Exploring The Caribbean: A Geographical And Historical Overview Of The Antilles
Exploring the Caribbean: A Geographical and Historical Overview of the Antilles
Related Articles: Exploring the Caribbean: A Geographical and Historical Overview of the Antilles
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Exploring the Caribbean: A Geographical and Historical Overview of the Antilles. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Exploring the Caribbean: A Geographical and Historical Overview of the Antilles

The Antilles, a chain of islands in the Caribbean Sea, hold a rich tapestry of history, culture, and natural beauty. Understanding their geographical location, diverse populations, and historical significance provides a compelling insight into this vibrant region.
Geographical Context
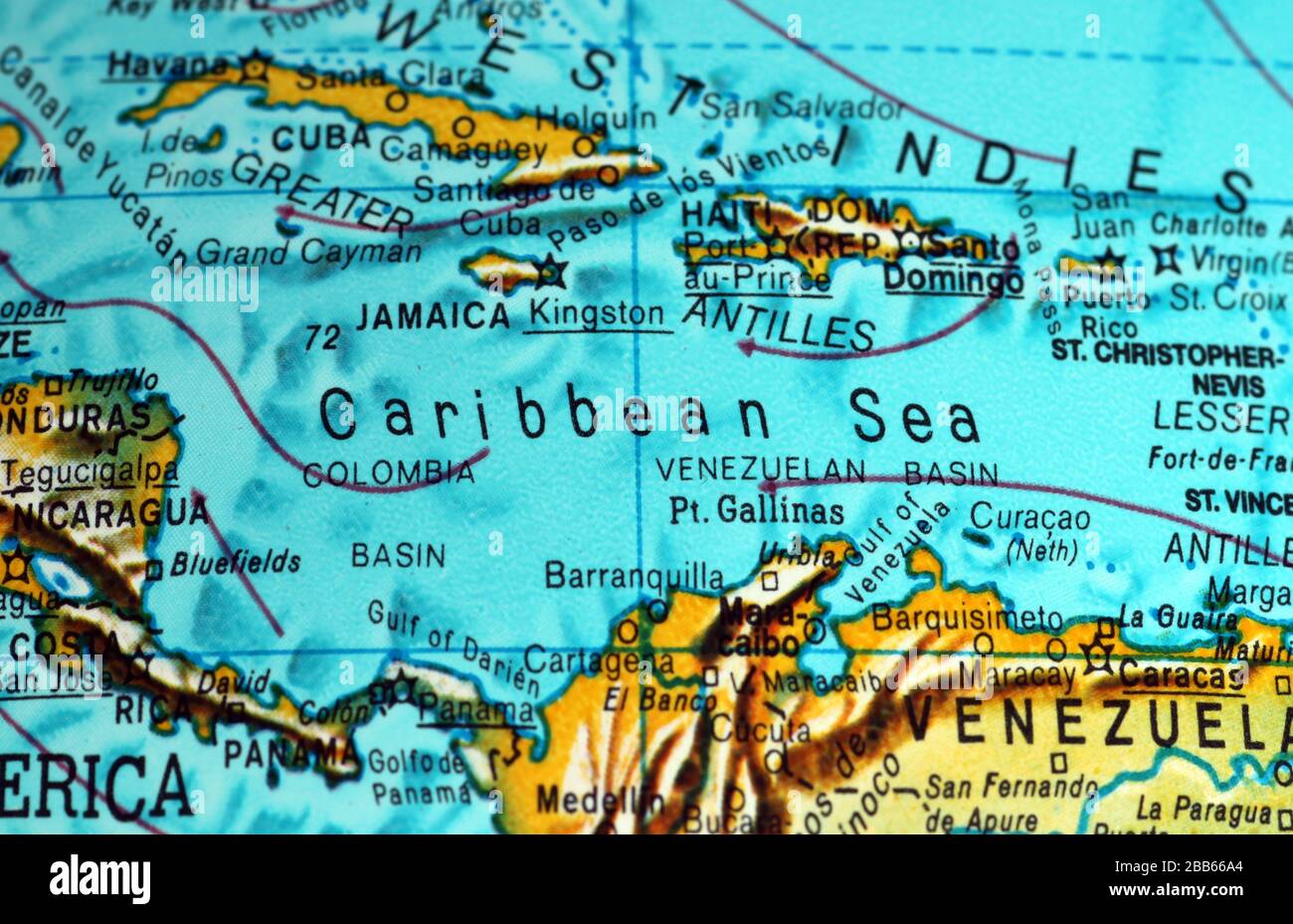
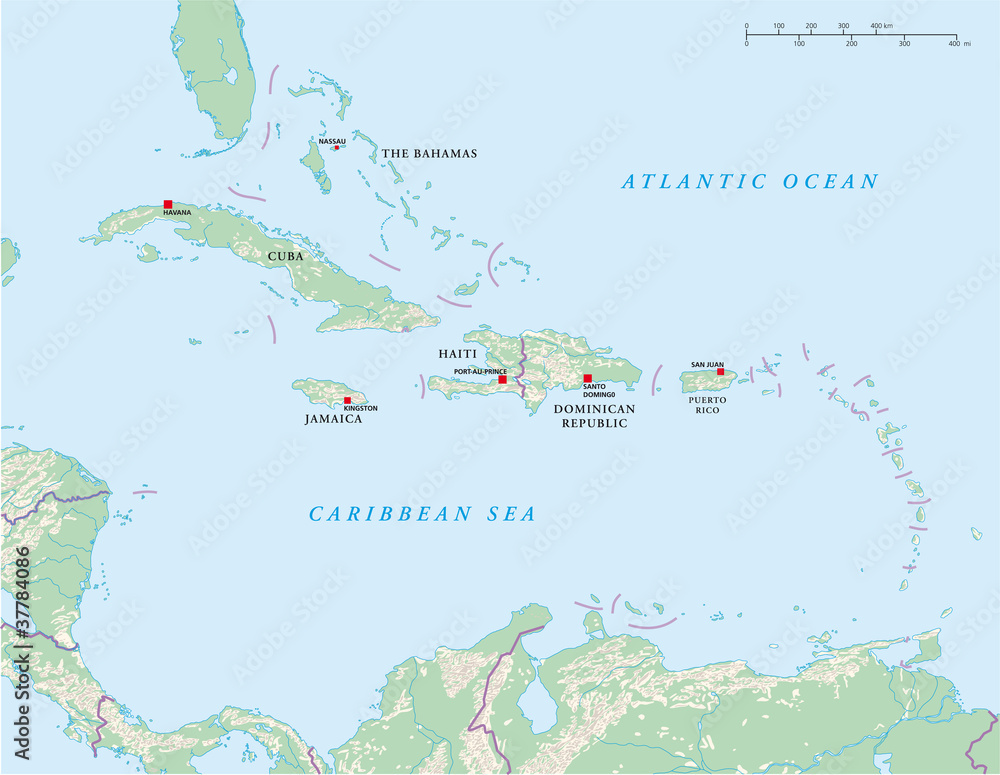
The Antilles are traditionally divided into two main archipelagos: the Greater Antilles and the Lesser Antilles. This distinction is based on size and geographical location, with the Greater Antilles forming a larger, more prominent arc north of the Lesser Antilles.
Greater Antilles:
- Cuba: The largest island in the Caribbean, Cuba boasts a diverse landscape, from fertile plains to rugged mountains.
- Hispaniola: This island is divided between Haiti and the Dominican Republic, each with distinct cultures and histories.
- Jamaica: Known for its vibrant reggae music and lush vegetation, Jamaica is a popular tourist destination.
- Puerto Rico: A U.S. territory, Puerto Rico offers a blend of American and Caribbean influences, with a rich history and vibrant culture.
Lesser Antilles:
- Windward Islands: These islands, stretching from Dominica to Grenada, are known for their volcanic landscapes and lush rainforests.
- Leeward Islands: These islands, from Anguilla to Antigua, are characterized by their flat, sandy coastlines and calm waters.
- Virgin Islands: Divided between the United States and the United Kingdom, these islands offer stunning beaches and a vibrant tourism industry.
Historical Significance
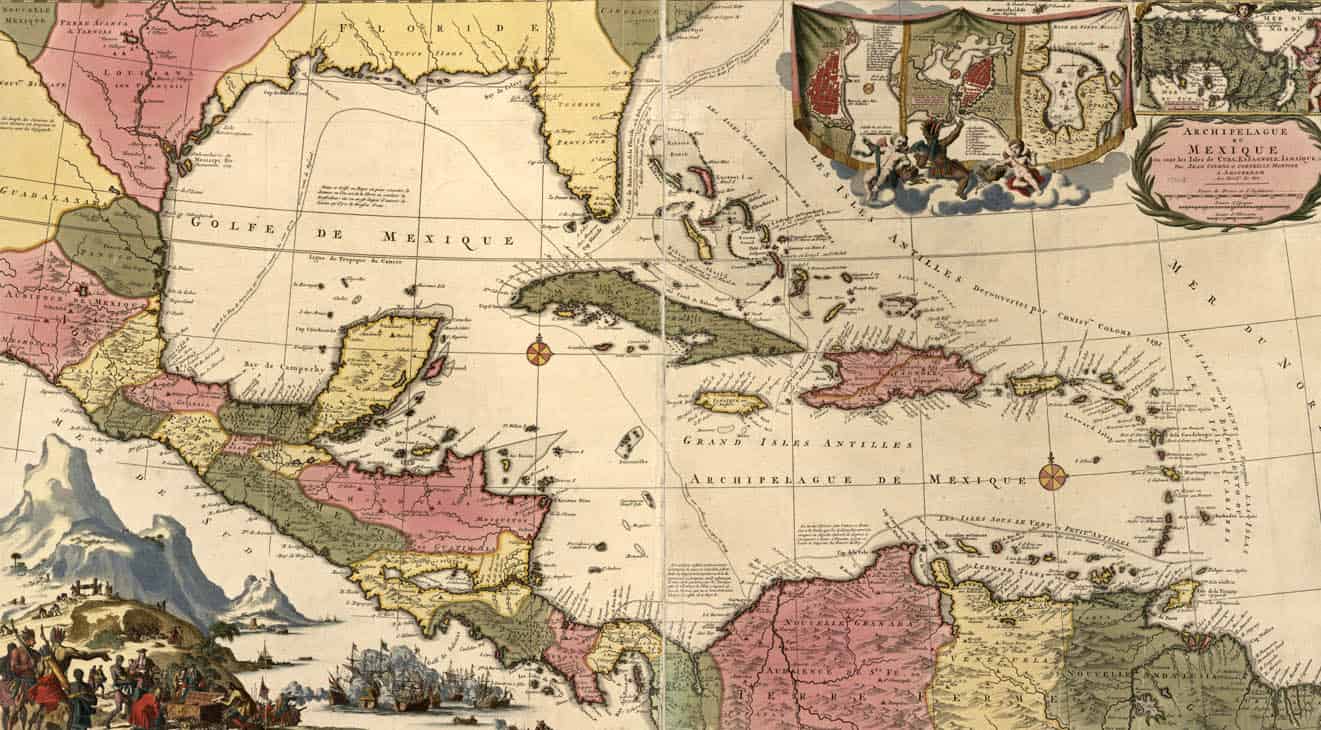
The Antilles have been a crossroads of cultures and civilizations for centuries. Their strategic location in the Caribbean Sea made them attractive to European powers, leading to colonization and a complex history of trade, slavery, and independence movements.
- Indigenous Peoples: Before European arrival, the Antilles were inhabited by various indigenous tribes, including the Taino, Arawak, and Carib.
- European Colonization: From the 15th century onwards, European powers, particularly Spain, France, and Britain, established colonies in the Antilles. This period witnessed the introduction of new crops, livestock, and cultural practices, but also the devastating impact of slavery and disease.
- Independence Movements: The 20th century saw a wave of independence movements across the Antilles, culminating in the establishment of independent nations like Jamaica, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic.
Cultural Diversity
The Antilles are home to a vibrant tapestry of cultures, shaped by their diverse history and heritage.
- Languages: The region boasts a multitude of languages, including Spanish, French, English, and Creole dialects.
- Music and Dance: The Antilles are known for their energetic and expressive music and dance traditions, including salsa, reggae, and calypso.
- Cuisine: The cuisine of the Antilles is a melting pot of flavors, influenced by indigenous ingredients, African culinary traditions, and European influences.
Environmental Importance
The Antilles are home to a rich and diverse ecosystem, with unique flora and fauna.
- Biodiversity: The islands are home to a variety of endemic species, including rare birds, reptiles, and plants.
- Coral Reefs: The Antilles boast some of the most extensive and vibrant coral reef systems in the world.
- Coastal Ecosystems: The region’s diverse coastal ecosystems include mangroves, seagrass beds, and sandy beaches, supporting a rich marine life.
Challenges and Opportunities
The Antilles face a number of challenges, including:
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels and extreme weather events pose a significant threat to the region’s coastal communities and ecosystems.
- Economic Development: Many islands struggle with economic inequality and limited opportunities for their citizens.
- Political Instability: Some islands face political instability and corruption, hindering their development.
However, the Antilles also offer significant opportunities:
- Tourism: The region’s stunning natural beauty and rich cultural heritage make it a popular tourist destination.
- Renewable Energy: The Antilles have significant potential for renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power.
- Sustainable Development: The region can leverage its natural resources and cultural heritage to promote sustainable development and economic growth.
Conclusion
The Antilles, with their diverse landscapes, cultures, and histories, represent a fascinating and vibrant region of the world. Understanding their geographical context, historical significance, cultural diversity, and environmental importance is essential for appreciating the complexities and opportunities that this region presents. As the Antilles continue to navigate the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, their future remains intertwined with the preservation of their unique heritage and the pursuit of sustainable development.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between the Greater Antilles and the Lesser Antilles?
A: The Greater Antilles are larger islands, including Cuba, Hispaniola, Jamaica, and Puerto Rico, located north of the Lesser Antilles. The Lesser Antilles are smaller islands, often volcanic, stretching from Dominica to Grenada in the Windward Islands and from Anguilla to Antigua in the Leeward Islands.
Q: What are the main languages spoken in the Antilles?
A: The main languages spoken in the Antilles include Spanish, French, English, and various Creole dialects, reflecting the region’s diverse colonial history.
Q: What are some of the major cultural contributions of the Antilles to the world?
A: The Antilles have made significant cultural contributions, including vibrant music genres like reggae, salsa, and calypso, as well as unique culinary traditions influenced by indigenous, African, and European influences.
Q: What are the main environmental challenges facing the Antilles?
A: The Antilles face significant environmental challenges, including rising sea levels due to climate change, pollution, and habitat loss, which threaten their biodiversity and coastal ecosystems.
Q: What are some of the opportunities for economic development in the Antilles?
A: The Antilles have potential for economic growth through tourism, renewable energy development, and sustainable agriculture, leveraging their natural resources and cultural heritage.
Tips
- Travel to the Antilles: Experience the region’s diverse landscapes, cultures, and history firsthand.
- Learn about the history of the Antilles: Understand the region’s complex colonial past and the struggles for independence.
- Support sustainable tourism: Choose eco-friendly accommodations and tour operators that prioritize environmental conservation.
- Engage with local communities: Learn about their traditions, languages, and perspectives.
- Advocate for environmental protection: Support organizations working to preserve the region’s biodiversity and ecosystems.
Conclusion
The Antilles stand as a testament to the enduring power of human resilience, cultural adaptation, and natural beauty. Understanding their geographical context, historical significance, cultural diversity, and environmental importance allows us to appreciate the complexities and opportunities that this region presents. By engaging with the Antilles and its people, we can contribute to its sustainable development and ensure that its unique heritage continues to thrive for generations to come.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/1280px-1732_Herman_Moll_Map_of_the_West_Indies_and_Caribbean_-_Geographicus_-_WestIndies-moll-1732-5945d8f43df78c537bdb6002.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the Caribbean: A Geographical and Historical Overview of the Antilles. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!