Mapping Blood Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Utilizing BP Maps
Mapping Blood Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing BP Maps
Related Articles: Mapping Blood Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing BP Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping Blood Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing BP Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Mapping Blood Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing BP Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Mapping Blood Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing BP Maps
- 3.1 What is BP Mapping?
- 3.2 Types of BP Mapping
- 3.3 Benefits of BP Mapping
- 3.4 Applications of BP Mapping
- 3.5 Interpreting BP Maps
- 3.6 FAQs on BP Mapping
- 3.7 Tips for Successful BP Mapping
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Mapping Blood Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing BP Maps

Blood pressure (BP) is a fundamental indicator of cardiovascular health. Its consistent monitoring and management are crucial for preventing and controlling hypertension, a significant risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and other health issues. While traditional methods of BP measurement provide snapshots in time, mapping blood pressure offers a more comprehensive and insightful approach. This method involves tracking BP readings over extended periods, creating a visual representation of fluctuations and trends. This article delves into the intricacies of BP mapping, exploring its significance, benefits, and applications.
What is BP Mapping?
BP mapping encompasses the systematic collection and analysis of blood pressure readings taken at various times throughout the day, week, or even month. Unlike single-point measurements, BP mapping captures the dynamic nature of BP, revealing patterns and variations that might otherwise go unnoticed. This information is then visualized in the form of a map, graphically depicting BP fluctuations across time.
Types of BP Mapping
The primary types of BP mapping include:
- Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM): This method utilizes a portable device worn by the individual, typically on the upper arm, to automatically record BP readings at pre-defined intervals throughout the day and night. ABPM provides a comprehensive overview of BP changes during daily activities, sleep, and rest.
- Home Blood Pressure Monitoring (HBPM): HBPM involves individuals using a home blood pressure monitor to measure their BP at specific times, usually in the morning and evening. While less comprehensive than ABPM, HBPM offers valuable insights into BP trends and allows for self-management.
- Office Blood Pressure Monitoring: This traditional method involves measuring BP in a healthcare setting, typically during a doctor’s visit. While convenient, it provides only a single snapshot of BP and may not accurately reflect the individual’s overall BP profile.
Benefits of BP Mapping
The advantages of BP mapping extend beyond simply tracking BP readings. This method offers a multifaceted approach to understanding and managing BP, bringing numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy: BP mapping helps identify individuals with masked hypertension (high BP only during specific periods) or white-coat hypertension (elevated BP solely in a clinical setting).
- Personalized Treatment Strategies: By revealing individual BP patterns, mapping enables healthcare professionals to tailor treatment plans, including medication adjustments and lifestyle modifications, more effectively.
- Improved Patient Engagement: BP mapping empowers individuals to take ownership of their health by providing them with a clear understanding of their BP fluctuations. This increased awareness can encourage adherence to treatment plans and healthy lifestyle choices.
- Early Detection of Complications: By monitoring BP trends, mapping can identify potential complications like nocturnal hypertension (high BP during sleep) or dipping patterns (normal BP during sleep), allowing for timely interventions.
- Risk Stratification: BP maps can assist in assessing individual risk for cardiovascular events based on the severity and duration of high BP readings.
- Monitoring Treatment Effectiveness: Mapping allows for continuous monitoring of treatment efficacy, enabling adjustments to ensure optimal BP control.
Applications of BP Mapping
BP mapping finds applications across diverse healthcare settings and populations:
- Hypertension Management: Mapping is a valuable tool for diagnosing, monitoring, and managing hypertension, optimizing treatment plans and improving patient outcomes.
- Pre-hypertension Screening: Mapping can identify individuals at risk for developing hypertension, allowing for early interventions and preventative measures.
- Cardiovascular Disease Prevention: By identifying individuals with high BP fluctuations and nocturnal hypertension, mapping contributes to reducing the risk of cardiovascular events.
- Pregnancy Management: Mapping is particularly useful in managing BP during pregnancy, as gestational hypertension can pose significant risks to both mother and baby.
- Research Studies: BP mapping plays a crucial role in clinical research, providing valuable data for understanding the dynamics of BP and evaluating the efficacy of new treatments.
Interpreting BP Maps
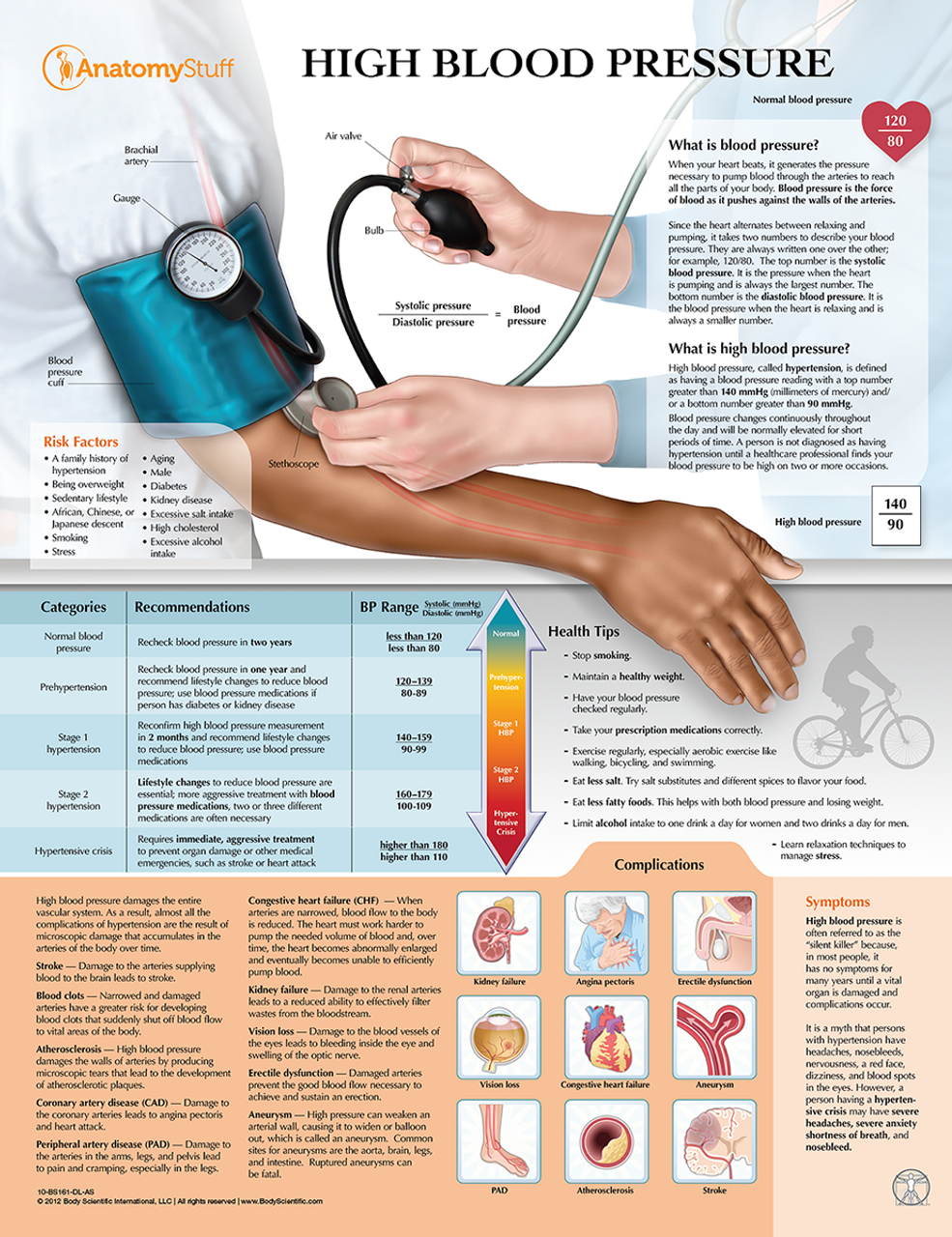
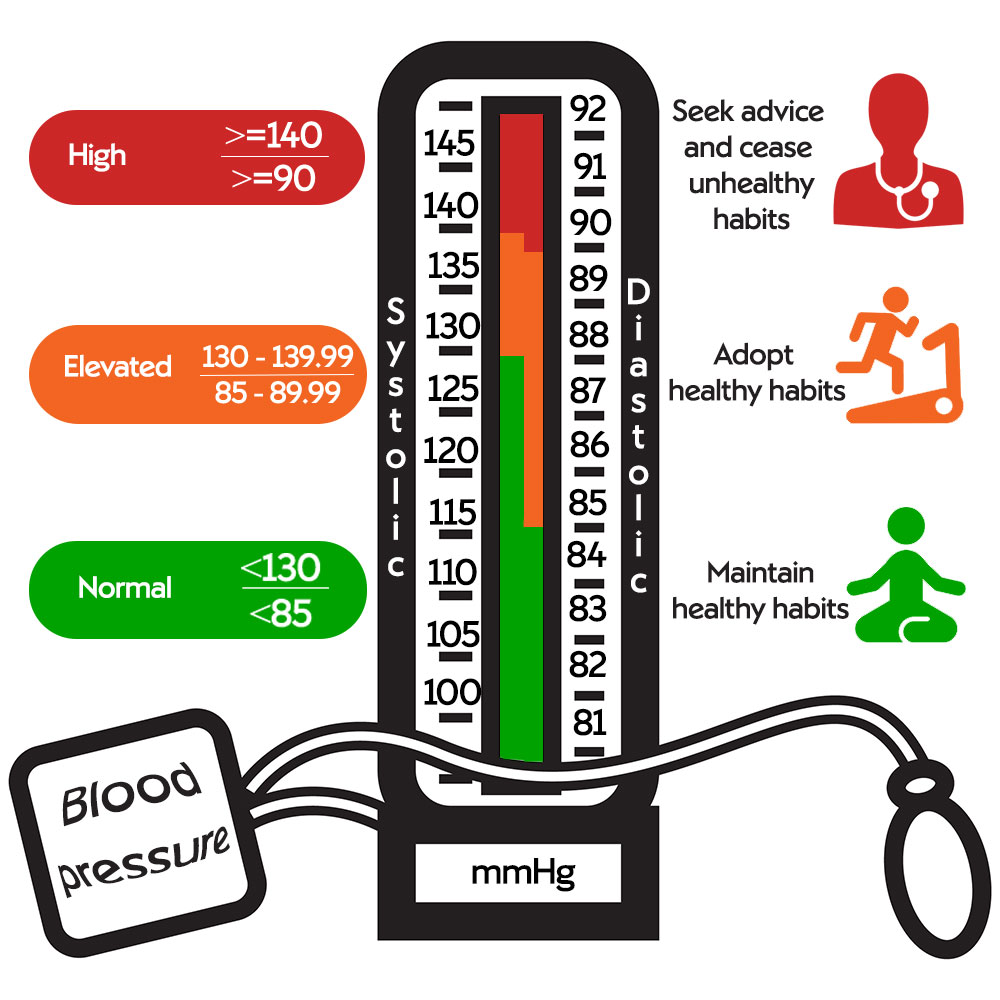
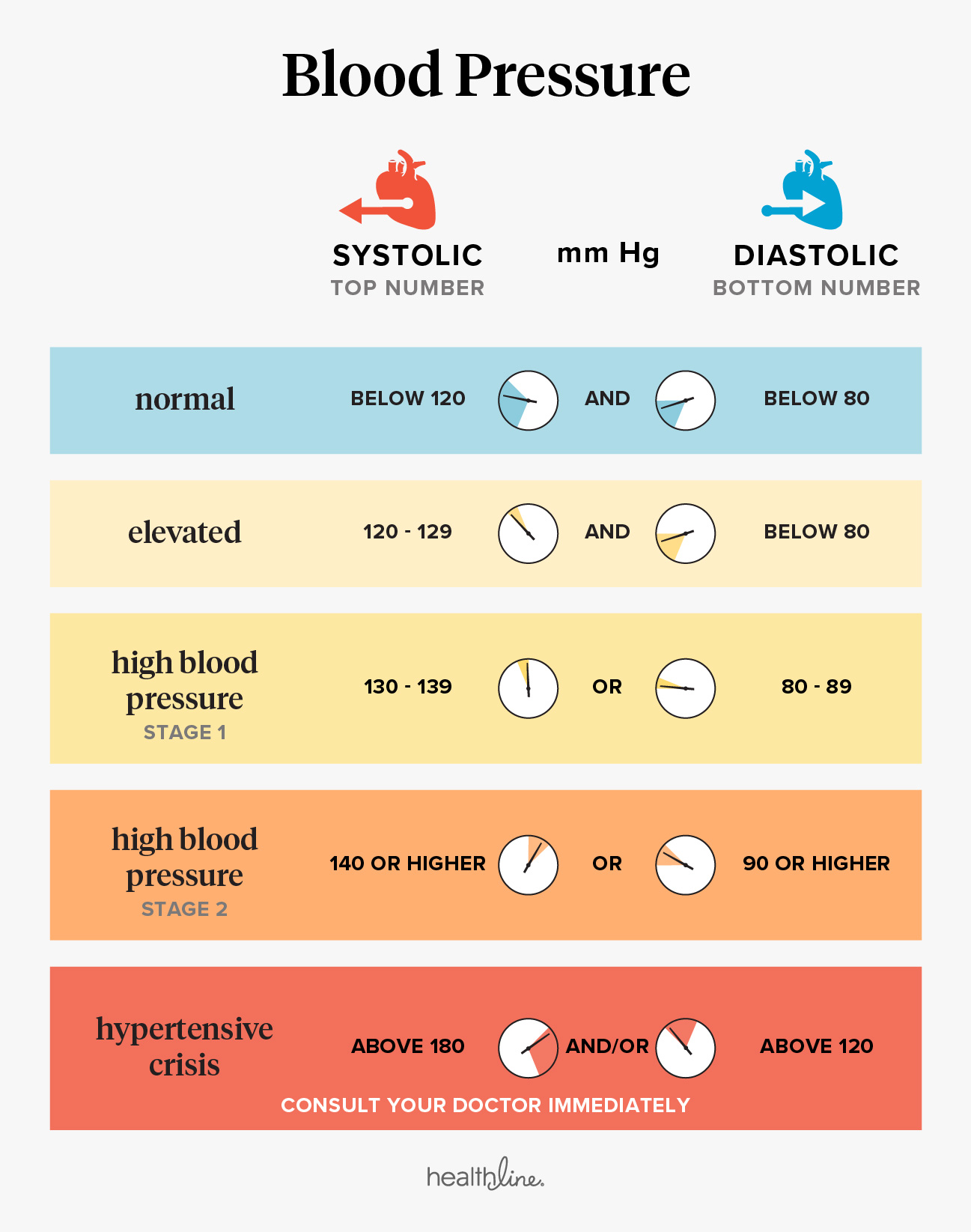
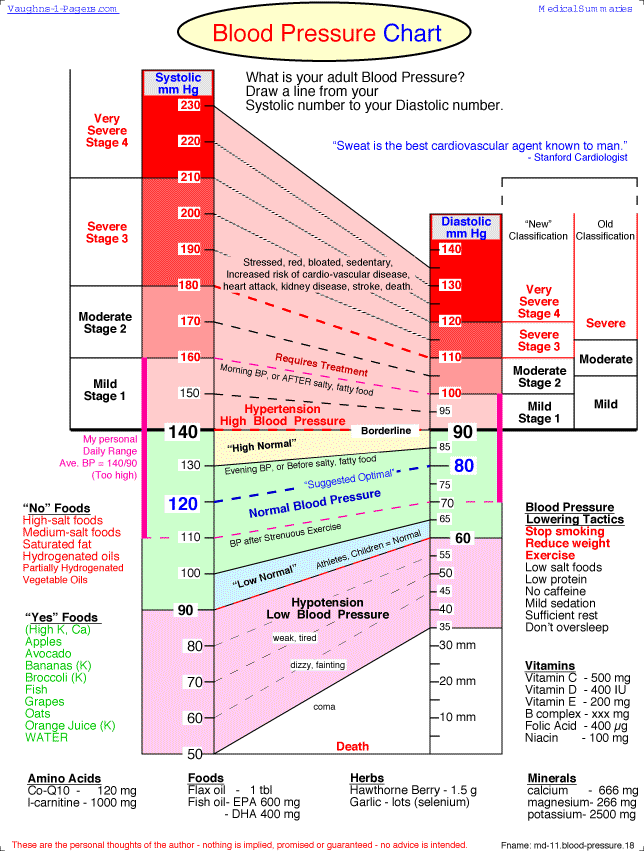
Understanding the information presented in a BP map is crucial for deriving meaningful insights. Key elements to consider include:
- Average BP: The overall average BP reading provides a baseline for comparison.
- BP Fluctuations: The extent of variation in BP readings throughout the day and night reflects the individual’s BP variability.
- Dipping Pattern: The change in BP between daytime and nighttime reveals whether the individual experiences a normal dip (lower BP during sleep) or a blunted or reversed dip (higher BP during sleep).
- Peak and Trough Readings: Identifying the highest and lowest BP readings helps determine the individual’s BP range.
- Trend Analysis: Observing changes in BP over time can indicate treatment effectiveness or the need for adjustments.
FAQs on BP Mapping
1. How often should I have my BP mapped?
The frequency of BP mapping depends on individual needs and factors like the severity of hypertension, risk factors, and treatment goals. Your healthcare provider will recommend the appropriate frequency based on your specific situation.
2. How long does BP mapping take?
ABPM typically involves wearing the monitoring device for 24 hours. HBPM readings are usually taken twice daily for a set period, often several weeks or months.
3. Are there any risks associated with BP mapping?
BP mapping is generally safe, with minimal risks. The device used for ABPM is non-invasive and comfortable to wear. However, some individuals may experience mild discomfort or skin irritation at the cuff site.
4. How do I get my BP mapped?
You can request a BP mapping test from your healthcare provider. They will guide you on the appropriate type of monitoring and provide instructions for using the device.
5. What are the costs associated with BP mapping?
The cost of BP mapping can vary depending on the type of monitoring and insurance coverage. Consult with your healthcare provider or insurance company for details.
Tips for Successful BP Mapping
- Follow instructions carefully: Ensure you understand and adhere to the instructions provided by your healthcare provider regarding the use of the monitoring device.
- Maintain a normal routine: Try to maintain your usual daily activities during the monitoring period to obtain accurate BP readings.
- Record any unusual events: Note any significant events that may have impacted your BP, such as stress, exercise, or medication changes.
- Communicate with your doctor: Share your BP map results with your healthcare provider to discuss the findings and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Conclusion
BP mapping offers a powerful tool for understanding and managing blood pressure, providing a comprehensive and personalized approach to cardiovascular health. By revealing dynamic BP patterns and trends, mapping enhances diagnostic accuracy, enables tailored treatment strategies, and promotes patient engagement in managing their health. It empowers healthcare professionals and individuals to make informed decisions, ultimately contributing to improved cardiovascular outcomes.
![Understanding Blood Pressure [Ultimate BP by Age Chart] - Vive Health](https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0763/4541/files/general_blood_pressure_ranges-min.png?v=1496246420)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Blood Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing BP Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!