Navigating The European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The World Atlas
Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the World Atlas
Related Articles: Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the World Atlas
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the World Atlas. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the World Atlas
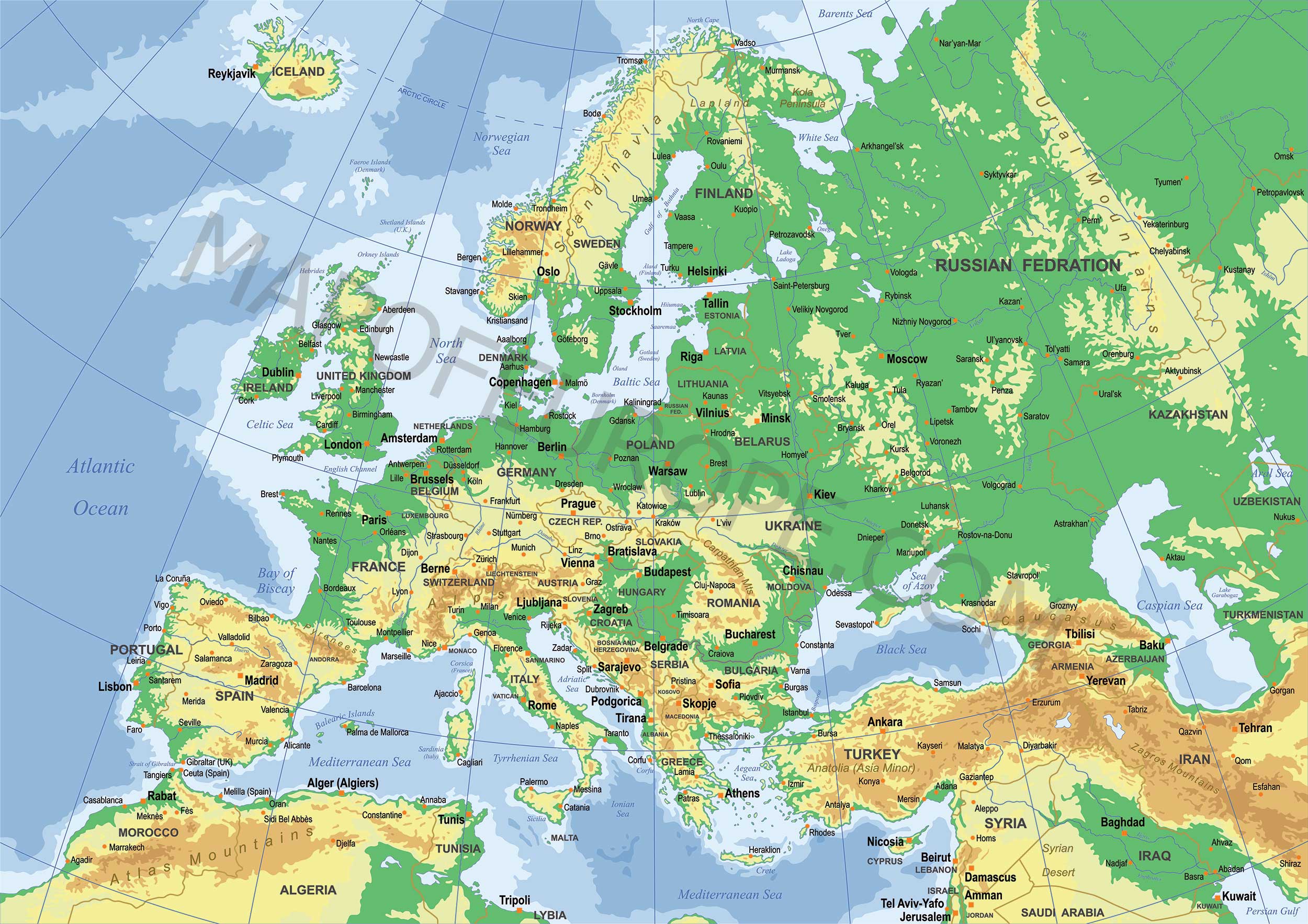
The world atlas is a fundamental tool for understanding the geography of our planet. Among its diverse sections, the European map holds a special significance, serving as a window into the continent’s rich history, diverse cultures, and intricate political landscape. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the European map within the world atlas, exploring its historical evolution, its key features, and its enduring relevance in the modern world.
Tracing the Evolution of the European Map
The depiction of Europe on maps has undergone a dynamic evolution, reflecting the changing understanding of the continent’s geography and its political landscape. Early maps, often influenced by ancient Greek and Roman cartographers, depicted Europe as a relatively small and isolated landmass. As exploration and trade expanded, the map of Europe gradually became more detailed and accurate, incorporating new discoveries and incorporating the growing influence of European powers.
The Renaissance period marked a significant turning point in cartography, with the development of more accurate projection methods and a renewed emphasis on scientific observation. This era witnessed the emergence of detailed maps that captured the intricate coastlines, mountain ranges, and river systems of Europe. The 17th and 18th centuries saw further advancements, driven by the Age of Exploration and the rise of colonialism. Maps began to incorporate political boundaries, reflecting the growing influence of European empires across the globe.
The 19th and 20th centuries brought about a dramatic shift in the European map. The Industrial Revolution fueled rapid urbanization and industrial growth, resulting in the emergence of new cities and transportation networks. The two World Wars and the subsequent rise of nationalism and communism led to significant redrawing of borders, shaping the contemporary political landscape of Europe.
Decoding the European Map: Key Features and Insights
The European map, as presented in a world atlas, provides a comprehensive overview of the continent’s geography, political structure, and cultural diversity. Here are some key features and insights that can be gleaned from studying the map:
-
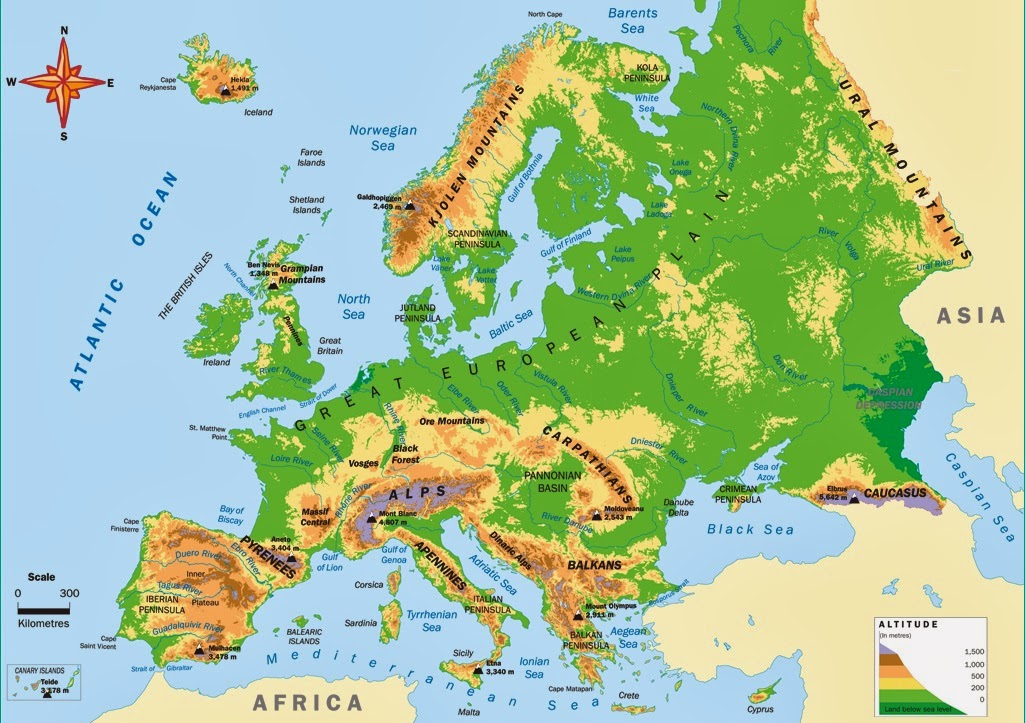
Physical Geography: The map clearly depicts Europe’s diverse physical geography, encompassing vast plains, towering mountain ranges, and extensive coastlines. The Alps, the Pyrenees, and the Carpathians stand as prominent mountain ranges, while the Danube, Rhine, and Volga Rivers are significant waterways. The map also highlights the continent’s peninsular structure, with the Iberian Peninsula, the Italian Peninsula, and the Balkan Peninsula extending into the Mediterranean Sea.
-
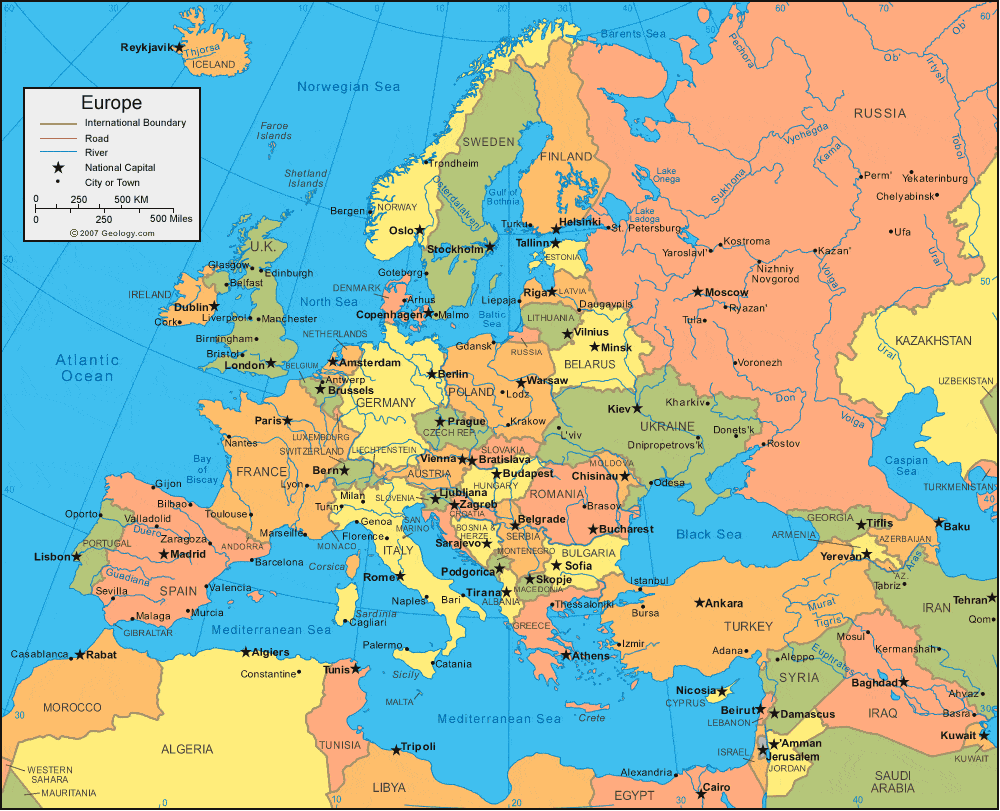
Political Boundaries: The European map showcases the continent’s intricate political landscape, with its 44 independent countries and numerous territories. The map clearly identifies the boundaries between nations, providing a visual representation of Europe’s political diversity. Studying the map can reveal the historical development of these boundaries, the impact of political events on their formation, and the ongoing challenges of maintaining stability and cooperation within the European Union.
-
Cultural Diversity: The map, while primarily focused on geographical and political features, offers glimpses into Europe’s cultural richness. Different colors or symbols may be used to highlight cultural regions or linguistic groups, providing a visual representation of the diverse languages, traditions, and artistic expressions that characterize Europe.
-
Population Distribution: The map often incorporates population data, indicating the density of population in different regions. This information provides insights into the patterns of urbanization, the concentration of people in specific areas, and the factors influencing population growth and migration.
The Enduring Relevance of the European Map
The European map, beyond its geographical and political significance, holds profound historical and cultural relevance. It serves as a visual record of the continent’s rich history, showcasing the rise and fall of empires, the impact of wars and revolutions, and the ongoing process of integration and cooperation.
For students, researchers, and policymakers, the European map is an indispensable tool for understanding the complex dynamics of the continent. It facilitates the analysis of historical events, the assessment of current trends, and the development of informed strategies for future cooperation.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about the European Map
Q: What are the main types of map projections used for depicting Europe?
A: The choice of map projection influences how the European map is presented, affecting the accuracy of shapes and distances. Common projections used for Europe include the Mercator projection, the Lambert Conformal Conic projection, and the Winkel Tripel projection. Each projection has its own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the intended purpose of the map.
Q: How does the European map reflect the continent’s historical evolution?
A: The European map reveals the continent’s historical evolution through the changing boundaries between countries, the emergence of new cities, and the development of infrastructure. It showcases the impact of historical events, such as the Roman Empire, the Renaissance, the Industrial Revolution, and the two World Wars, on the continent’s geography and political landscape.
Q: What are some of the challenges associated with mapping Europe?
A: Mapping Europe presents challenges due to its complex political landscape, the ongoing process of integration and cooperation within the European Union, and the need to balance accuracy with readability. The changing boundaries, the emergence of new political entities, and the need to represent diverse cultural and linguistic groups all contribute to the complexities of mapping the continent.
Tips for Understanding and Utilizing the European Map
-
Pay attention to scale: The scale of the map determines the level of detail that can be shown. Smaller-scale maps provide an overview of the continent, while larger-scale maps focus on specific regions or countries.
-
Consider the projection: Different map projections distort shapes and distances in different ways. Understanding the projection used for a particular map is crucial for interpreting the information it presents.
-
Analyze symbols and colors: Maps often use symbols and colors to represent different features, such as cities, mountains, rivers, and political boundaries. Understanding the legend or key is essential for interpreting the information on the map.
-
Explore historical maps: Comparing maps from different periods can provide valuable insights into the historical evolution of the European landscape, the changing boundaries between countries, and the impact of historical events on the continent’s geography.
Conclusion: The European Map as a Window into the Continent’s History and Future
The European map, as presented in the world atlas, is more than just a collection of lines and symbols. It is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s diverse geography, its intricate political landscape, and its rich history and culture. It serves as a visual record of the continent’s past, a guide to its present, and a source of insights into its future. By studying the European map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities and interconnectedness of the continent, its enduring influence on the world, and its ongoing journey towards a shared future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the World Atlas. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!