Navigating The Eastern Atlantic: A Comprehensive Exploration Of A Vital Ocean Basin
Navigating the Eastern Atlantic: A Comprehensive Exploration of a Vital Ocean Basin
Related Articles: Navigating the Eastern Atlantic: A Comprehensive Exploration of a Vital Ocean Basin
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Eastern Atlantic: A Comprehensive Exploration of a Vital Ocean Basin. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Eastern Atlantic: A Comprehensive Exploration of a Vital Ocean Basin
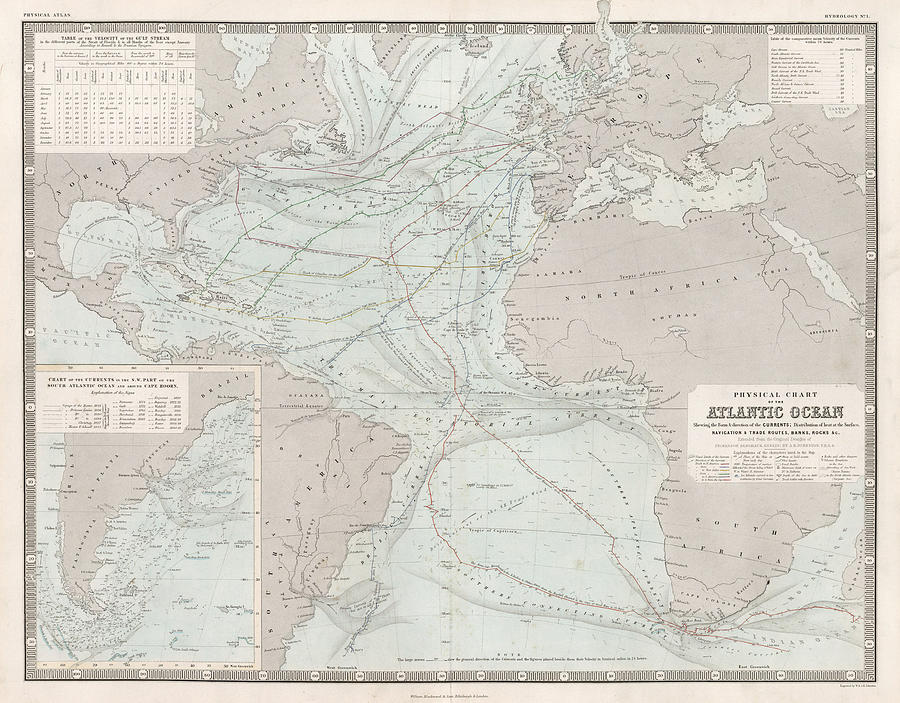
The Eastern Atlantic Ocean, a vast and dynamic expanse of water, plays a pivotal role in global climate regulation, marine biodiversity, and human civilization. This article delves into the intricate features of this oceanic region, exploring its geography, currents, ecosystems, and the profound impact it has on our planet.
A Geographical Overview
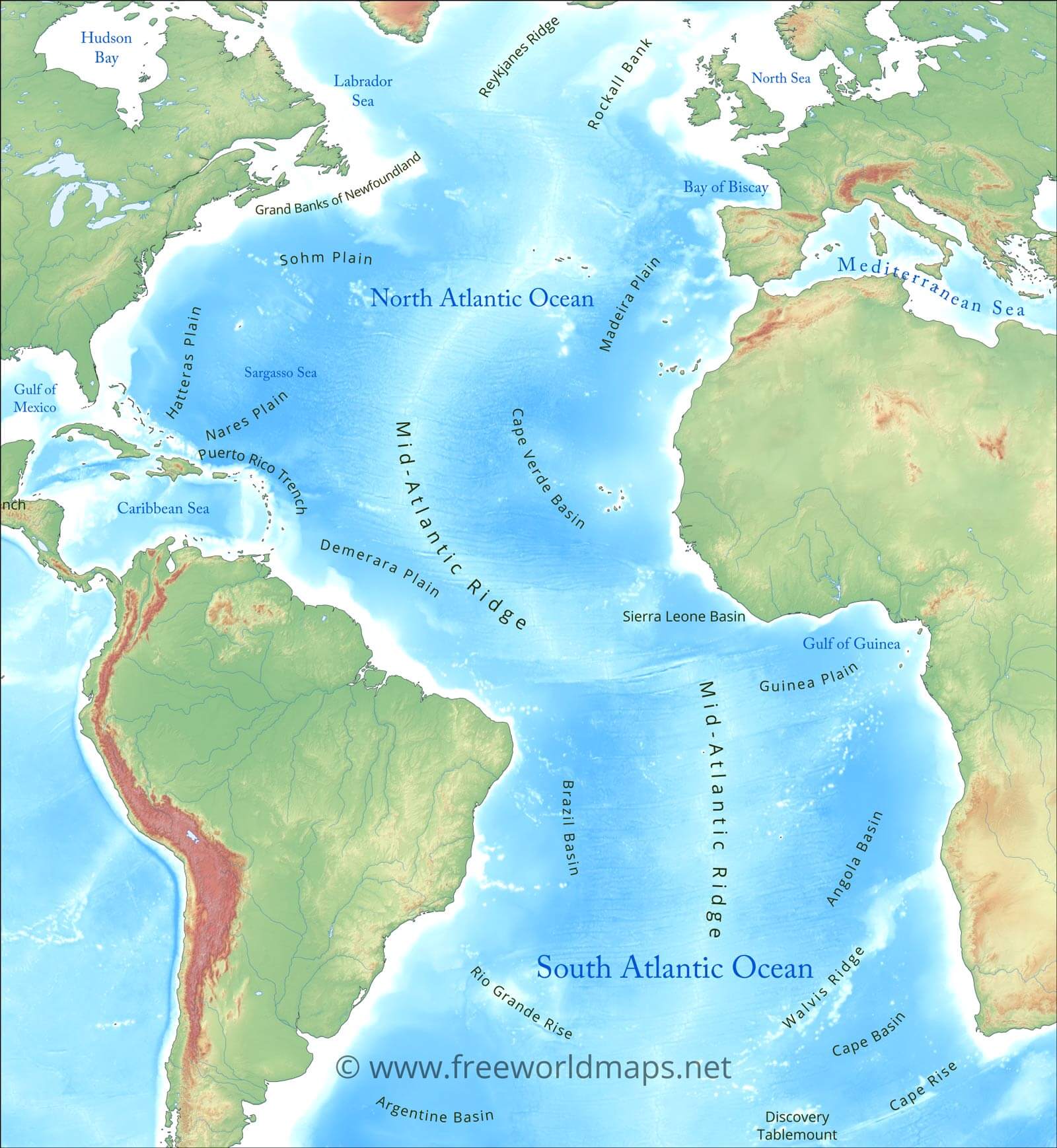
The Eastern Atlantic, as its name suggests, encompasses the eastern portion of the Atlantic Ocean, stretching from the western coast of Europe and Africa to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. This vast basin is characterized by a complex interplay of currents, winds, and geological formations, shaping its unique environmental characteristics.
Key Geographical Features:
- The Mid-Atlantic Ridge: A prominent underwater mountain range that runs down the center of the Atlantic, marking the boundary between the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates. This ridge is a site of intense volcanic activity and hydrothermal vents, supporting unique ecosystems.
- The Canary Current: A cold, northward-flowing current that originates near the Canary Islands. It brings cool, nutrient-rich waters to the western coast of Europe, supporting a rich marine ecosystem.
- The Gulf Stream: A warm, northward-flowing current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows up the eastern coast of North America before crossing the Atlantic towards Europe. It transports significant amounts of heat, influencing the climate of Western Europe.
- The Benguela Current: A cold, southward-flowing current that originates off the coast of Namibia. It brings nutrient-rich waters to the west coast of Africa, supporting a thriving ecosystem.
- The Guinea Current: A warm, westward-flowing current that originates in the Gulf of Guinea. It carries warm, saline waters towards the Caribbean Sea, influencing the climate of the region.
A Tapestry of Marine Life
The Eastern Atlantic is home to a remarkable diversity of marine life, ranging from microscopic plankton to majestic whales. The abundance of nutrients and varied habitats support a complex food web that sustains a multitude of species.
Key Marine Ecosystems:
- Coral Reefs: Found in the warmer regions of the Eastern Atlantic, these vibrant ecosystems provide shelter and food for a wide array of marine life.
- Seagrass Meadows: Extensive underwater grasslands that serve as important habitats for fish, invertebrates, and sea turtles.
- Kelp Forests: Dense underwater forests of kelp algae, providing essential habitat and food for a variety of marine species.
- Deep-Sea Vents: Unique ecosystems fueled by geothermal energy, supporting specialized organisms that thrive in extreme conditions.
The Importance of the Eastern Atlantic
The Eastern Atlantic plays a vital role in global climate regulation, marine biodiversity, and human civilization.
Climate Regulation:
- Heat Transport: Currents like the Gulf Stream transport significant amounts of heat from the tropics towards higher latitudes, influencing the climate of Western Europe and other regions.
- Carbon Sequestration: The ocean acts as a vast carbon sink, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and mitigating the effects of climate change.
Marine Biodiversity:
- Species Richness: The Eastern Atlantic is home to a vast array of marine species, many of which are endemic to this region.
- Ecosystem Services: Healthy marine ecosystems provide essential services, including food production, tourism, and coastal protection.
Human Civilization:
- Economic Activities: The Eastern Atlantic supports a range of economic activities, including fishing, shipping, tourism, and energy production.
- Cultural Heritage: The ocean has played a significant role in human history and culture, influencing trade routes, exploration, and artistic expression.
Challenges and Conservation
The Eastern Atlantic faces a number of challenges, including overfishing, pollution, climate change, and habitat degradation. These threats have significant consequences for marine ecosystems and the livelihoods of people who depend on the ocean.
Conservation Efforts:
- Marine Protected Areas: Establishing protected areas helps conserve marine biodiversity and protect important ecosystems.
- Sustainable Fishing Practices: Implementing sustainable fishing practices, such as quotas and fishing gear restrictions, helps prevent overfishing and maintain healthy fish populations.
- Pollution Reduction: Reducing pollution from land-based sources, such as industrial waste and agricultural runoff, is essential for protecting marine ecosystems.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Addressing climate change through reducing greenhouse gas emissions is crucial for mitigating the impacts on the Eastern Atlantic and its ecosystems.
FAQs about the Eastern Atlantic Ocean:
Q: What is the largest ocean in the world?
A: The Pacific Ocean is the largest ocean in the world.
Q: How deep is the Eastern Atlantic Ocean?
A: The average depth of the Eastern Atlantic Ocean is approximately 3,300 meters (10,800 feet). However, the deepest point in the Atlantic Ocean is the Puerto Rico Trench, which reaches a depth of 8,605 meters (28,232 feet).
Q: What are some of the major currents in the Eastern Atlantic?
A: The major currents in the Eastern Atlantic include the Canary Current, the Gulf Stream, the Benguela Current, and the Guinea Current.
Q: What are some of the major threats to the Eastern Atlantic Ocean?
A: The major threats to the Eastern Atlantic Ocean include overfishing, pollution, climate change, and habitat degradation.
Q: What can be done to protect the Eastern Atlantic Ocean?
A: Protecting the Eastern Atlantic Ocean requires a multi-pronged approach that includes establishing marine protected areas, implementing sustainable fishing practices, reducing pollution, and mitigating climate change.
Tips for Exploring the Eastern Atlantic Ocean:
- Visit a coastal area: Observe the unique marine life and coastal ecosystems.
- Take a boat trip: Experience the vastness and beauty of the ocean.
- Learn about ocean currents: Understand the forces that shape the Eastern Atlantic.
- Support sustainable fishing practices: Choose seafood from responsible sources.
- Reduce your environmental impact: Minimize plastic use and support organizations working to protect the ocean.
Conclusion:
The Eastern Atlantic Ocean is a vital part of our planet, supporting a rich tapestry of life and playing a crucial role in global climate regulation. Understanding its intricate features and the challenges it faces is essential for ensuring its continued health and the well-being of our planet. By promoting responsible stewardship and conservation efforts, we can safeguard this magnificent ocean for future generations.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Eastern Atlantic: A Comprehensive Exploration of a Vital Ocean Basin. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!