Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The Provinces Of Spain
Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Provinces of Spain
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Provinces of Spain
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Provinces of Spain. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Provinces of Spain
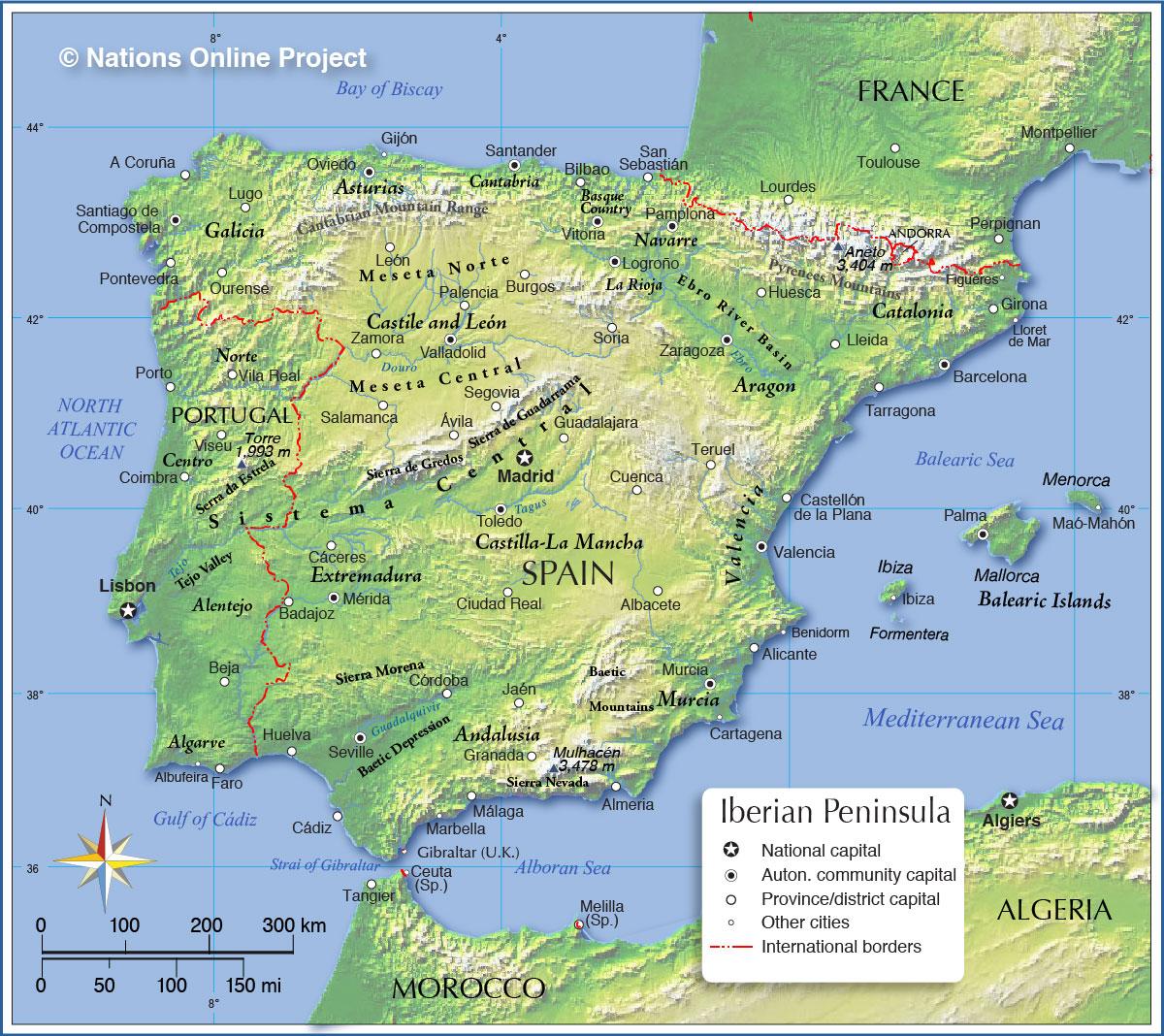
Spain, a nation steeped in history and cultural diversity, is geographically divided into 17 autonomous communities, each with its unique identity and administrative structure. Understanding these divisions, known as "provincias" in Spanish, is essential for comprehending the country’s political, economic, and social landscape. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the provinces of Spain, exploring their historical evolution, geographical characteristics, and cultural significance.
A Historical Journey: From Kingdoms to Autonomous Communities
The current provincial structure of Spain has its roots in the historical evolution of the Iberian Peninsula. The country’s diverse geography and centuries of political fragmentation led to the formation of numerous kingdoms and principalities. The Reconquista, the gradual Christian reconquest of the Iberian Peninsula from the Moors, further shaped the political landscape, culminating in the unification of Spain under the Catholic Monarchs in the late 15th century.
The modern administrative structure of Spain emerged during the reign of King Philip II in the 16th century. The country was divided into "reinos" (kingdoms) and "provincias" (provinces), which served as the primary administrative units. This system remained largely unchanged for centuries, with minor adjustments made over time.
The 20th century witnessed significant changes in Spain’s political landscape. The Second Republic (1931-1939) introduced a new provincial structure based on a more decentralized model. However, the Spanish Civil War and the subsequent Francoist regime (1939-1975) reversed these changes, centralizing power once again.
Following the death of Franco and the transition to democracy, Spain embarked on a process of decentralization. The 1978 Constitution established a system of autonomous communities, granting them significant autonomy in areas such as education, healthcare, and culture. This move marked a shift from a centralized state to a more decentralized model, reflecting the diverse cultural and linguistic identities of the Spanish regions.
Exploring the Provinces: A Geographical and Cultural Overview
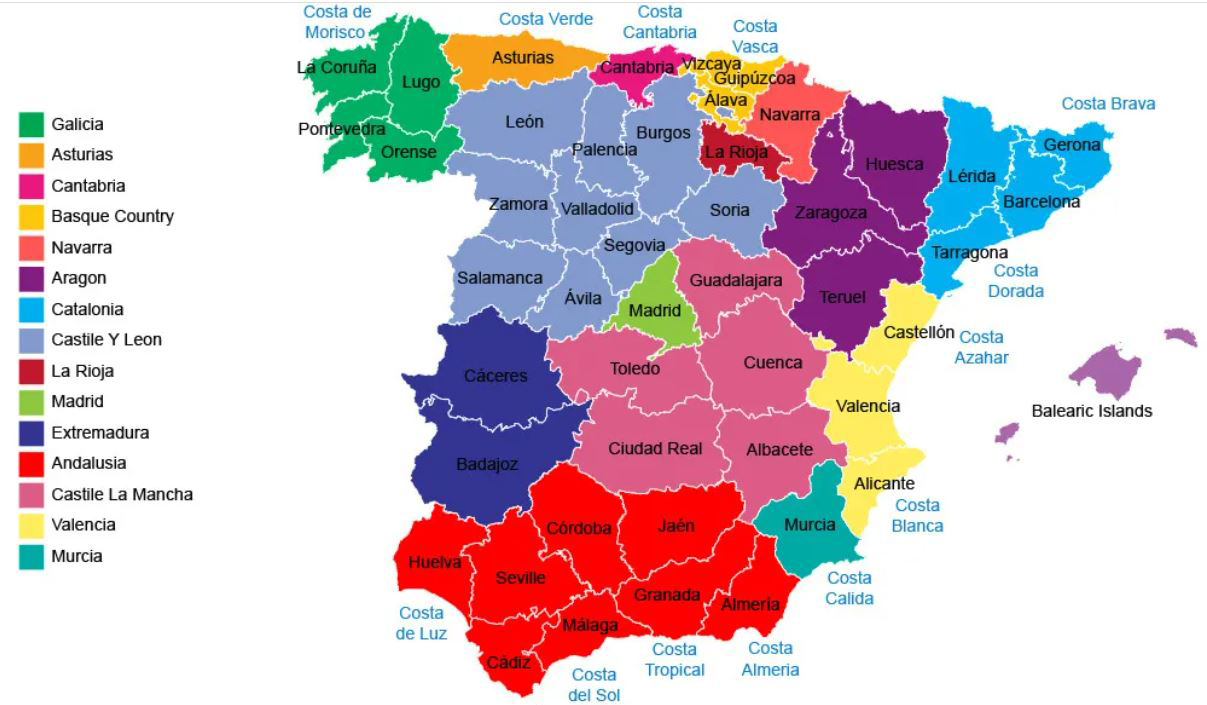
Each of Spain’s 17 autonomous communities is further subdivided into provinces, totaling 50 in all. These provinces are not simply administrative divisions; they represent distinct geographical, cultural, and historical entities.
The Northern Frontier:
- Galicia: Located in the northwest corner of Spain, Galicia is known for its rugged coastline, lush green valleys, and Celtic heritage. Its provinces, A Coruña, Lugo, Ourense, and Pontevedra, each possess unique cultural traditions and breathtaking landscapes.
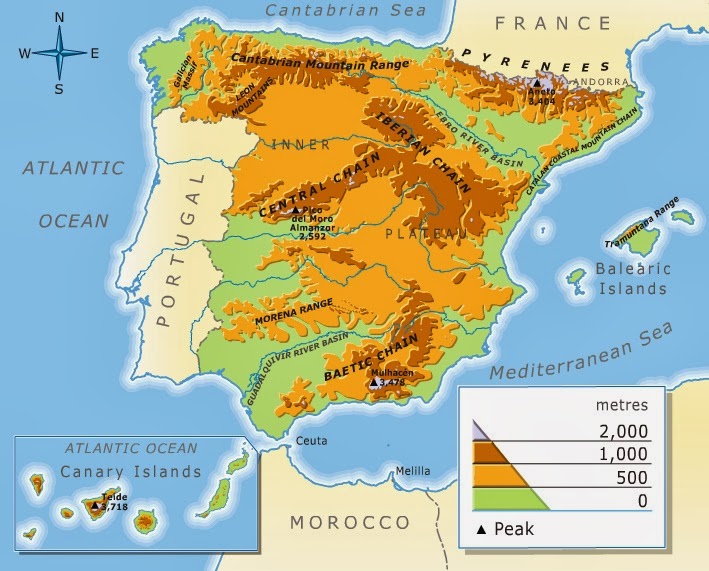
- Asturias: Situated along the Bay of Biscay, Asturias is a region with a rich mining history and dramatic mountain scenery. Its province, Asturias, is home to the Picos de Europa, a stunning mountain range that attracts outdoor enthusiasts.
- Cantabria: Sharing a border with Asturias, Cantabria boasts a stunning coastline, with beaches and cliffs that offer breathtaking views. Its province, Cantabria, is known for its cave paintings and its vibrant capital city, Santander.
- País Vasco: Located in the north of Spain, País Vasco is a region with a strong Basque identity and a distinct language, Euskara. Its provinces, Álava, Bizkaia, and Gipuzkoa, are known for their industrial centers, traditional villages, and stunning natural landscapes.
- Navarra: Bordering País Vasco and Aragón, Navarra is a region with a rich history and a unique cultural identity. Its province, Navarra, is known for its wine production, its traditional festivals, and its picturesque capital city, Pamplona.
The Central Plateau:
- Castilla y León: The largest autonomous community in Spain, Castilla y León encompasses a vast plateau with a rich history and a strong agricultural tradition. Its provinces, Ávila, Burgos, León, Palencia, Salamanca, Segovia, Soria, Valladolid, and Zamora, each possess unique historical and cultural treasures.
- Castilla-La Mancha: Situated in the heart of Spain, Castilla-La Mancha is a region known for its windmills, vineyards, and its connection to the literary works of Miguel de Cervantes. Its provinces, Albacete, Ciudad Real, Cuenca, Guadalajara, and Toledo, offer a glimpse into the region’s rich history and cultural heritage.
- Madrid: The capital of Spain, Madrid is a vibrant metropolis with a rich cultural and artistic scene. Its province, Madrid, encompasses the city of Madrid and its surrounding areas, offering a mix of urban life and rural charm.
The Eastern Coast:
- Aragón: Located in northeastern Spain, Aragón is a region with a rich history and a strong agricultural tradition. Its provinces, Huesca, Teruel, and Zaragoza, each boast unique landscapes and cultural attractions.
- Catalunya: Catalonia is a vibrant region in northeastern Spain with a strong cultural identity and a distinct language, Catalan. Its provinces, Barcelona, Girona, Lleida, and Tarragona, each offer a blend of urban life, historical sites, and stunning natural beauty.
- Valencia: Situated on the Mediterranean coast, Valencia is a region known for its beaches, its citrus groves, and its vibrant cultural scene. Its provinces, Alicante, Castellón, and Valencia, each offer a unique blend of traditional and modern influences.
The Southern Coast:
- Andalucía: Located in the south of Spain, Andalucía is a region known for its sunny climate, its Moorish heritage, and its vibrant culture. Its provinces, Almería, Cádiz, Córdoba, Granada, Huelva, Jaén, Málaga, and Seville, each possess unique historical and cultural treasures.
- Murcia: Situated on the southeastern coast of Spain, Murcia is a region known for its fertile plains, its beaches, and its vibrant cultural scene. Its province, Murcia, offers a glimpse into the region’s rich history and its traditional way of life.
The Islands:
- Islas Baleares: This archipelago in the Mediterranean Sea comprises the islands of Mallorca, Menorca, Ibiza, and Formentera. Each island possesses its own unique character and charm, offering a blend of beaches, historical sites, and vibrant nightlife.
- Islas Canarias: Located off the coast of Africa, the Canary Islands are a volcanic archipelago known for its subtropical climate, its stunning beaches, and its diverse landscapes. Its provinces, Las Palmas and Santa Cruz de Tenerife, each offer a unique blend of Spanish and African influences.
The Importance of Understanding the Provinces
Understanding the provinces of Spain is crucial for several reasons:
- Political Context: The provinces provide a framework for understanding the country’s decentralized political structure. Each province has its own elected government and plays a significant role in shaping local policies and initiatives.
- Cultural Diversity: The provinces represent distinct cultural identities, reflecting the diverse historical and geographical influences that have shaped Spain. Each province has its unique traditions, dialects, and cultural expressions.
- Economic Development: The provinces play a significant role in Spain’s economic landscape. Each province has its own economic strengths and challenges, influencing its development trajectory.
- Tourism: The provinces offer a diverse range of tourist attractions, from historical sites and cultural events to natural landscapes and beaches. Understanding the provinces helps travelers plan their trips and explore the unique offerings of each region.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between a "provincia" and an "autonomous community"?
A: An autonomous community is a larger administrative unit that encompasses several provinces. Provinces are the primary administrative divisions within an autonomous community.
Q: How are the provinces governed?
A: Each province has a provincial government, led by a "presidente" (president) and a "diputación provincial" (provincial council). The provincial government is responsible for managing local services and implementing regional policies.
Q: What are some of the key cultural differences between the provinces?
A: The provinces of Spain exhibit significant cultural differences, ranging from language and dialect to traditional customs and cuisine. For example, Catalonia has its own distinct language, Catalan, while Galicia has its own unique musical traditions.
Q: How do the provinces contribute to Spain’s economy?
A: The provinces play a vital role in Spain’s economic development. Each province has its own economic strengths and challenges, contributing to the overall economic landscape of the country. For example, Catalonia is a major industrial center, while Andalucia is known for its agricultural production.
Tips for Exploring the Provinces
- Research the Provinces: Before traveling to Spain, take time to research the different provinces and their unique offerings. This will help you plan your trip and maximize your experience.
- Visit Historical Sites: Each province boasts a wealth of historical sites, from ancient ruins to medieval castles. Explore these sites to gain a deeper understanding of the region’s past.
- Experience the Culture: Immerse yourself in the local culture by attending festivals, trying traditional cuisine, and learning about local customs.
- Explore the Natural Landscape: Spain’s diverse geography offers a wide range of natural landscapes, from rugged mountains to pristine beaches. Explore these landscapes to appreciate the beauty of the country.
Conclusion
The provinces of Spain offer a fascinating glimpse into the country’s rich history, cultural diversity, and geographical variety. Understanding the provinces is essential for appreciating the unique character of each region and for navigating the country’s political, economic, and social landscape. By exploring the provinces and their unique offerings, travelers can gain a deeper understanding of Spain’s complex and fascinating tapestry.


![[OC] Different landscapes from every province of Spain : r/MapPorn](https://i.redd.it/zut17szb12a31.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Provinces of Spain. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!