Mapping Israel: A Geographic Perspective In The World Atlas
Mapping Israel: A Geographic Perspective in the World Atlas
Related Articles: Mapping Israel: A Geographic Perspective in the World Atlas
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping Israel: A Geographic Perspective in the World Atlas. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Israel: A Geographic Perspective in the World Atlas
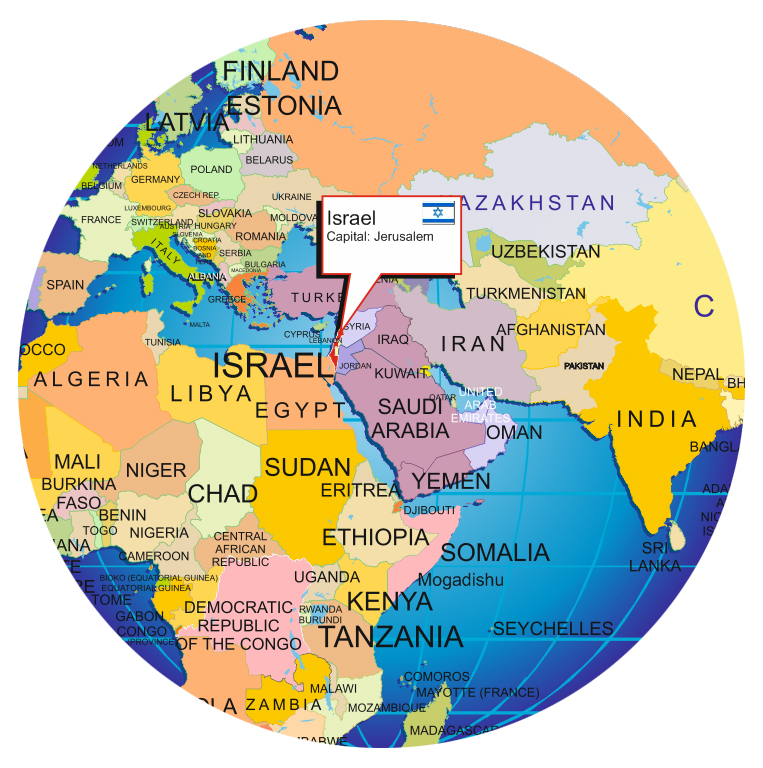
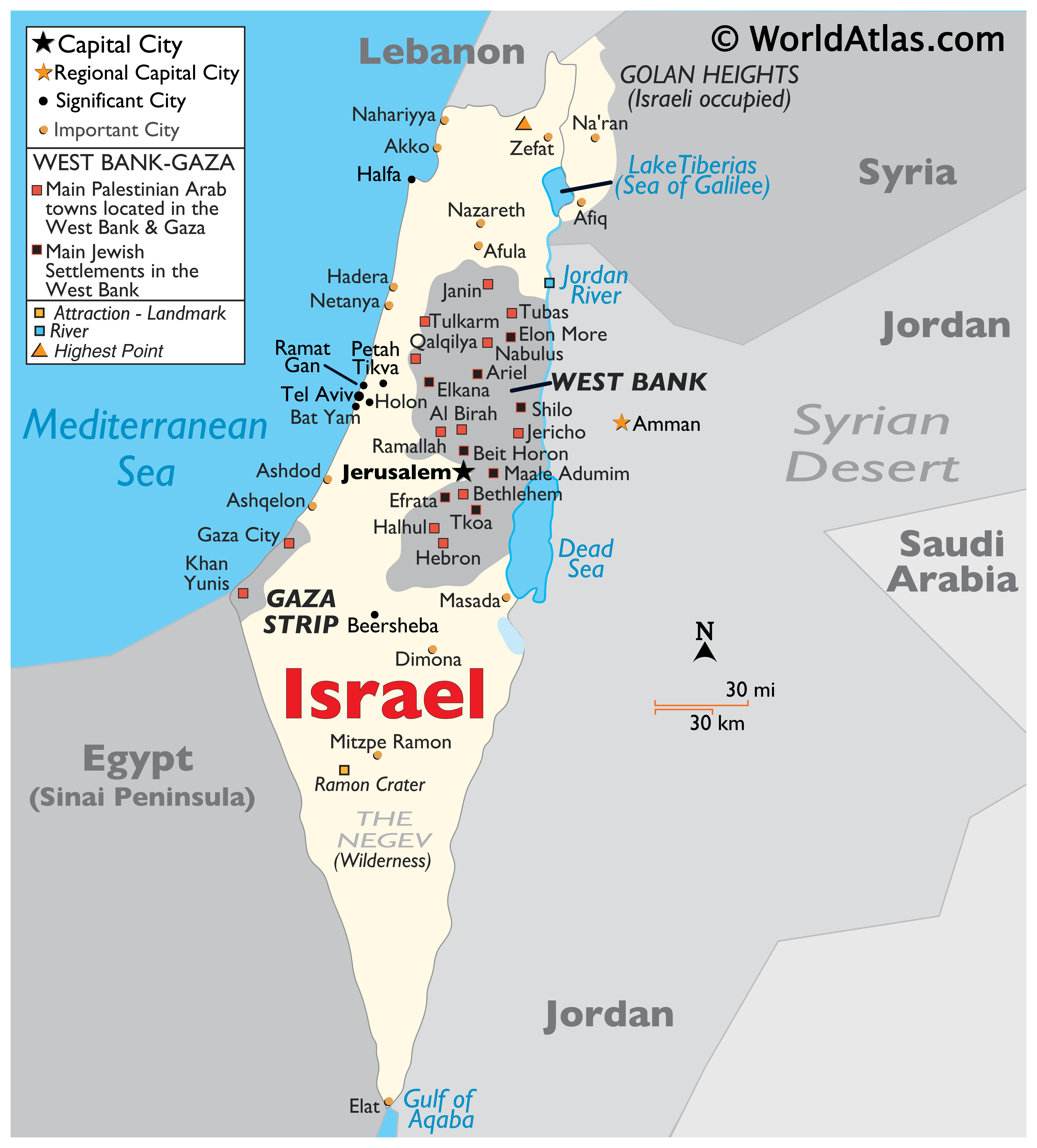
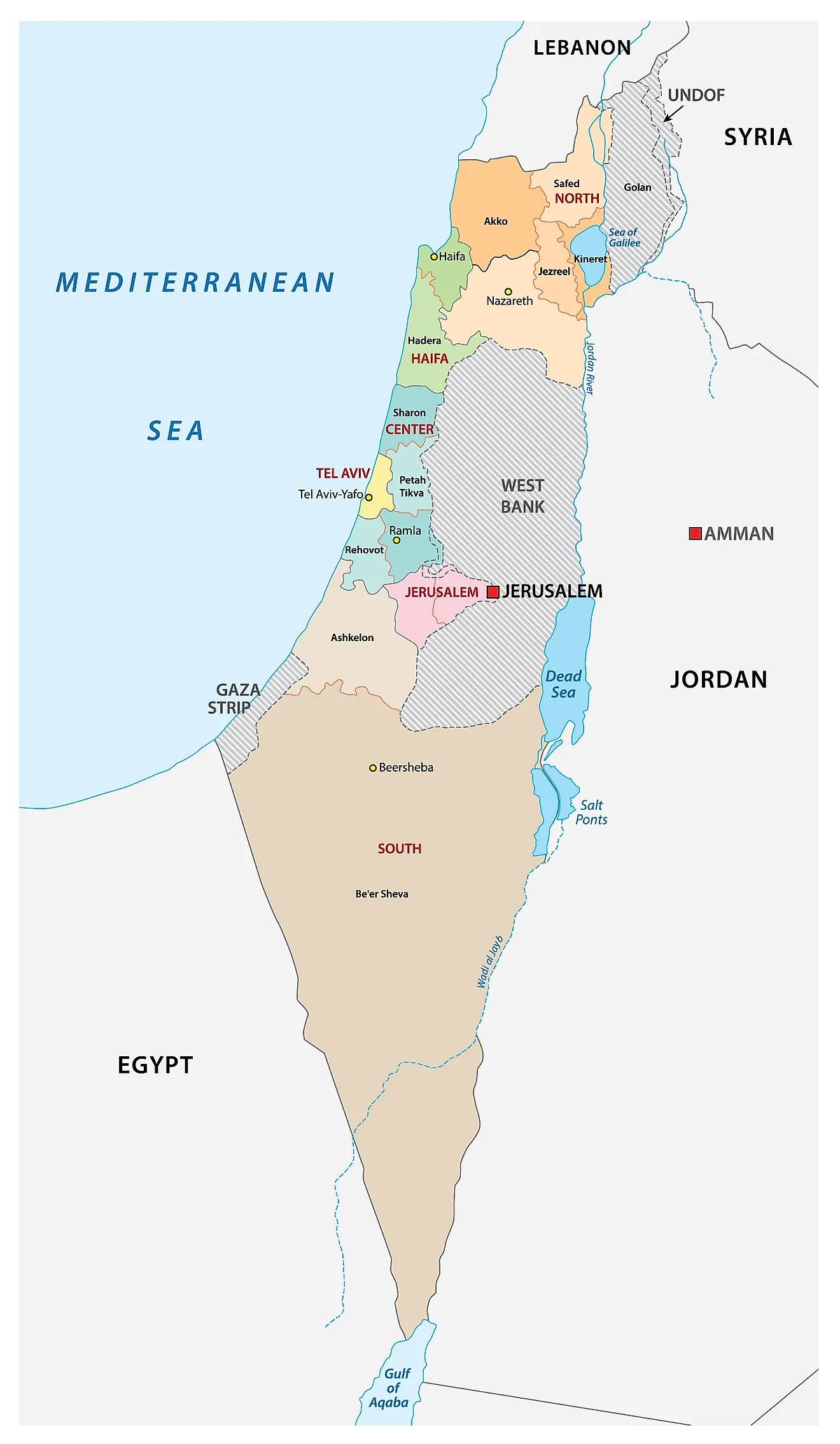
The inclusion of Israel in the world atlas is a testament to its geopolitical significance and the complexities surrounding its borders and territorial claims. Studying Israel’s geographical representation on a world map provides insights into its historical development, political landscape, and contemporary challenges. This article explores the various aspects of mapping Israel in a world atlas, analyzing its historical evolution, territorial disputes, and the impact of cartographic representations on understanding the region.
Historical Context: From Ancient Kingdoms to Modern State
The land we know as Israel has been inhabited for millennia, bearing witness to the rise and fall of ancient empires, the development of religions, and the emergence of diverse cultures. The map of Israel in a world atlas reflects this rich history, highlighting its location at the crossroads of continents and its role as a cultural bridge between the East and West.
Early Maps: Ancient maps, often depicted on clay tablets or papyrus scrolls, show the region as part of larger empires like the Roman Empire or the Ottoman Empire. These maps provide valuable information about the historical borders and political affiliations of the land, showcasing its strategic importance throughout history.
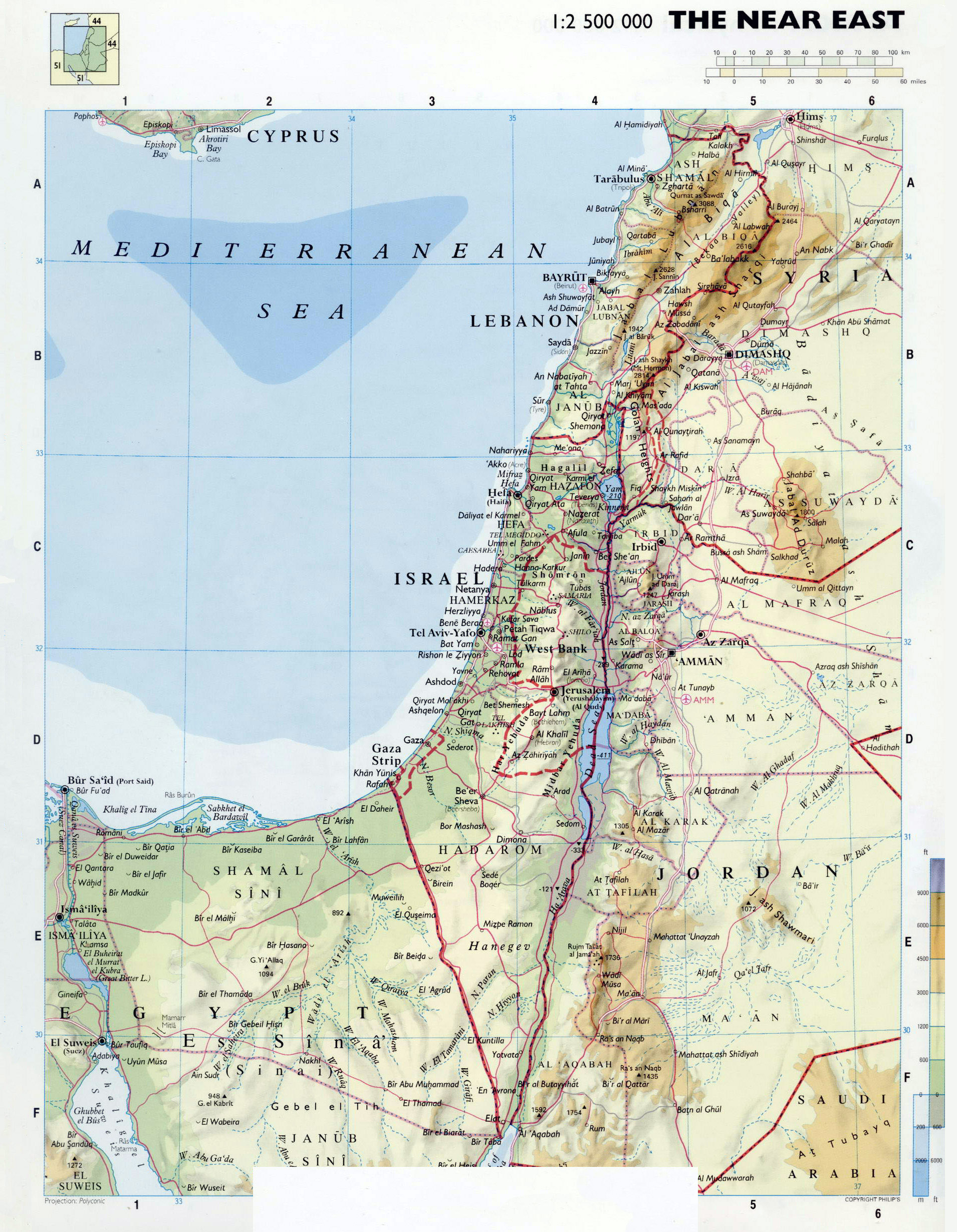
Modern Mapping: The modern map of Israel emerged after the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948. The borders of modern Israel, however, remain a subject of intense debate and conflict, with the Palestinian territories and the Golan Heights forming contentious areas.
Territorial Disputes and the Palestinian Territories
The map of Israel in a world atlas often depicts the West Bank and Gaza Strip as separate territories from Israel, reflecting their current political status. These territories, claimed by the Palestinians for their future state, remain a major point of contention in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
The Golan Heights: A Contested Territory
The Golan Heights, a plateau region bordering Syria, was captured by Israel during the Six-Day War in 1967. Israel annexed the Golan Heights in 1981, a move not recognized by the international community. The map of Israel in a world atlas often indicates the Golan Heights as disputed territory, acknowledging its contested status.
Cartographic Representations and Political Bias
The depiction of Israel in world atlases is not without its biases. Different atlases may choose to emphasize certain aspects of the region, potentially reflecting political or ideological leanings. For instance, some maps may highlight the Palestinian territories with greater emphasis, while others may focus on the Israeli perspective, potentially minimizing the Palestinian presence.
The Importance of Critical Analysis
It is crucial to analyze the maps of Israel in world atlases critically, considering the potential biases and the historical context. Understanding the cartographic choices made by mapmakers and the underlying political agendas can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the region’s complexities.
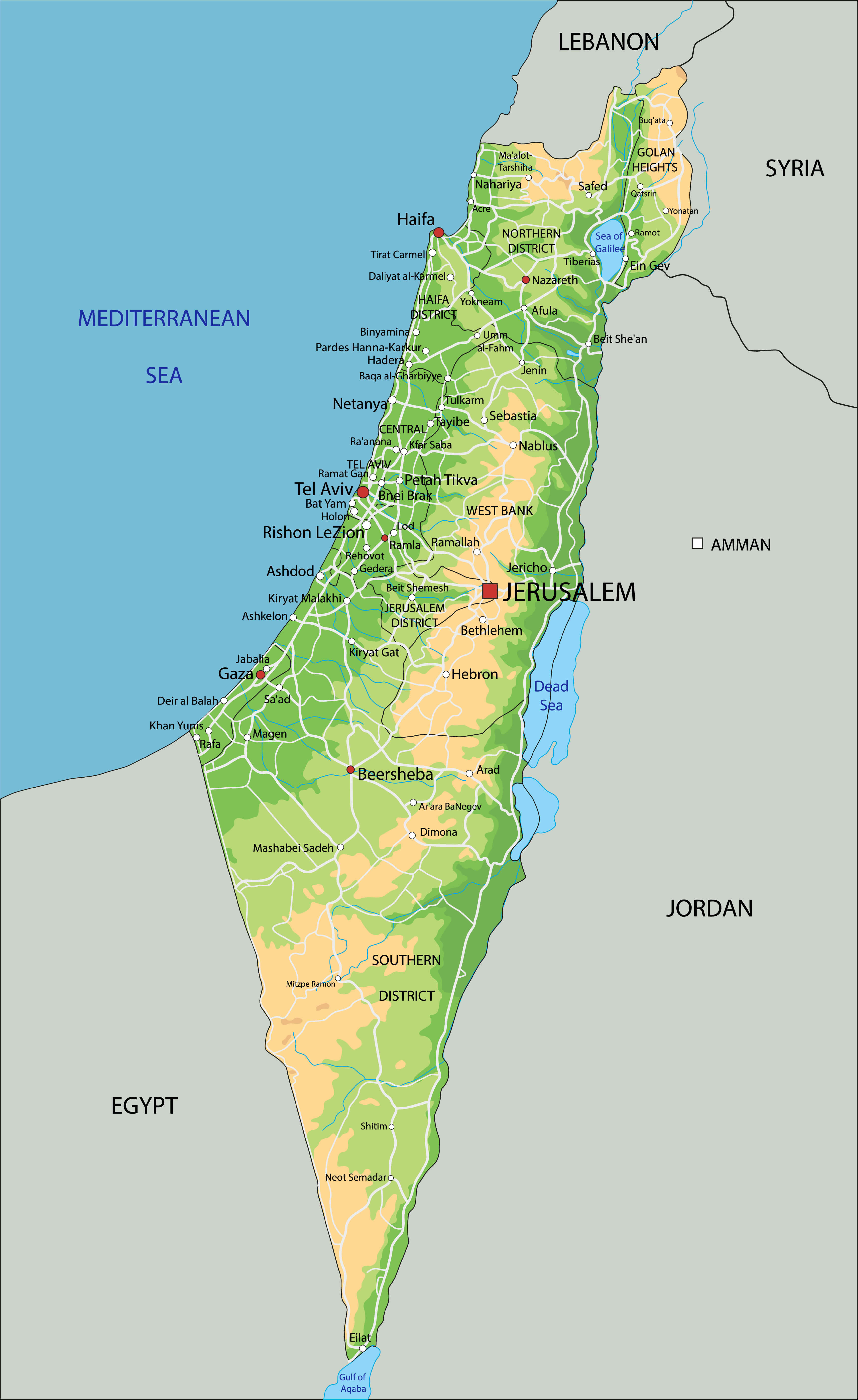
Beyond Borders: Exploring the Geography of Israel
While the borders of Israel are a focal point of debate, understanding the geography of the region extends beyond political boundaries. The map of Israel in a world atlas can reveal a diverse landscape, including:
- The Mediterranean Coast: Israel boasts a beautiful Mediterranean coastline, offering stunning beaches, bustling port cities, and a thriving tourism industry.
- The Negev Desert: The Negev Desert, covering a significant portion of southern Israel, presents a unique arid landscape, home to diverse flora and fauna and a growing agricultural sector.
- The Galilee Region: Located in northern Israel, the Galilee region is known for its rolling hills, fertile valleys, and ancient historical sites, including the Sea of Galilee.
- The Jordan River Valley: This fertile valley, running along the eastern border of Israel, plays a crucial role in agriculture and water resources.
Benefits of Studying the Map of Israel
Studying the map of Israel in a world atlas offers several benefits:
- Historical Perspective: The map provides a visual representation of the region’s historical development, highlighting its role in ancient civilizations and its significance in the modern world.
- Geopolitical Understanding: The map helps understand the complex geopolitical landscape of the region, including the territorial disputes and the ongoing conflict.
- Cultural Appreciation: The map reveals the diversity of cultures and religions within the region, showcasing its rich cultural heritage.
- Environmental Awareness: The map illustrates the unique geographical features of Israel, including its coastline, deserts, and fertile valleys, raising awareness about the environmental challenges and opportunities.
FAQs about the Map of Israel in a World Atlas
Q: Why is the map of Israel so controversial?
A: The map of Israel is controversial due to the ongoing territorial disputes and the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The boundaries of Israel, particularly the West Bank and the Golan Heights, are contested territories, leading to differing interpretations and representations on maps.
Q: What are the different perspectives on the map of Israel?
A: Different perspectives on the map of Israel arise from the conflicting claims of Israelis and Palestinians. Israeli maps often depict the West Bank and Gaza Strip as part of Israel, while Palestinian maps emphasize their separate status as future independent states.
Q: How can I understand the map of Israel objectively?
A: To understand the map of Israel objectively, it is crucial to consider multiple perspectives, analyze historical context, and recognize the potential biases in cartographic representations. Engaging with different sources and critically evaluating information is essential.
Tips for Studying the Map of Israel
- Consult multiple atlases: Compare different atlases to observe variations in the depiction of Israel and its borders.
- Research historical maps: Explore historical maps to gain insights into the region’s evolving political boundaries and territorial claims.
- Read scholarly articles: Engage with academic research on the cartography of Israel and its political implications.
- Consider the context: Remember that maps are not neutral representations but reflect the perspectives and biases of their creators.
Conclusion: A Complex and Dynamic Landscape
The map of Israel in a world atlas serves as a visual representation of a complex and dynamic landscape. It encapsulates the region’s rich history, ongoing conflicts, and the diverse cultural and geographical features. By studying the map critically and considering multiple perspectives, we can gain a more nuanced understanding of the complexities of the region and the challenges facing its people. Understanding the map of Israel is not merely about geographical knowledge but also about appreciating the intricate web of history, politics, and culture that shapes the region.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Israel: A Geographic Perspective in the World Atlas. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!