Navigating The Landscape: Understanding Topographic Maps Of Michigan By County
Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Topographic Maps of Michigan by County
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Topographic Maps of Michigan by County
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Topographic Maps of Michigan by County. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Topographic Maps of Michigan by County
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Topographic Maps of Michigan by County
- 3.1 Decoding the Terrain: A County-by-County Exploration
- 3.2 Unveiling the Significance: Applications of Topographic Maps
- 3.3 Navigating the Data: FAQs
- 3.4 Tips for Effective Use: Unlocking the Potential
- 3.5 Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Managing Michigan’s Landscape
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Topographic Maps of Michigan by County

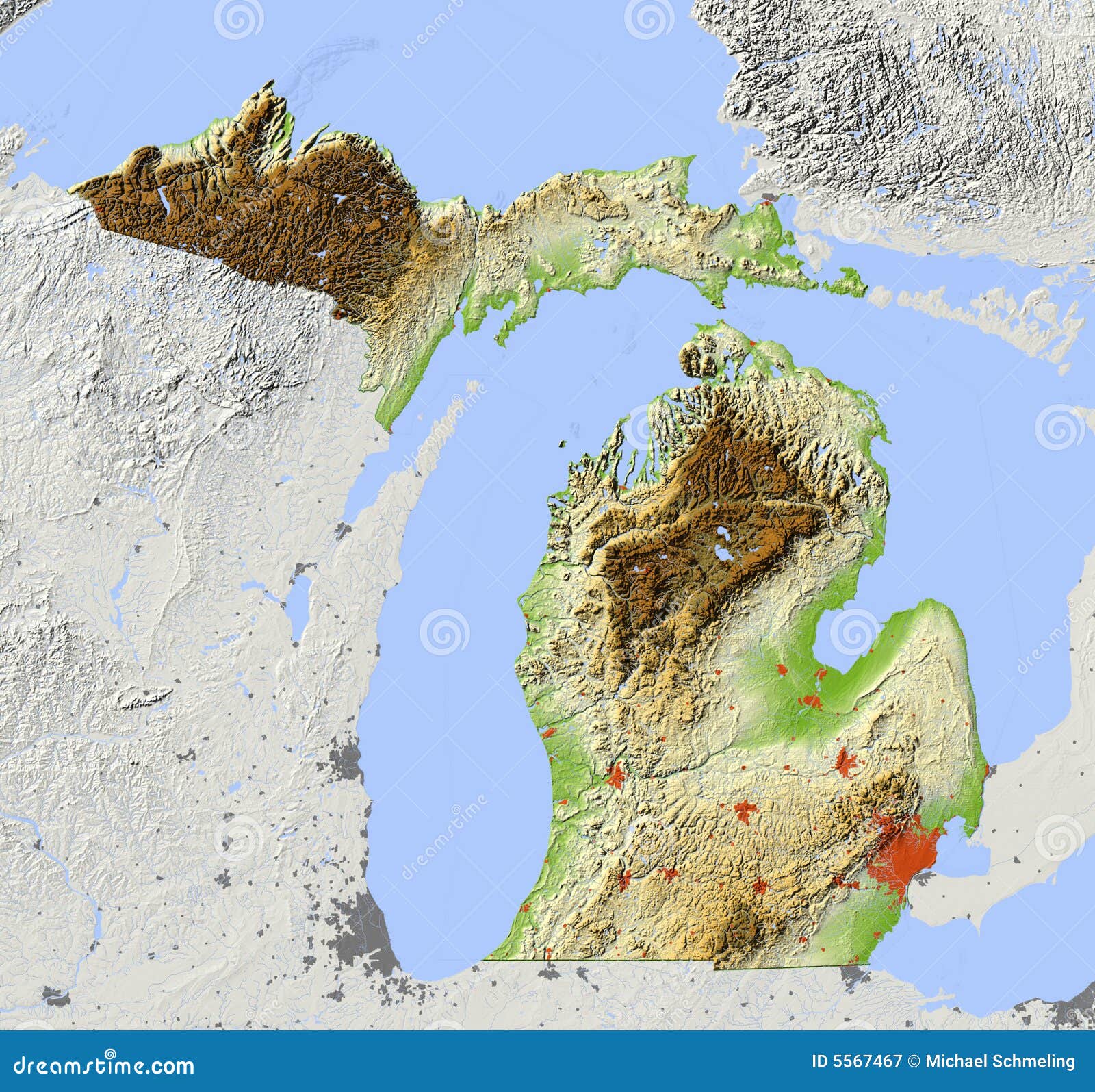
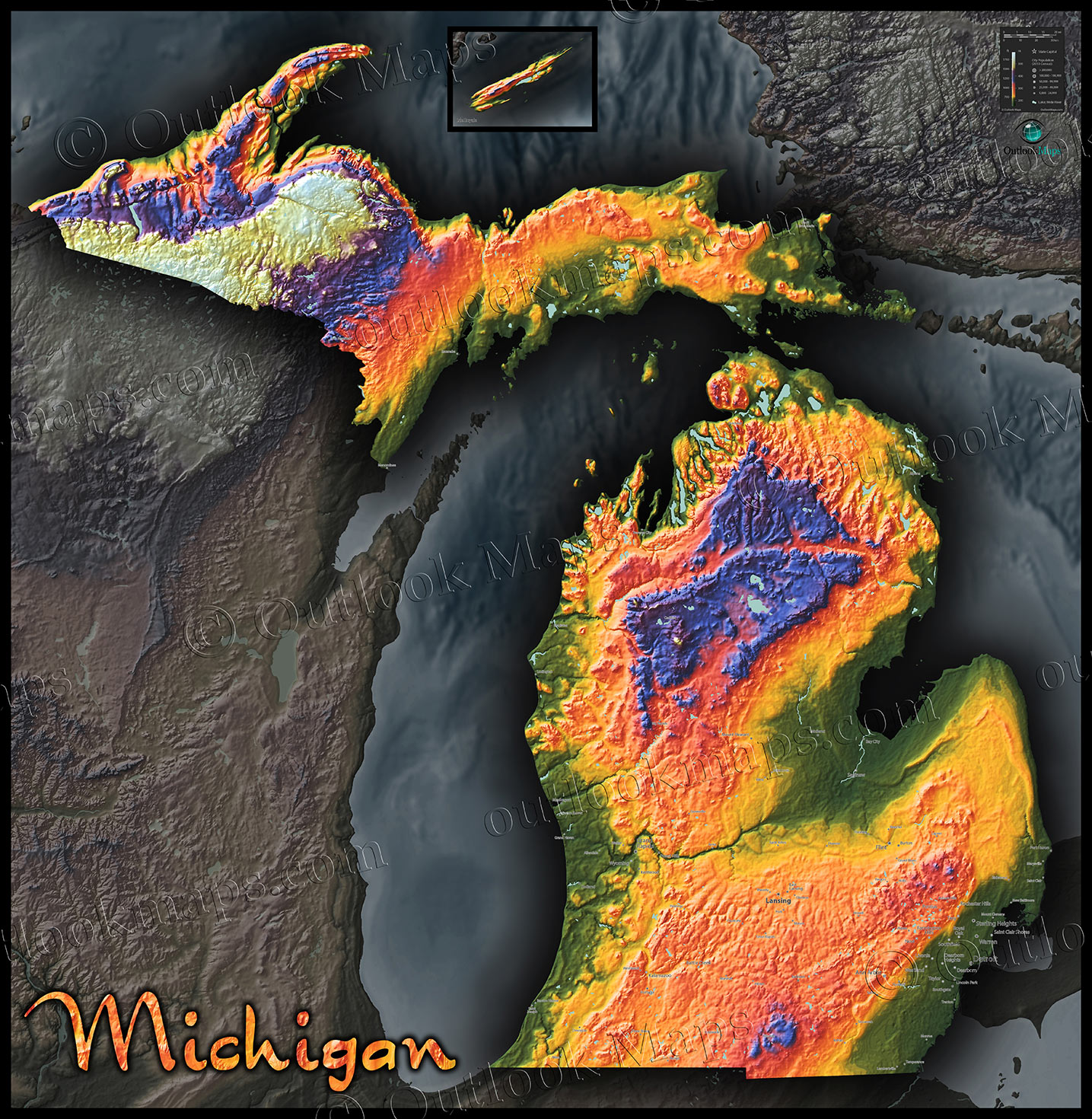
Michigan’s diverse landscape, encompassing vast stretches of Great Lakes coastline, rolling hills, and fertile plains, is a testament to its geological history and dynamic natural processes. Understanding this landscape, its intricacies, and its potential impact on human activities requires a specialized tool: topographic maps. These maps, meticulously crafted to depict the Earth’s surface features and their elevation, provide a comprehensive view of Michigan’s terrain, revealing its hidden secrets and informing crucial decisions.
Decoding the Terrain: A County-by-County Exploration
Michigan’s topography is not uniform; each of its 83 counties boasts a unique character shaped by glacial activity, river erosion, and geological formations. Analyzing topographic maps on a county-by-county basis unveils this intricate tapestry:
1. The Upper Peninsula:
- Alger County: Characterized by rugged, forested hills and the dramatic shoreline of Lake Superior. Topographic maps reveal the dramatic elevation changes along the Pictured Rocks National Lakeshore, a popular destination for hiking and kayaking.
- Chippewa County: Home to the iconic Mackinac Bridge and the Straits of Mackinac, this county features rolling hills, dense forests, and a network of inland lakes. Topographic maps highlight the varying elevations of the Mackinac Island and the surrounding waters.
- Marquette County: Known for its rich iron ore deposits and the picturesque Keweenaw Peninsula, this county showcases a rugged landscape with steep hills, deep valleys, and the dramatic shoreline of Lake Superior. Topographic maps reveal the dramatic elevation changes along the rugged coast and the intricate network of rivers and streams.
2. The Lower Peninsula:
- Alpena County: This county features a diverse landscape of rolling hills, forested areas, and a long coastline along Lake Huron. Topographic maps showcase the gradual elevation changes leading to the Thunder Bay National Marine Sanctuary, a popular destination for diving and exploring shipwrecks.
- Barry County: Located in the southern part of the Lower Peninsula, this county features rolling hills, fertile farmland, and a network of rivers and streams. Topographic maps reveal the gradual elevation changes across the county, highlighting the location of the Thornapple River and the surrounding wetlands.
- Oakland County: This county, part of the Detroit metropolitan area, features a mix of urban development, rolling hills, and forested areas. Topographic maps reveal the gradual elevation changes across the county, highlighting the location of the Clinton River and the surrounding parks and recreational areas.
3. Coastal Counties:
- Ottawa County: This county, located on the western shore of Lake Michigan, features a diverse landscape of beaches, dunes, and rolling hills. Topographic maps highlight the dramatic elevation changes along the shoreline, revealing the location of the iconic Holland State Park and the surrounding dune formations.
- Wayne County: Home to the city of Detroit, this county features a mix of urban development, flatlands, and the Detroit River. Topographic maps reveal the gradual elevation changes leading to the Detroit River, highlighting the location of the Belle Isle State Park and the surrounding urban landscape.
- Emmet County: Located in the northern part of the Lower Peninsula, this county features a diverse landscape of rolling hills, forested areas, and a long coastline along Lake Michigan. Topographic maps showcase the gradual elevation changes leading to the Mackinaw City area, highlighting the location of the Mackinac Bridge and the surrounding waters.
Unveiling the Significance: Applications of Topographic Maps
Topographic maps are not just static representations of the land; they are powerful tools with numerous applications, influencing various aspects of life in Michigan:
1. Infrastructure Development:
- Road and Bridge Construction: Topographic maps guide engineers in planning and constructing roads, bridges, and other infrastructure projects by providing crucial information about terrain, elevation, and potential obstacles.
- Pipeline and Utility Installation: Topographic maps help utilities companies plan the most efficient routes for pipelines, power lines, and other utilities, minimizing disruption and optimizing resource utilization.
2. Environmental Management:
- Flood Risk Assessment: Topographic maps are essential for identifying flood-prone areas, helping communities prepare for and mitigate the impact of natural disasters.
- Wildlife Habitat Management: Understanding the elevation changes and terrain features helps conservationists manage wildlife habitats and create suitable environments for diverse species.
3. Recreation and Tourism:
- Hiking and Biking Trails: Topographic maps guide outdoor enthusiasts in planning hiking and biking routes, highlighting challenging terrains and scenic overlooks.
- Boating and Fishing: Navigating waterways and identifying optimal fishing spots becomes easier with the help of topographic maps, providing information on water depths and underwater features.
4. Agriculture and Land Use:
- Soil and Water Management: Topographic maps provide insight into soil types and water drainage patterns, aiding farmers in optimizing crop yields and managing water resources.
- Land Use Planning: Understanding the topography helps planners make informed decisions regarding land use, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing resource utilization.
Navigating the Data: FAQs
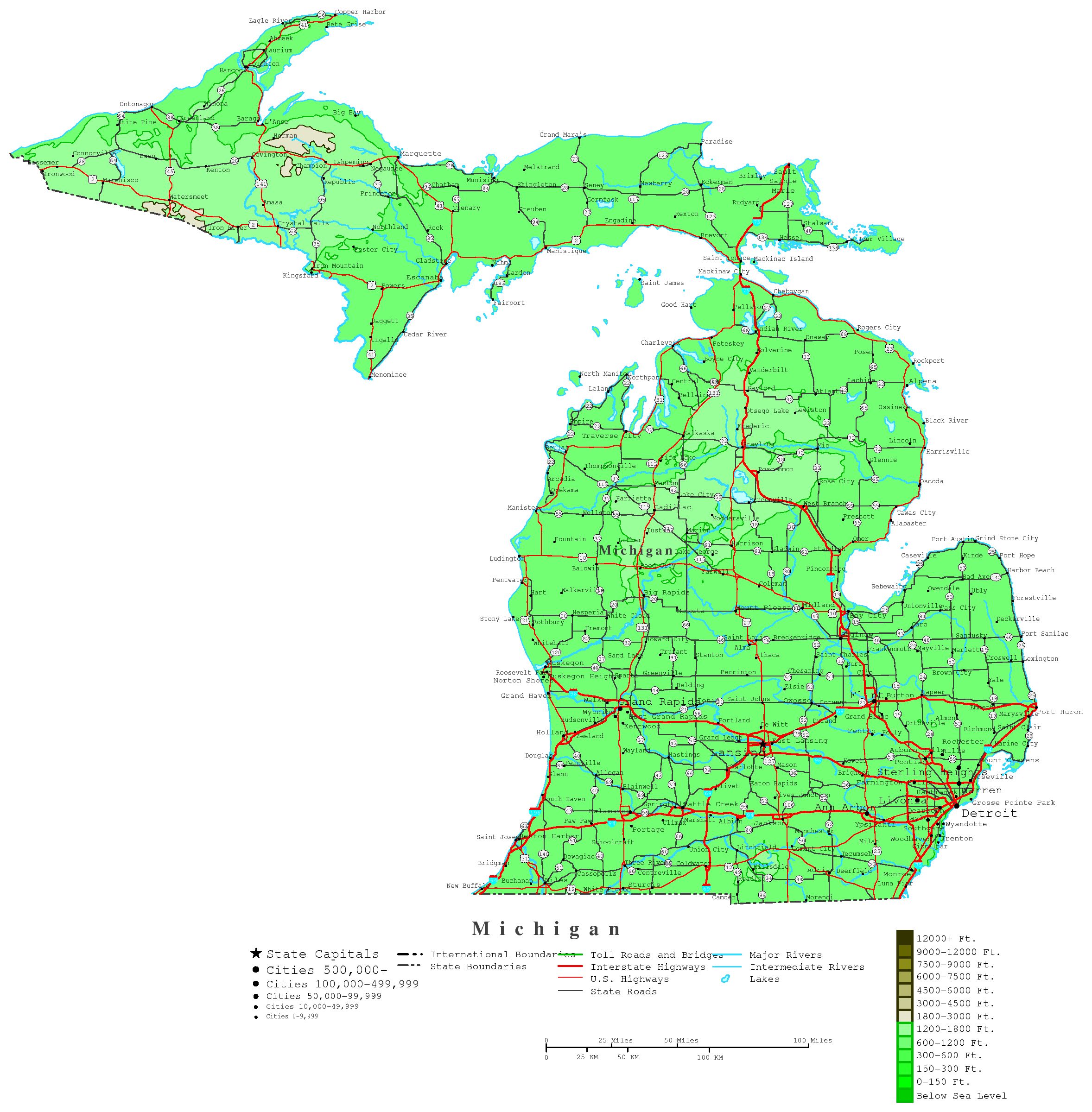
1. What is the best resource for accessing topographic maps of Michigan by county?
Several resources offer high-quality topographic maps of Michigan, including:
- United States Geological Survey (USGS): The USGS provides a vast collection of topographic maps, including digital versions available for download.
- Michigan Department of Natural Resources (MDNR): The MDNR offers topographic maps specific to Michigan, often focusing on recreational areas and natural resources.
- Online Mapping Services: Several online platforms like Google Maps and ArcGIS offer interactive topographic maps with varying levels of detail.
2. How do I interpret the elevation information on a topographic map?
Topographic maps utilize contour lines to represent elevation. Each contour line connects points of equal elevation. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the terrain.
3. What are the different types of topographic maps available?
Topographic maps are available in various formats, including:
- Paper Maps: Traditional paper maps offer a comprehensive overview of the terrain.
- Digital Maps: Digital maps offer interactive features, allowing users to zoom, pan, and measure distances.
- 3D Models: 3D models provide a realistic visual representation of the terrain, enhancing understanding of elevation changes.
4. How can I use topographic maps for hiking and backpacking?
Topographic maps are essential for planning hiking and backpacking trips. They help identify trails, estimate distances, and assess the difficulty of the terrain.
5. Are there any specific topographic maps for recreational areas in Michigan?
Yes, many recreational areas in Michigan have dedicated topographic maps available. These maps often include detailed information about trails, campsites, and other amenities.
Tips for Effective Use: Unlocking the Potential
- Understanding Scale and Legend: Familiarize yourself with the map’s scale and legend to accurately interpret distances, elevations, and symbols.
- Identifying Key Features: Focus on identifying key features such as rivers, lakes, hills, and valleys to understand the overall terrain.
- Using Contour Lines: Practice interpreting contour lines to visualize elevation changes and identify steep slopes.
- Combining with Other Resources: Integrate topographic maps with other data sources, such as satellite imagery and aerial photographs, for a more comprehensive view.
- Staying Updated: Ensure you are using the most up-to-date topographic maps, as terrain features can change over time.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Managing Michigan’s Landscape
Topographic maps serve as indispensable tools for understanding and managing Michigan’s complex and dynamic landscape. From guiding infrastructure development and environmental management to enhancing recreational experiences and informing land use decisions, these maps provide invaluable insights into the terrain, its intricacies, and its influence on human activities. By embracing the power of topographic maps, we can navigate Michigan’s diverse landscape with greater awareness, efficiency, and responsibility, ensuring its preservation and sustainable utilization for generations to come.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Topographic Maps of Michigan by County. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!