Mapping The Giants: A Comprehensive Look At Map Atlas Mountains
Mapping the Giants: A Comprehensive Look at Map Atlas Mountains
Related Articles: Mapping the Giants: A Comprehensive Look at Map Atlas Mountains
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Giants: A Comprehensive Look at Map Atlas Mountains. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Giants: A Comprehensive Look at Map Atlas Mountains
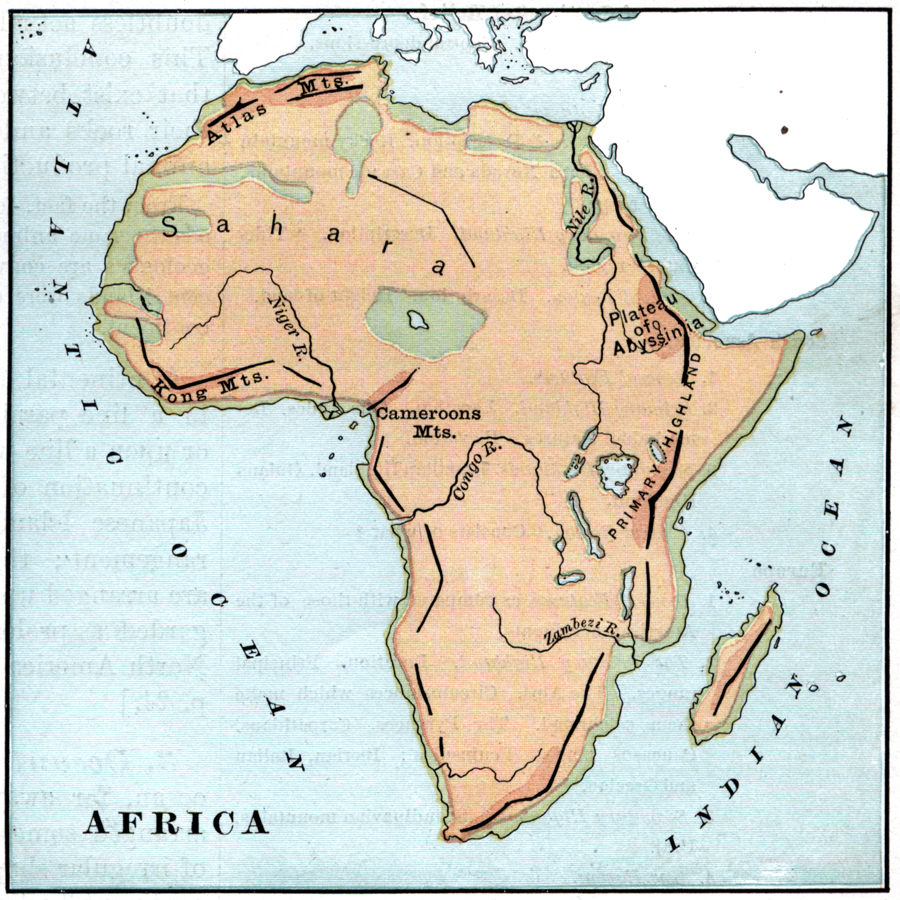
Mountains, those majestic peaks that pierce the sky, have captivated human imagination for millennia. They are not just breathtaking landscapes but also crucial components of our planet’s ecosystems, influencing weather patterns, water cycles, and biodiversity. Understanding these towering structures requires a robust tool: the map atlas.
A map atlas dedicated to mountains is more than a collection of maps; it’s a comprehensive resource that unveils the intricate relationship between these geological formations and the world around them. It serves as a window into the complex interplay of altitude, topography, climate, and human activity, providing insights that are crucial for various fields, from environmental science and geography to tourism and disaster management.
The Importance of a Dedicated Mountain Map Atlas:
The sheer diversity of mountains across the globe necessitates a dedicated atlas to effectively visualize and analyze their unique characteristics. Traditional atlases often depict mountains as mere lines on a map, failing to capture their three-dimensional complexity and the diverse ecosystems they harbor. A mountain map atlas, however, goes beyond surface level representation, offering:
- Detailed Topography: High-resolution topographic maps provide a precise representation of mountain ranges, including elevation contours, slopes, and valleys. This allows for a nuanced understanding of the terrain, crucial for planning expeditions, studying ecological patterns, and assessing potential hazards.
- Climate and Weather Patterns: Mountains significantly influence regional climates, creating microclimates within their slopes. A dedicated atlas can depict the unique climatic zones within a mountain range, including precipitation patterns, temperature variations, and wind direction. This information is vital for understanding the distribution of flora and fauna, predicting natural disasters, and planning sustainable development.
- Biodiversity and Ecosystems: Mountains are often biodiversity hotspots, harboring unique species adapted to their specific environment. A map atlas can highlight the distribution of different ecosystems, from alpine meadows to glacial valleys, allowing researchers to track species diversity, identify conservation priorities, and study the impact of climate change on fragile mountain ecosystems.
- Human Interaction: Mountains have played a crucial role in human history, shaping cultures, influencing migration patterns, and providing resources. A dedicated atlas can illustrate the relationship between human settlements and mountain ranges, including the location of ancient trails, agricultural practices, and the impact of infrastructure development on the surrounding environment.
- Natural Hazards and Disaster Management: Mountains are often associated with natural hazards like landslides, avalanches, and earthquakes. A map atlas can depict areas prone to these hazards, allowing for better risk assessment, early warning systems, and disaster preparedness. This information is critical for ensuring the safety of local communities and managing the potential consequences of natural disasters.
Beyond Maps: A Multifaceted Resource:
A truly comprehensive mountain map atlas goes beyond static maps, incorporating various features to enhance its value:
- Satellite Imagery: High-resolution satellite images provide a detailed view of mountain landscapes, revealing vegetation patterns, glacial formations, and human settlements. This visual data complements the topographic maps, offering a comprehensive perspective on the terrain.
- Geospatial Data: The atlas can incorporate geospatial data layers, such as soil type, water resources, and infrastructure, to provide a multi-layered understanding of the mountain environment. This allows for more detailed analysis of specific areas and facilitates the development of targeted conservation and development strategies.
- Historical Data: Historical maps, photographs, and narratives can provide insights into the changing landscape of mountains over time, revealing the impact of human activity, climate change, and natural disasters. This historical perspective is crucial for understanding the long-term trends in mountain environments and developing sustainable management practices.
- Interactive Features: Modern atlases can incorporate interactive features, allowing users to zoom in on specific areas, access detailed information about different locations, and explore the data through various visualizations. This user-friendly interface makes the atlas accessible to a wider audience, promoting understanding and engagement with mountain environments.
A Powerful Tool for Research and Education:
The benefits of a comprehensive mountain map atlas extend beyond scientific research. It serves as a powerful tool for education, raising awareness about the importance of these ecosystems and inspiring action for their conservation.
- Enhancing Geographical Literacy: The atlas can be used as an educational tool to teach students about the physical processes that shape mountains, their role in the global ecosystem, and the diverse cultures that have developed around them. This fosters a deeper understanding of geography and its relevance to our lives.
- Promoting Environmental Awareness: By highlighting the interconnectedness of mountain ecosystems and their vulnerability to human activities and climate change, the atlas can inspire action for conservation and sustainable development. This promotes a sense of responsibility towards protecting these fragile environments for future generations.
- Facilitating Public Engagement: The atlas can serve as a platform for public engagement, enabling communities to share their knowledge and experiences of mountain environments. This participatory approach fosters collaboration and strengthens the connection between people and the natural world.
FAQs about Mountain Map Atlases:
Q: What types of maps are included in a mountain map atlas?
A: A comprehensive mountain map atlas incorporates a variety of maps, including topographic maps, satellite imagery, thematic maps depicting climate, vegetation, soil types, and human settlements.
Q: What are the benefits of using a mountain map atlas for research?
A: A mountain map atlas provides researchers with a detailed understanding of the terrain, climate, biodiversity, and human interaction within mountain environments. This information is vital for studying ecological processes, assessing environmental impacts, and developing conservation strategies.
Q: How can a mountain map atlas be used for education?
A: A mountain map atlas can be used to teach students about the physical geography of mountains, their role in the global ecosystem, and the impact of human activity on these environments. It fosters geographical literacy and promotes environmental awareness.
Q: What are some examples of mountain map atlases?
A: There are numerous mountain map atlases available, including the "Atlas of the World’s Mountains" by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), the "National Geographic Atlas of the World," and various regional atlases focusing on specific mountain ranges.
Tips for Using a Mountain Map Atlas:
- Explore the different map layers: Analyze the different maps and data layers to gain a comprehensive understanding of the mountain environment.
- Focus on specific areas of interest: Use the atlas to explore specific mountain ranges or regions, focusing on the characteristics that are most relevant to your research or interests.
- Combine data from different sources: Integrate data from the atlas with other sources, such as scientific publications, field observations, and local knowledge, to gain a more holistic understanding.
- Use the atlas for planning and decision-making: Utilize the information provided by the atlas to plan expeditions, assess environmental impacts, and develop sustainable management strategies for mountain ecosystems.
Conclusion:
A mountain map atlas is not just a collection of maps; it’s a powerful tool that unlocks a deeper understanding of these majestic geological formations. It provides a comprehensive view of their topography, climate, biodiversity, human interaction, and the challenges they face. By leveraging the insights offered by a dedicated mountain map atlas, we can better appreciate the intricate beauty and vital role of these ecosystems, fostering responsible stewardship and ensuring their preservation for generations to come.


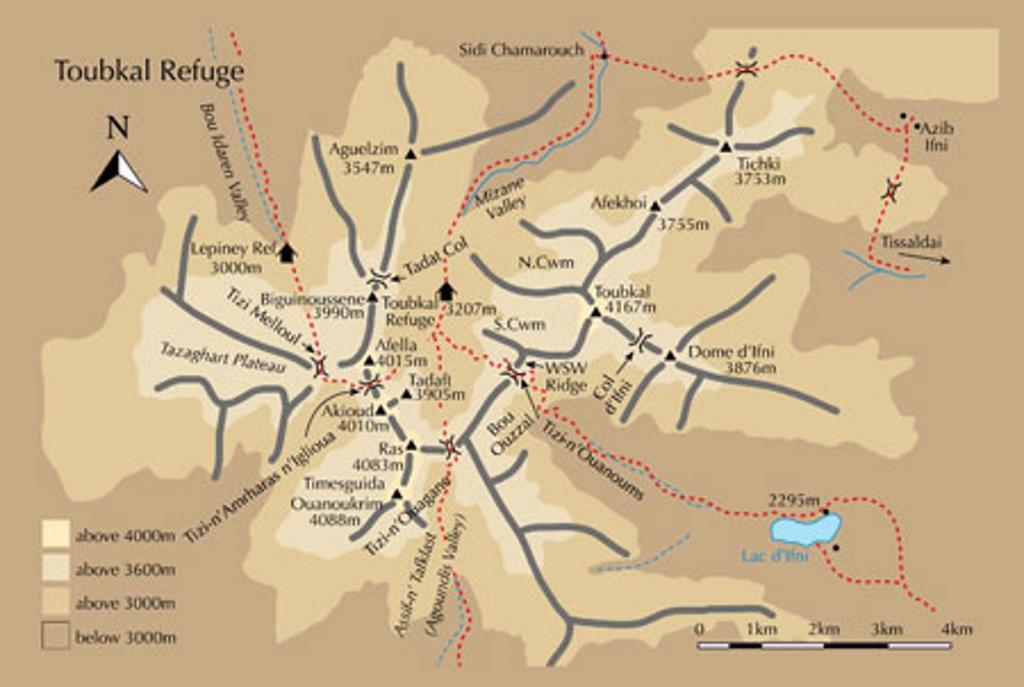




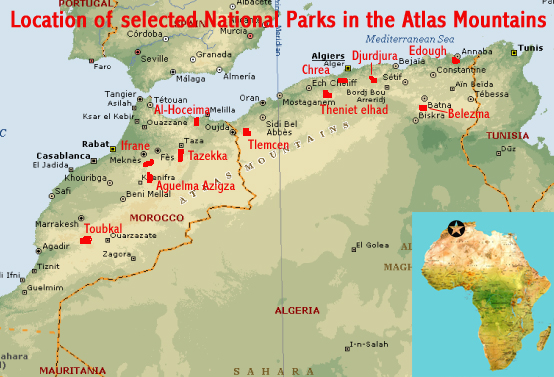
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Giants: A Comprehensive Look at Map Atlas Mountains. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!