Navigating The Storm: Understanding The Hurricane Weather Map Of The Atlantic Ocean
Navigating the Storm: Understanding the Hurricane Weather Map of the Atlantic Ocean
Related Articles: Navigating the Storm: Understanding the Hurricane Weather Map of the Atlantic Ocean
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Storm: Understanding the Hurricane Weather Map of the Atlantic Ocean. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Storm: Understanding the Hurricane Weather Map of the Atlantic Ocean
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Storm: Understanding the Hurricane Weather Map of the Atlantic Ocean
- 3.1 Deciphering the Atlantic Hurricane Weather Map
- 3.2 The Importance of Hurricane Weather Maps
- 3.3 Navigating the Information: FAQs
- 3.4 Tips for Interpreting Hurricane Weather Maps
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Storm: Understanding the Hurricane Weather Map of the Atlantic Ocean
![]()
The Atlantic Ocean, a vast expanse of water, is a breeding ground for powerful hurricanes, posing significant threats to coastal communities. Understanding the intricacies of hurricane weather maps is crucial for mitigating risks and ensuring the safety of lives and property. This article delves into the significance of these maps, their components, and the critical role they play in hurricane preparedness and response.
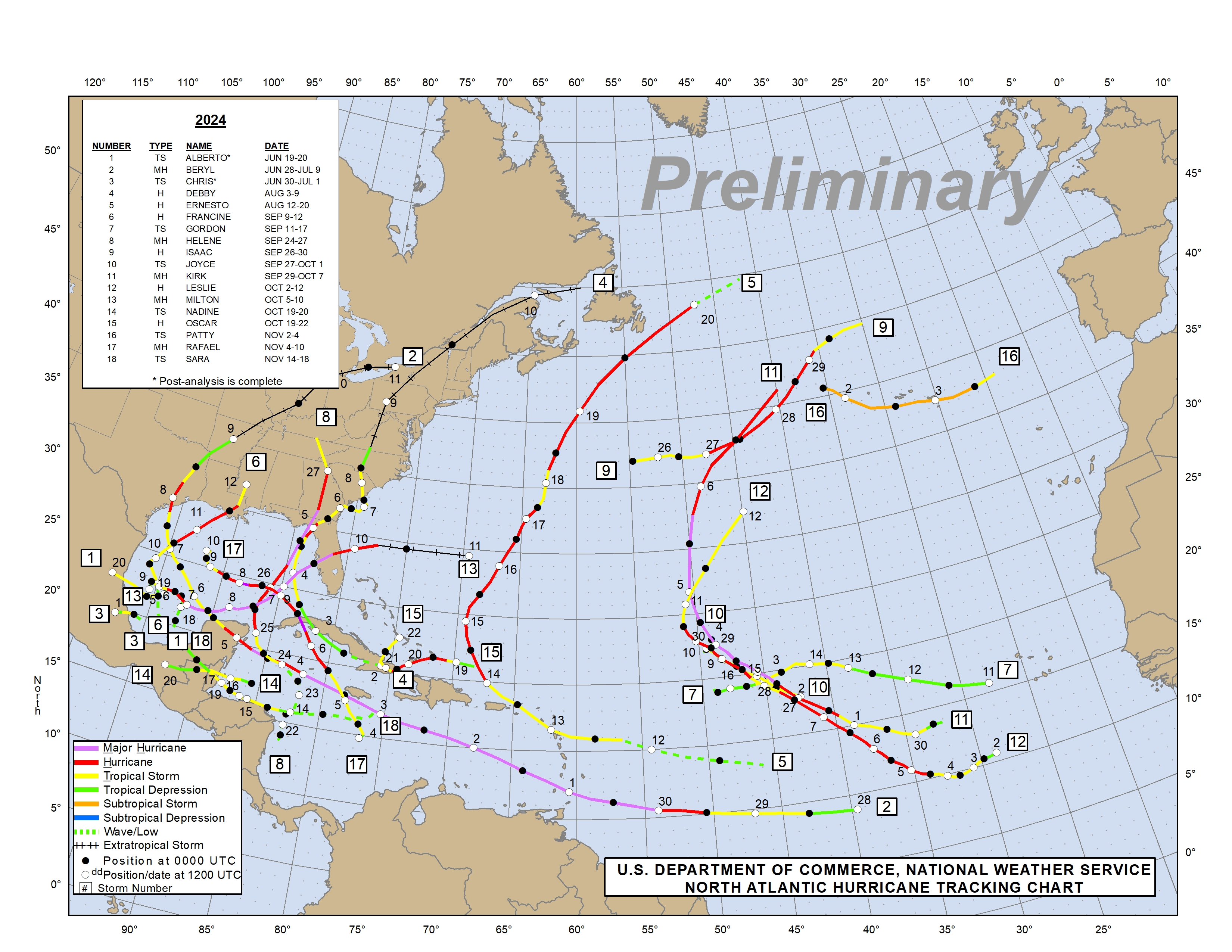
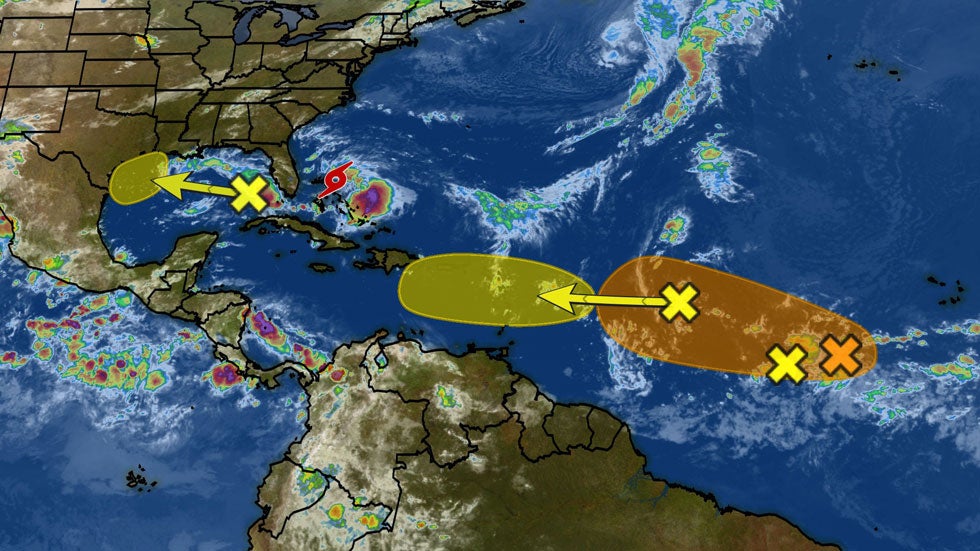
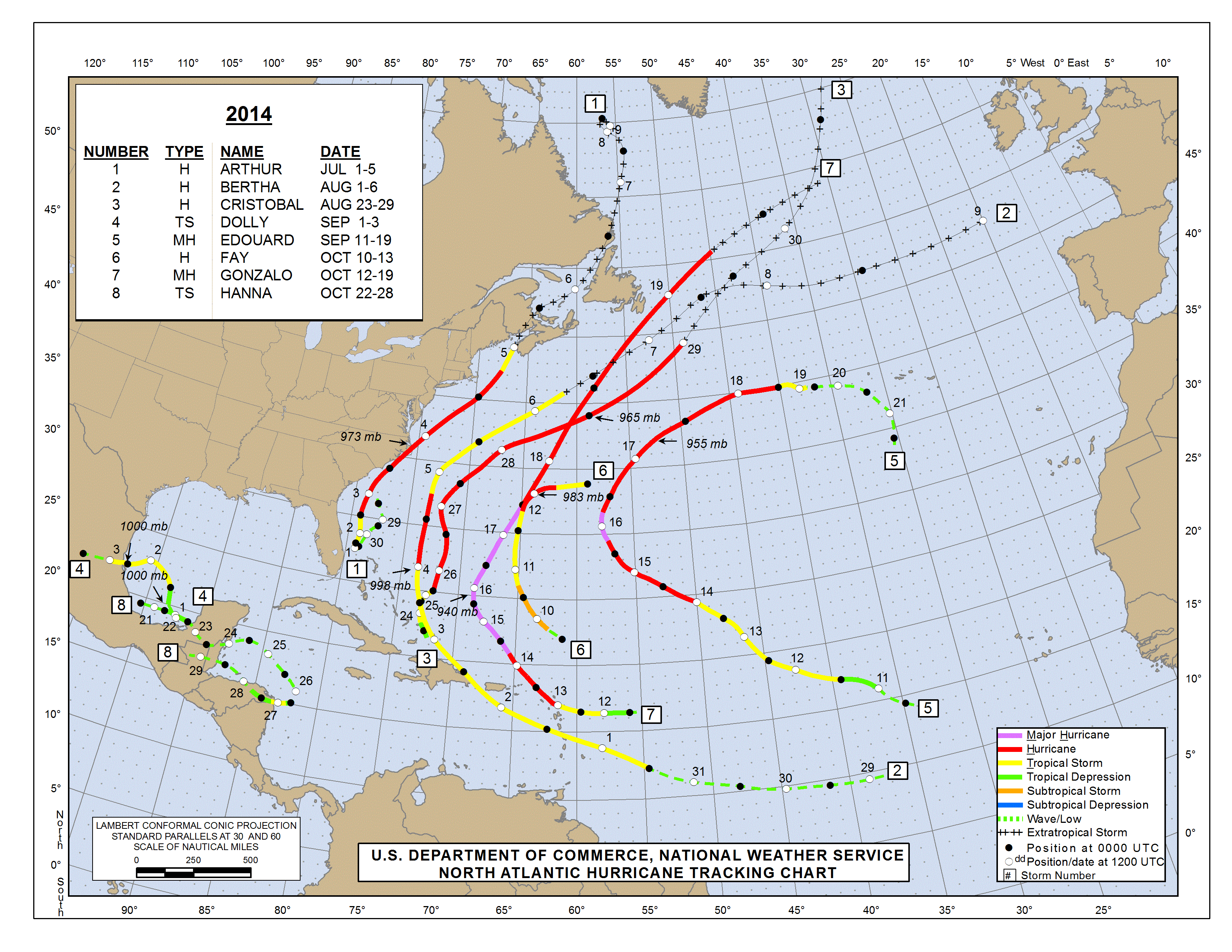
Deciphering the Atlantic Hurricane Weather Map
A hurricane weather map, a visual representation of weather conditions, serves as a vital tool for tracking and predicting the path of hurricanes. These maps, typically created by meteorological agencies like the National Hurricane Center (NHC), provide a comprehensive overview of storm activity in the Atlantic basin.
Key Components of a Hurricane Weather Map:
- Hurricane Track: A curved line depicting the projected path of the hurricane, based on complex computer models and historical data.
- Hurricane Intensity: Represented by a color-coded scale, indicating the hurricane’s wind speed and potential for damage. The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale, ranging from Category 1 to 5, is commonly used.
- Storm Surge: Indicated by shaded areas, illustrating the potential rise in sea level caused by the storm’s strong winds, posing a significant flooding risk.
- Tropical Wave: A line denoting a region of low pressure in the tropics, which can potentially develop into a hurricane.
- Tropical Depression/Storm: Depicted as a circle, representing a storm with wind speeds below hurricane force.
- Isobars: Lines connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure, providing insights into the storm’s structure and potential movement.
- Wind Speed and Direction: Arrows indicating wind speed and direction around the storm, aiding in understanding its potential impact on coastal areas.
The Importance of Hurricane Weather Maps
Hurricane weather maps are indispensable for:
- Early Warning: Providing timely alerts to coastal communities, allowing for effective evacuation and preparedness measures.
- Accurate Forecasting: Guiding emergency response teams and disaster management agencies in anticipating the storm’s trajectory and intensity, enabling targeted interventions.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying areas at risk of storm surge, flooding, and high winds, facilitating informed decision-making for infrastructure protection and public safety.
- Public Awareness: Educating the public about hurricane threats, encouraging preparedness and promoting responsible actions during storms.
- Scientific Research: Providing valuable data for understanding hurricane dynamics, improving forecasting models, and advancing scientific knowledge.
Navigating the Information: FAQs
Q: How often are hurricane weather maps updated?
A: Hurricane weather maps are updated regularly, typically every few hours, based on the latest satellite imagery, radar data, and weather models.
Q: How accurate are hurricane forecasts?
A: While hurricane forecasts have significantly improved over the years, they are not perfect. The accuracy of forecasts varies depending on the storm’s stage of development and the time horizon.
Q: What is the difference between a hurricane watch and a hurricane warning?
A: A hurricane watch indicates that hurricane conditions are possible within the specified area, while a hurricane warning signifies that hurricane conditions are expected within the specified area.
Q: What should I do if a hurricane warning is issued?
A: If a hurricane warning is issued, it is crucial to take necessary precautions, such as securing your home, stocking up on supplies, and following evacuation orders.
Tips for Interpreting Hurricane Weather Maps
- Consult Reliable Sources: Obtain hurricane weather maps from official sources like the NHC or your local weather agency.
- Pay Attention to Color Coding: Understand the color-coded scale representing hurricane intensity to assess the potential for damage.
- Track the Storm’s Path: Observe the projected track and consider the potential impact on your location.
- Stay Informed: Regularly check for updates and be prepared to adjust your plans based on the latest information.
- Prepare for the Worst: Assume the worst-case scenario and have a plan in place for potential evacuation or shelter-in-place.
Conclusion
Hurricane weather maps are powerful tools for safeguarding lives and property in hurricane-prone regions. By understanding their components and utilizing them effectively, individuals and communities can enhance their preparedness and response capabilities, mitigating the risks associated with these powerful storms. Continuous advancements in weather forecasting and the accessibility of information empower us to navigate the turbulent waters of hurricane season with greater resilience and safety.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Storm: Understanding the Hurricane Weather Map of the Atlantic Ocean. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!