Digital Age
The advent of digital technologies has revolutionized the process of map editing. Modern map editors utilize sophisticated software tools that offer advanced capabilities for:
- Geospatial Data Management: Storing, manipulating, and analyzing large datasets with greater efficiency and accuracy.
- Automated Map Production: Generating maps automatically from digital data sources, streamlining the map production process and reducing manual errors.
- Interactive Mapping: Creating dynamic maps that allow users to explore and interact with data in real-time, enhancing user engagement and understanding.
- Data Visualization: Utilizing advanced visualization techniques to represent complex data in visually compelling and informative ways.
Challenges and Opportunities in Map Editing
While digital technologies have brought significant advancements, map editing remains a complex and challenging field. Key challenges include:
- Data Quality and Accuracy: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data sources, especially in rapidly changing landscapes and with the increasing availability of user-generated content.
- Data Security and Privacy: Protecting sensitive geospatial data and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
- Ethical Considerations: Addressing potential biases in data representation and ensuring responsible use of geospatial data.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: Making maps accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, and ensuring representation of diverse perspectives.
Despite these challenges, map editing offers exciting opportunities for innovation and growth. Emerging trends include:
- 3D Mapping: Creating immersive and interactive 3D maps that provide a more realistic and detailed representation of the world.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): Integrating AR and VR technologies to enhance map visualization and user interaction.
- Big Data Analytics: Utilizing big data analytics to extract valuable insights from geospatial data and create more informative maps.
- Citizen Science: Engaging citizen scientists in data collection and map editing, fostering collaborative mapping initiatives.
FAQs about Map Editing for Atlases
Q: What qualifications are needed to be a map editor?
A: A strong foundation in geography, cartography, and GIS is essential. Additionally, proficiency in map editing software, excellent communication skills, and attention to detail are crucial.
Q: What are the different types of atlases that require map editing?
A: Atlases come in various forms, including world atlases, regional atlases, thematic atlases (focusing on specific topics like climate or population), historical atlases, and road atlases.
Q: What are the key considerations for map editing in a world atlas?
A: Accuracy of geographic boundaries, consistent use of cartographic symbols, representation of diverse cultures and landscapes, and clear labeling of features are paramount.
Q: How does map editing contribute to the accuracy of historical atlases?
A: Historical atlases rely on accurate representation of past geographical features, including historical boundaries, settlements, and infrastructure. Map editors carefully research and verify data from historical sources to ensure accuracy.
Q: What are some ethical considerations in map editing?
A: Map editors must be mindful of potential biases in data representation, ensure inclusivity of diverse perspectives, and avoid perpetuating harmful stereotypes.
Tips for Effective Map Editing
- Thorough Data Verification: Cross-reference data from multiple sources to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Clear and Concise Labeling: Use clear and concise labels that are legible and appropriately sized.
- Effective Color Schemes: Select color schemes that are visually appealing and enhance the readability of the map.
- Appropriate Scale and Projection: Choose a scale and projection that best suit the purpose and scope of the map.
- Consistent Style and Design: Maintain a consistent style across all maps in the atlas, ensuring a cohesive visual language.
Conclusion
Map editing for atlases is a crucial aspect of creating accurate, informative, and engaging publications. It involves a meticulous process of data verification, cartographic design, style consistency, and content management. The field continues to evolve with the integration of digital technologies, opening new possibilities for innovation and enhancing our understanding of the world. As we navigate an increasingly complex and interconnected world, the importance of accurate and accessible maps, meticulously crafted by skilled map editors, will only continue to grow.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Art and Science of Map Editing for Atlases: Ensuring Accuracy and Clarity in a World of Data. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!