Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To Map Calculation In SAP
Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Calculation in SAP
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Calculation in SAP
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Calculation in SAP. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Calculation in SAP
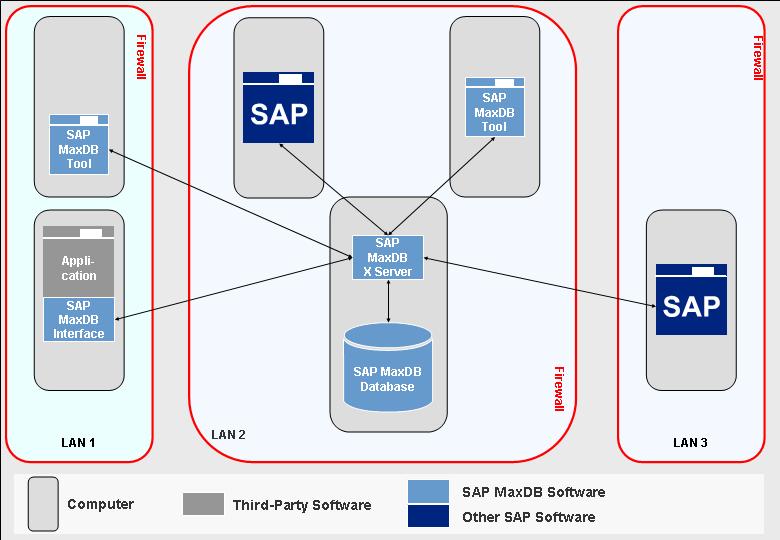
In the intricate world of enterprise resource planning (ERP), SAP stands as a dominant force, providing a robust framework for managing diverse business operations. At the heart of this framework lies a powerful tool: map calculation. This seemingly simple concept plays a pivotal role in optimizing business processes, streamlining data flow, and enhancing overall efficiency. This article delves into the intricacies of map calculation within the SAP environment, exploring its significance, functionalities, and practical applications.
Understanding the Essence of Map Calculation
At its core, map calculation in SAP involves defining and applying rules to transform data from one format to another. It acts as a bridge between disparate data structures, enabling seamless data integration and analysis. Imagine a scenario where data from a legacy system needs to be integrated into SAP. Map calculation facilitates this transition, ensuring that the data is accurately transformed and reconciled with the SAP system’s structure.
The Power of Flexibility and Customization
One of the key strengths of map calculation lies in its adaptability. It provides a flexible framework that allows users to define custom rules based on specific business requirements. This flexibility extends to various scenarios, including:
- Data Conversion: Transforming data from external sources, such as spreadsheets or legacy systems, into SAP-compatible formats.
- Data Aggregation: Consolidating data from multiple sources into a single, unified view.
- Data Validation: Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of data by applying predefined rules and checks.
- Data Enrichment: Adding context and value to existing data through calculations and transformations.
A Glimpse into the Technical Landscape
Map calculation in SAP is primarily implemented through the "Data Transfer Workbench" (BW) module, which provides a comprehensive set of tools for data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL). Within this module, the "Transformation" object serves as the cornerstone for defining map calculations. Users leverage the transformation object to create complex rules, involving various mathematical operations, logical comparisons, and data manipulations.
Practical Applications of Map Calculation in SAP
The applications of map calculation extend beyond mere data manipulation. They play a crucial role in various business processes, including:
- Financial Reporting: Consolidating financial data from multiple sources into accurate and timely reports.
- Supply Chain Management: Tracking inventory levels, optimizing procurement processes, and managing logistics operations.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Analyzing customer data to identify trends, personalize marketing campaigns, and enhance customer service.
- Human Resources (HR): Managing employee data, payroll processing, and talent acquisition.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Concepts in Map Calculation
Beyond the fundamental principles, map calculation in SAP offers advanced functionalities to cater to complex business requirements:
- Hierarchical Structures: Handling data that exists in hierarchical structures, such as organizational charts or product hierarchies.
- Data Validation and Error Handling: Implementing robust validation rules and error handling mechanisms to ensure data integrity.
- Conditional Logic: Applying conditional logic to perform calculations based on specific criteria.
- Looping and Iteration: Executing calculations iteratively to process large datasets.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
1. What are the benefits of using map calculation in SAP?
- Data Consistency: Ensuring uniformity and accuracy across different data sources.
- Improved Efficiency: Automating data transformations and reducing manual effort.
- Enhanced Data Visibility: Providing a comprehensive and integrated view of business data.
- Increased Agility: Adapting to changing business requirements through flexible mapping rules.
2. What are the different types of map calculations available in SAP?
- Field Mapping: Directly mapping fields from one data source to another.
- Formula Mapping: Applying mathematical formulas to transform data.
- Lookup Mapping: Retrieving data from external tables or databases based on specific criteria.
- Conditional Mapping: Executing calculations based on predefined conditions.
3. How can I learn more about map calculation in SAP?
- SAP Documentation: Consult the official SAP documentation for detailed information and tutorials.
- Online Resources: Explore online forums, blogs, and communities dedicated to SAP development.
- Training Courses: Enroll in SAP-certified training courses to gain practical expertise.
4. What are the potential challenges associated with map calculation?
- Complexity: Designing complex mapping rules can be challenging, requiring technical expertise.
- Data Integrity: Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of data throughout the transformation process.
- Performance: Handling large datasets can impact system performance, requiring optimization techniques.
Tips for Effective Map Calculation in SAP
- Plan and Design Carefully: Define clear mapping rules and test them thoroughly before implementation.
- Utilize Standard Functions: Leverage built-in SAP functions for data manipulation and validation.
- Document Your Work: Maintain comprehensive documentation of mapping rules and processes.
- Monitor and Optimize: Regularly monitor the performance of map calculations and optimize them as needed.
Conclusion: A Foundation for Business Success
Map calculation in SAP serves as a powerful tool for data integration, transformation, and analysis. By leveraging its flexibility, customization, and advanced functionalities, businesses can streamline processes, enhance decision-making, and gain a competitive edge. As businesses continue to rely on data-driven insights, the role of map calculation within the SAP ecosystem will only grow in importance, paving the way for smarter, more efficient operations.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Calculation in SAP. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!