Navigating The Complexities Of Cost: A Comprehensive Guide To Material Allocation Planning (MAP) In SAP
Navigating the Complexities of Cost: A Comprehensive Guide to Material Allocation Planning (MAP) in SAP
Related Articles: Navigating the Complexities of Cost: A Comprehensive Guide to Material Allocation Planning (MAP) in SAP
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complexities of Cost: A Comprehensive Guide to Material Allocation Planning (MAP) in SAP. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Complexities of Cost: A Comprehensive Guide to Material Allocation Planning (MAP) in SAP
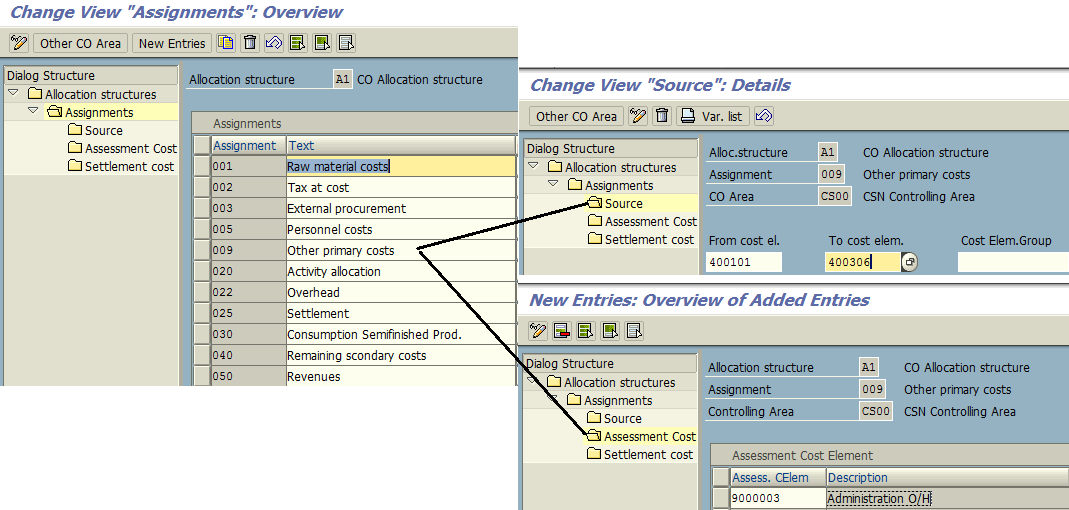
Material Allocation Planning (MAP) in SAP is a crucial element in managing and optimizing costs within an organization. This intricate process involves the precise allocation of material costs to various cost objects, such as products, projects, or cost centers. By accurately distributing these costs, businesses gain valuable insights into their profitability, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions regarding pricing, production, and resource allocation.
Understanding the Importance of MAP
The significance of MAP in SAP extends beyond mere cost accounting. It acts as a foundational pillar for a wide range of critical business functions:
- Accurate Costing: MAP provides a reliable foundation for calculating the true cost of goods and services. This information is essential for setting competitive prices, evaluating product profitability, and making informed decisions regarding pricing strategies.
- Profitability Analysis: By allocating material costs to specific products or projects, MAP facilitates in-depth profitability analysis. Businesses can identify which products or projects are most profitable and allocate resources accordingly.
- Inventory Management: MAP plays a crucial role in inventory management by providing insights into material consumption patterns. This information aids in optimizing inventory levels, reducing storage costs, and minimizing waste.
- Production Planning: Accurate material cost allocation helps in developing efficient production plans. By understanding the cost of materials used in different production processes, businesses can identify areas for cost optimization and streamline production activities.
- Financial Reporting: MAP is essential for accurate financial reporting. By providing a clear picture of material cost allocation, it ensures that financial statements accurately reflect the organization’s financial performance.
The Mechanics of MAP in SAP
MAP in SAP involves a series of steps, each contributing to the overall accuracy and effectiveness of the process:
- Material Cost Determination: The process begins with determining the actual cost of materials. This involves considering factors like purchase price, freight costs, duties, and taxes.
- Cost Object Identification: The next step involves identifying the cost objects to which these costs will be allocated. This could include products, projects, cost centers, or other relevant entities.
- Allocation Rules: Defining allocation rules is crucial for distributing material costs to the identified cost objects. These rules can be based on various factors, such as material consumption, production volume, or sales revenue.
- Cost Allocation: Once the allocation rules are established, the material costs are allocated to the respective cost objects. This involves applying the defined rules to distribute the costs proportionally.
- Cost Analysis: The final step involves analyzing the allocated costs to gain insights into profitability, identify cost drivers, and make informed decisions for optimization.
Key Features of MAP in SAP
SAP offers a comprehensive set of features to support MAP, enabling businesses to streamline the process and achieve greater accuracy:
- Material Ledger: The Material Ledger in SAP provides a detailed tracking of material costs, including purchase price variances, inventory valuation, and consumption patterns. This data is essential for accurate cost allocation.
- Cost Object Planning: SAP offers tools for planning and managing cost objects, including defining cost object hierarchies, assigning cost centers, and tracking cost object-specific data.
- Allocation Rules: SAP provides a flexible framework for defining allocation rules, allowing businesses to tailor the process to their specific needs. Users can configure rules based on various factors, including material type, production process, or sales region.
- Cost Analysis Reports: SAP provides a range of reports and dashboards for analyzing allocated costs. These reports offer insights into profitability, cost drivers, and areas for improvement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about MAP in SAP
1. What are the benefits of implementing MAP in SAP?
Implementing MAP in SAP offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Cost Accuracy: MAP provides a more accurate picture of material costs, leading to better decision-making regarding pricing, production, and resource allocation.
- Enhanced Profitability Analysis: MAP enables businesses to analyze profitability at a granular level, identifying profitable products and projects and areas for improvement.
- Optimized Inventory Management: MAP provides insights into material consumption patterns, helping businesses optimize inventory levels and reduce storage costs.
- Streamlined Production Planning: Accurate material cost allocation supports efficient production planning, optimizing resource utilization and reducing waste.
2. What are some common challenges associated with MAP in SAP?
Implementing and managing MAP in SAP can present challenges, including:
- Data Accuracy: Maintaining accurate material cost data is crucial for MAP. Inaccurate data can lead to distorted cost allocation and misleading results.
- Complexity of Allocation Rules: Defining and managing allocation rules can be complex, requiring careful consideration of business requirements and data availability.
- System Integration: MAP requires seamless integration with other SAP modules, such as Materials Management (MM), Production Planning (PP), and Financial Accounting (FI).
- User Training: Effective MAP implementation requires adequate training for users to understand the process and utilize the available tools.
3. How can businesses ensure the success of MAP implementation in SAP?
To ensure successful MAP implementation in SAP, businesses should consider the following:
- Clear Objectives: Defining clear objectives for MAP implementation is essential for aligning the process with business goals.
- Data Quality: Prioritize data accuracy and integrity, ensuring that material cost data is reliable and up-to-date.
- User Involvement: Involve key users in the design and implementation process, ensuring that the system meets their needs and expectations.
- Testing and Validation: Thoroughly test and validate the implemented MAP process to ensure accuracy and effectiveness.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Regularly monitor the MAP process, identifying areas for improvement and making necessary adjustments.
Tips for Effective MAP Implementation
- Start Small: Begin with a pilot implementation for a specific product or project, gradually expanding the scope to encompass other areas.
- Document Processes: Document all MAP processes, including allocation rules, cost object definitions, and data sources, for clarity and consistency.
- Automate Processes: Utilize SAP’s automation capabilities to streamline repetitive tasks, reducing manual effort and improving efficiency.
- Collaborate with Stakeholders: Foster collaboration between Finance, Production, and Procurement teams to ensure alignment and data consistency.
- Continuously Improve: Regularly review and refine the MAP process, identifying areas for optimization and incorporating new technologies and best practices.
Conclusion
MAP in SAP is a powerful tool for managing and optimizing costs within an organization. By accurately allocating material costs, businesses can gain valuable insights into their profitability, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions regarding pricing, production, and resource allocation. Implementing MAP effectively requires careful planning, data accuracy, user involvement, and ongoing monitoring. By embracing these principles, businesses can leverage the power of MAP in SAP to achieve greater cost efficiency and drive sustainable growth.


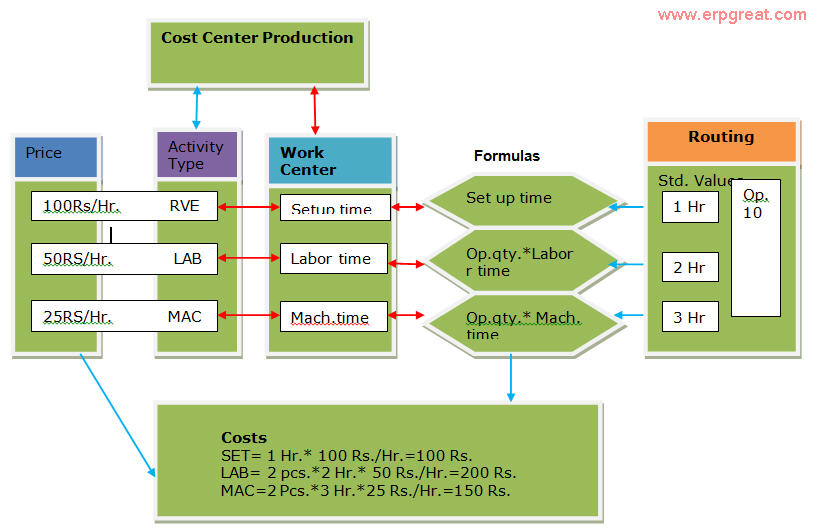


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complexities of Cost: A Comprehensive Guide to Material Allocation Planning (MAP) in SAP. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!