Navigating The South Atlantic: A Comprehensive Exploration
Navigating the South Atlantic: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: Navigating the South Atlantic: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the South Atlantic: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the South Atlantic: A Comprehensive Exploration

The South Atlantic Ocean, a vast expanse of water stretching from the equator to Antarctica, is a vital component of the global ocean system. Its influence extends far beyond its geographical boundaries, impacting weather patterns, marine ecosystems, and global trade. Understanding its geography, unique characteristics, and significance is crucial to appreciating its role in the intricate web of life on Earth.
A Glimpse into the South Atlantic’s Geography
The South Atlantic Ocean is defined by its distinctive borders. To the north, it merges with the Atlantic Ocean, sharing the equator as a boundary. The eastern edge is marked by the African continent, while the western edge is defined by the South American continent. The southernmost point of the ocean is marked by the convergence of the Atlantic and Indian Oceans near the icy shores of Antarctica.
Delving Deeper: Key Features and Their Significance
1. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge: This underwater mountain range, stretching for thousands of kilometers, is a defining feature of the South Atlantic. It represents a tectonic boundary where the African and South American plates are slowly drifting apart. This divergence results in volcanic activity, creating new ocean floor and contributing to the ocean’s unique topography.
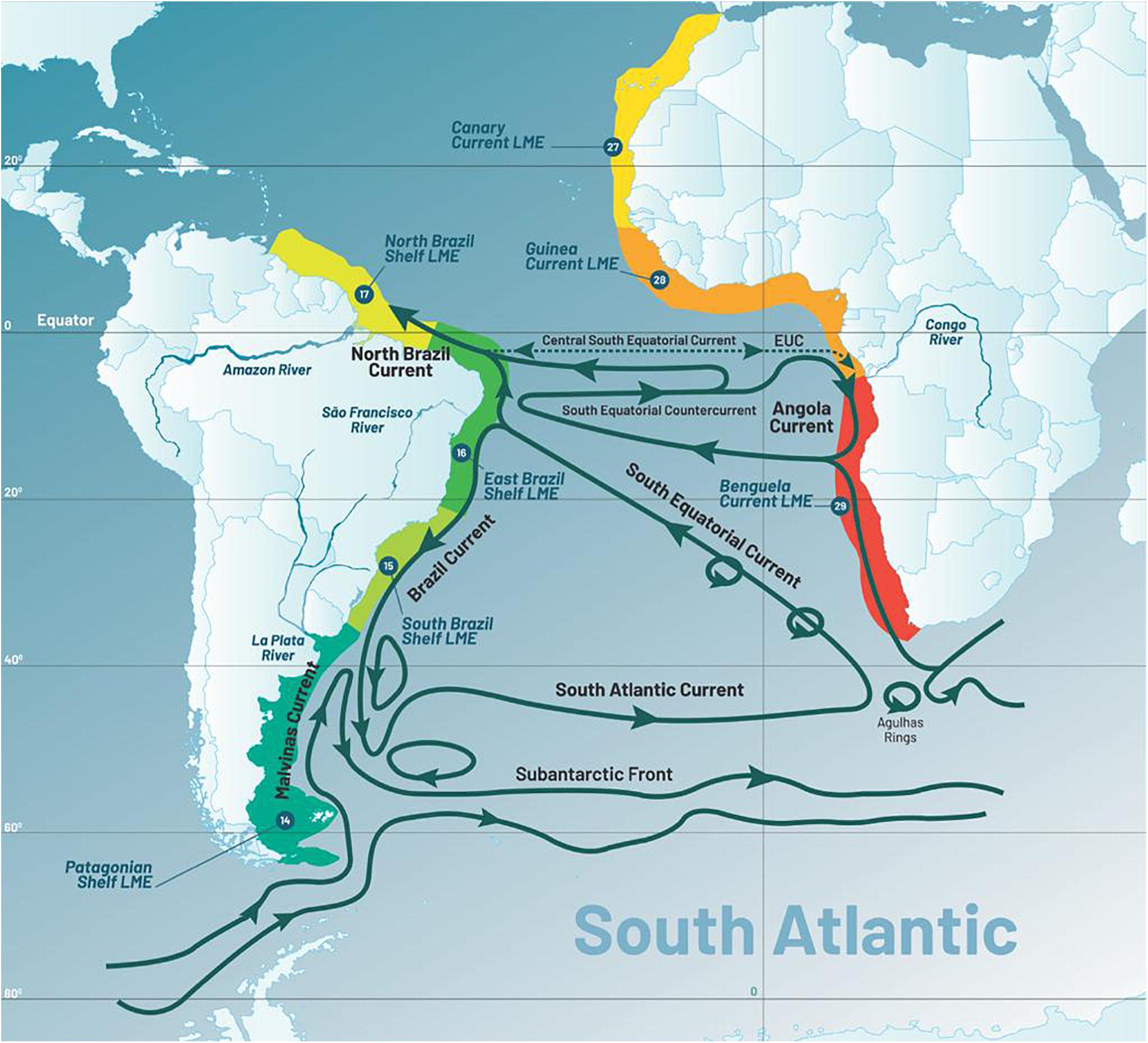
2. The Benguela Current: This cold, nutrient-rich current flowing northward along the western coast of Africa is a vital component of the South Atlantic ecosystem. It supports a rich biodiversity, including vast populations of fish, seabirds, and marine mammals. The Benguela Current also plays a crucial role in regulating regional climate by moderating temperatures and influencing rainfall patterns.
3. The Brazilian Current: A warm current flowing southward along the eastern coast of South America, the Brazilian Current carries tropical waters to higher latitudes, influencing regional weather patterns and contributing to the diverse marine life found in the South Atlantic.
4. The Falkland Current: This cold current flowing northward along the eastern coast of Argentina brings nutrient-rich waters from the Antarctic region, supporting a unique ecosystem characterized by cold-water species.
5. The Agulhas Current: This warm current flowing southward along the eastern coast of Africa is a powerful current that plays a significant role in transporting heat and salt from the Indian Ocean into the South Atlantic. It also contributes to the formation of eddies, which are swirling bodies of water that influence marine productivity and nutrient distribution.
The South Atlantic’s Ecological Importance
The South Atlantic Ocean is a biodiversity hotspot, home to a wide range of marine life, including:
- Fish: The ocean supports a vast fishing industry, with species like tuna, hake, and anchovies being commercially important.
- Marine Mammals: Whales, dolphins, seals, and sea lions thrive in the South Atlantic, utilizing its diverse habitats for breeding, feeding, and migration.
- Seabirds: The ocean provides essential breeding grounds and foraging areas for various seabird species, including penguins, albatrosses, and petrels.
- Coral Reefs: While not as extensive as in other oceans, coral reefs in the South Atlantic, particularly around Brazil and the Falkland Islands, provide vital habitat for a multitude of marine species.
Navigating the Challenges: Threats to the South Atlantic
Despite its ecological richness, the South Atlantic faces various threats:
- Overfishing: Unsustainable fishing practices deplete fish populations, disrupting the delicate balance of the ecosystem.
- Pollution: Industrial and agricultural runoff, oil spills, and plastic waste contaminate the ocean, harming marine life and disrupting habitats.
- Climate Change: Rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and changes in currents threaten marine ecosystems and their inhabitants.
The South Atlantic: A Lifeline for Global Trade
The South Atlantic plays a crucial role in global trade, serving as a vital waterway for shipping goods between continents. Its strategic location facilitates the transportation of oil, gas, minerals, agricultural products, and manufactured goods, connecting economies around the world.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the major ports in the South Atlantic?
Major ports in the South Atlantic include:
- Rio de Janeiro (Brazil)
- Buenos Aires (Argentina)
- Cape Town (South Africa)
- Santos (Brazil)
- Salvador (Brazil)
- Montevideo (Uruguay)
2. What are the main currents in the South Atlantic?
The main currents in the South Atlantic are:
- The Benguela Current
- The Brazilian Current
- The Falkland Current
- The Agulhas Current
- The South Atlantic Gyre
3. How does the South Atlantic influence weather patterns?
The South Atlantic’s currents and winds play a significant role in shaping weather patterns around the region. The Benguela Current, for example, moderates temperatures along the western coast of Africa, while the Brazilian Current influences rainfall patterns in South America.
4. What are the main environmental challenges facing the South Atlantic?
The South Atlantic faces significant environmental challenges, including:
- Overfishing
- Pollution
- Climate Change
- Habitat Loss
5. What are the economic benefits of the South Atlantic?
The South Atlantic provides significant economic benefits, including:
- Fishing
- Shipping
- Tourism
- Oil and Gas Exploration
Tips for Exploring the South Atlantic
- Plan your trip: Research the best time to visit, considering weather patterns and marine life activity.
- Choose your destination: Explore the diverse ecosystems of the South Atlantic, from the vibrant coral reefs of Brazil to the icy landscapes of Antarctica.
- Respect the environment: Practice responsible tourism by minimizing your impact on the marine environment.
- Learn about conservation efforts: Support organizations working to protect the South Atlantic’s unique ecosystems.
Conclusion
The South Atlantic Ocean is a dynamic and vital body of water, playing a crucial role in global climate, marine biodiversity, and international trade. Understanding its geography, characteristics, and challenges is essential for appreciating its significance and for developing strategies to ensure its sustainable future. By recognizing the interconnectedness of the ocean with the rest of the planet, we can work towards protecting this valuable resource for generations to come.




![[South Atlantic Ocean] To The Honble. The Court of Directors of the United East India Company](https://storage.googleapis.com/raremaps/img/large/60625op.jpg)

.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the South Atlantic: A Comprehensive Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!