Delving Into The Depths: A Comprehensive Look At The Atlantic Ocean’s Topography
Delving into the Depths: A Comprehensive Look at the Atlantic Ocean’s Topography
Related Articles: Delving into the Depths: A Comprehensive Look at the Atlantic Ocean’s Topography
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Depths: A Comprehensive Look at the Atlantic Ocean’s Topography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Depths: A Comprehensive Look at the Atlantic Ocean’s Topography
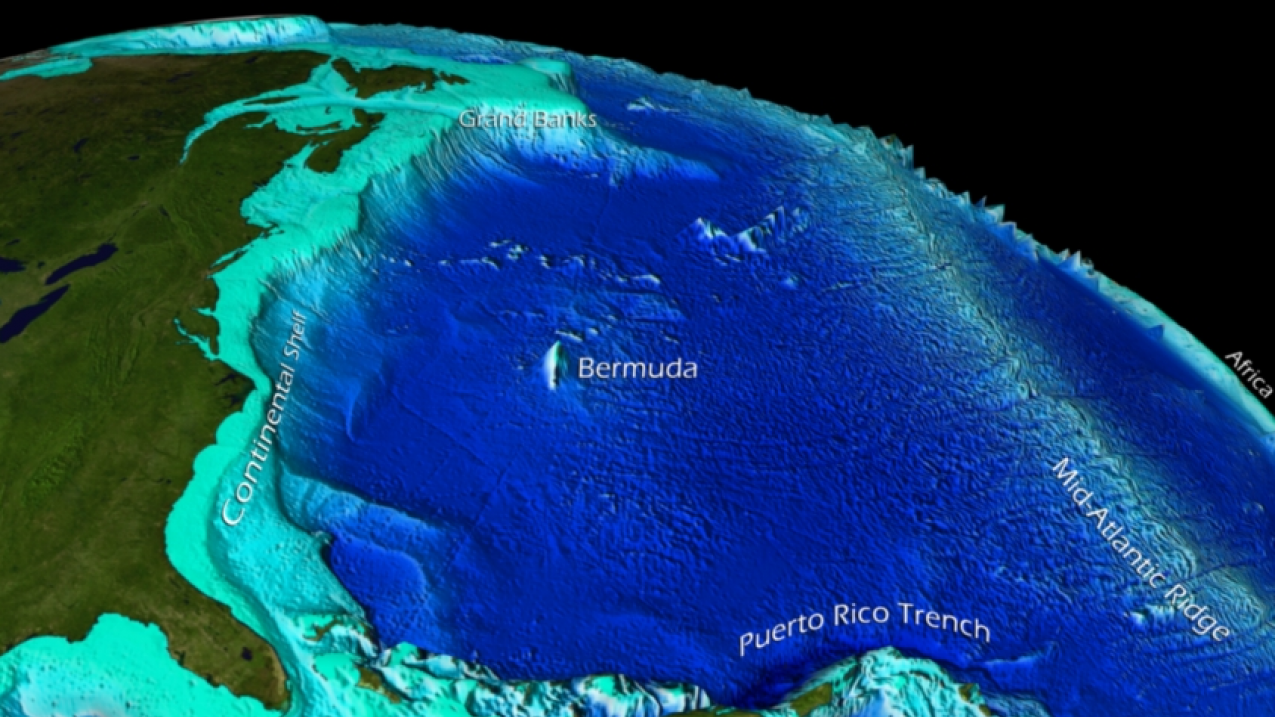
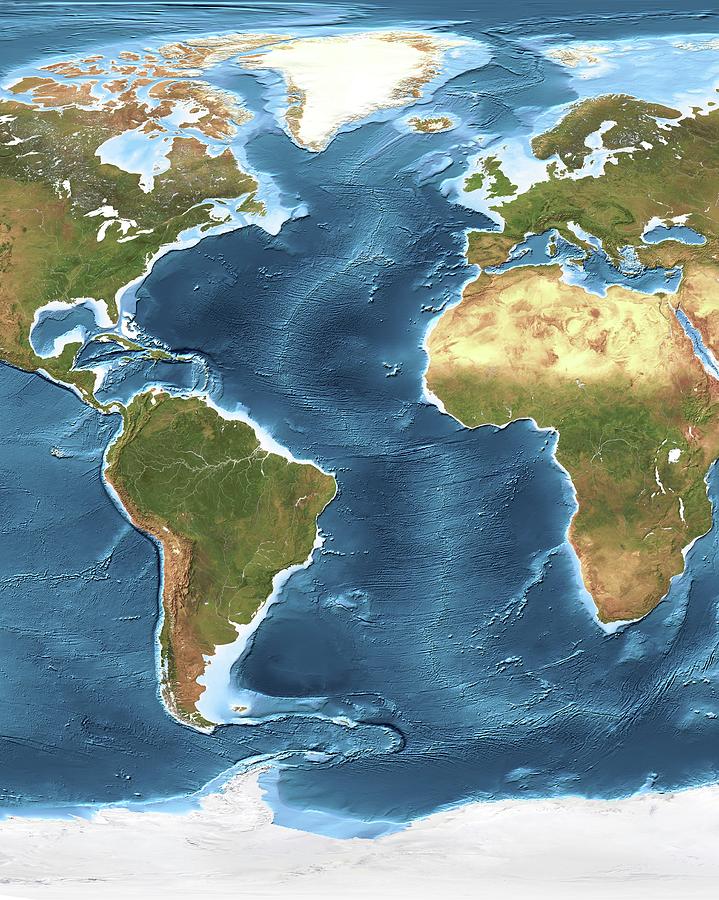
The Atlantic Ocean, a vast expanse of water covering approximately 20% of the Earth’s surface, is far from a uniform body. Its floor is a complex tapestry of mountains, valleys, plains, and trenches, each feature contributing to the ocean’s unique characteristics and playing a crucial role in global oceanographic processes. A topographic map of the Atlantic Ocean, with its intricate depiction of depths, provides a window into this hidden world, revealing the underlying structure and dynamic nature of this vital body of water.
Understanding the Atlantic’s Floor: A Journey Through Depths
The Atlantic Ocean’s topography is characterized by a central mid-ocean ridge, a prominent underwater mountain range that stretches for thousands of kilometers, bisecting the basin from north to south. This ridge, a product of plate tectonics, is a site of intense geological activity, with volcanic eruptions and earthquakes shaping its landscape. The ridge’s crest, often referred to as the "Mid-Atlantic Ridge," is marked by a deep rift valley, a fissure where new oceanic crust is constantly being generated.
Flanking the mid-ocean ridge are vast abyssal plains, flat, sediment-covered areas that extend for hundreds of kilometers. These plains represent the most common feature of the ocean floor, formed by the accumulation of fine sediments carried by currents and deposited over millions of years. Their relative flatness contrasts sharply with the dramatic topography of the mid-ocean ridge.
Scattered across the abyssal plains are numerous seamounts, isolated underwater mountains that rise from the ocean floor. These formations, often volcanic in origin, can reach heights of several kilometers. Some seamounts are extinct volcanoes, while others remain active, releasing heat and contributing to the dynamic nature of the ocean floor.
The Atlantic Ocean’s topography is further punctuated by deep trenches, narrow, elongated depressions that mark the convergence of tectonic plates. The Puerto Rico Trench, located in the northwestern Atlantic, is the deepest point in the Atlantic Ocean, reaching depths of over 8,600 meters. These trenches are sites of intense geological activity, often associated with earthquakes and volcanic activity.
The Significance of Atlantic Ocean Topography: A Symphony of Processes
The intricate topography of the Atlantic Ocean plays a vital role in shaping the ocean’s physical, chemical, and biological processes. The mid-ocean ridge, with its active volcanic activity, releases heat into the ocean, influencing ocean currents and contributing to the global heat budget. The ridge also acts as a barrier, separating the Atlantic basin into distinct water masses with varying properties.
The abyssal plains, while seemingly flat, are far from stagnant. They are home to unique ecosystems adapted to the extreme conditions of the deep ocean, and their sediment layers hold valuable records of past climate and oceanographic conditions. The seamounts, with their diverse ecosystems, provide habitat for a wide array of marine life, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the Atlantic Ocean.
The deep trenches, with their extreme pressures and lack of sunlight, are among the least explored environments on Earth. They are home to unique and often bizarre organisms that have adapted to survive in these harsh conditions. These environments also play a role in regulating the flow of ocean currents, influencing the distribution of nutrients and organisms throughout the basin.
Navigating the Depths: The Importance of Topographic Maps
Topographic maps of the Atlantic Ocean are essential tools for understanding and navigating this vast body of water. They provide detailed information about the ocean floor, allowing scientists and researchers to study the distribution of marine life, the movement of ocean currents, and the impact of human activities on the marine environment.
For example, topographic maps are crucial for marine conservation efforts, allowing scientists to identify sensitive habitats and areas of high biodiversity, enabling the development of effective conservation strategies. They are also essential for understanding the effects of climate change on the ocean, allowing scientists to monitor changes in ocean currents, sea level, and the distribution of marine organisms.
FAQs: Unveiling the Mysteries of the Atlantic’s Depths
1. What are the key features of the Atlantic Ocean’s topography?
The Atlantic Ocean’s topography is characterized by a central mid-ocean ridge, vast abyssal plains, numerous seamounts, and deep trenches.
2. How does the mid-ocean ridge influence the Atlantic Ocean?
The mid-ocean ridge releases heat into the ocean, influencing ocean currents and contributing to the global heat budget. It also acts as a barrier, separating the Atlantic basin into distinct water masses.
3. What is the significance of abyssal plains in the Atlantic Ocean?
Abyssal plains are home to unique ecosystems adapted to the extreme conditions of the deep ocean and hold valuable records of past climate and oceanographic conditions.
4. Why are seamounts important to the Atlantic Ocean?
Seamounts provide habitat for a wide array of marine life, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the Atlantic Ocean.
5. What role do deep trenches play in the Atlantic Ocean?
Deep trenches are home to unique organisms adapted to extreme conditions and play a role in regulating the flow of ocean currents, influencing the distribution of nutrients and organisms.
6. How are topographic maps used in marine research?
Topographic maps are essential tools for studying the distribution of marine life, the movement of ocean currents, and the impact of human activities on the marine environment.
Tips for Understanding Atlantic Ocean Topography
- Visualize the topography: Use online resources and interactive maps to visualize the different features of the Atlantic Ocean floor.
- Study the processes: Learn about the geological processes that have shaped the Atlantic Ocean’s topography, such as plate tectonics and volcanism.
- Explore the ecosystems: Research the unique ecosystems found in different areas of the Atlantic Ocean, such as abyssal plains, seamounts, and deep trenches.
- Consider the impact of human activities: Explore how human activities, such as fishing, pollution, and climate change, are affecting the Atlantic Ocean’s topography and its ecosystems.
Conclusion: A Window into the Hidden World
The Atlantic Ocean’s topography, with its intricate depths and diverse features, provides a captivating glimpse into the hidden world beneath the waves. Understanding this topography is crucial for comprehending the ocean’s complex processes, its role in the global climate system, and the challenges it faces from human activities. Topographic maps serve as invaluable tools for navigating this vast and dynamic environment, enabling us to explore, understand, and protect this vital part of our planet.


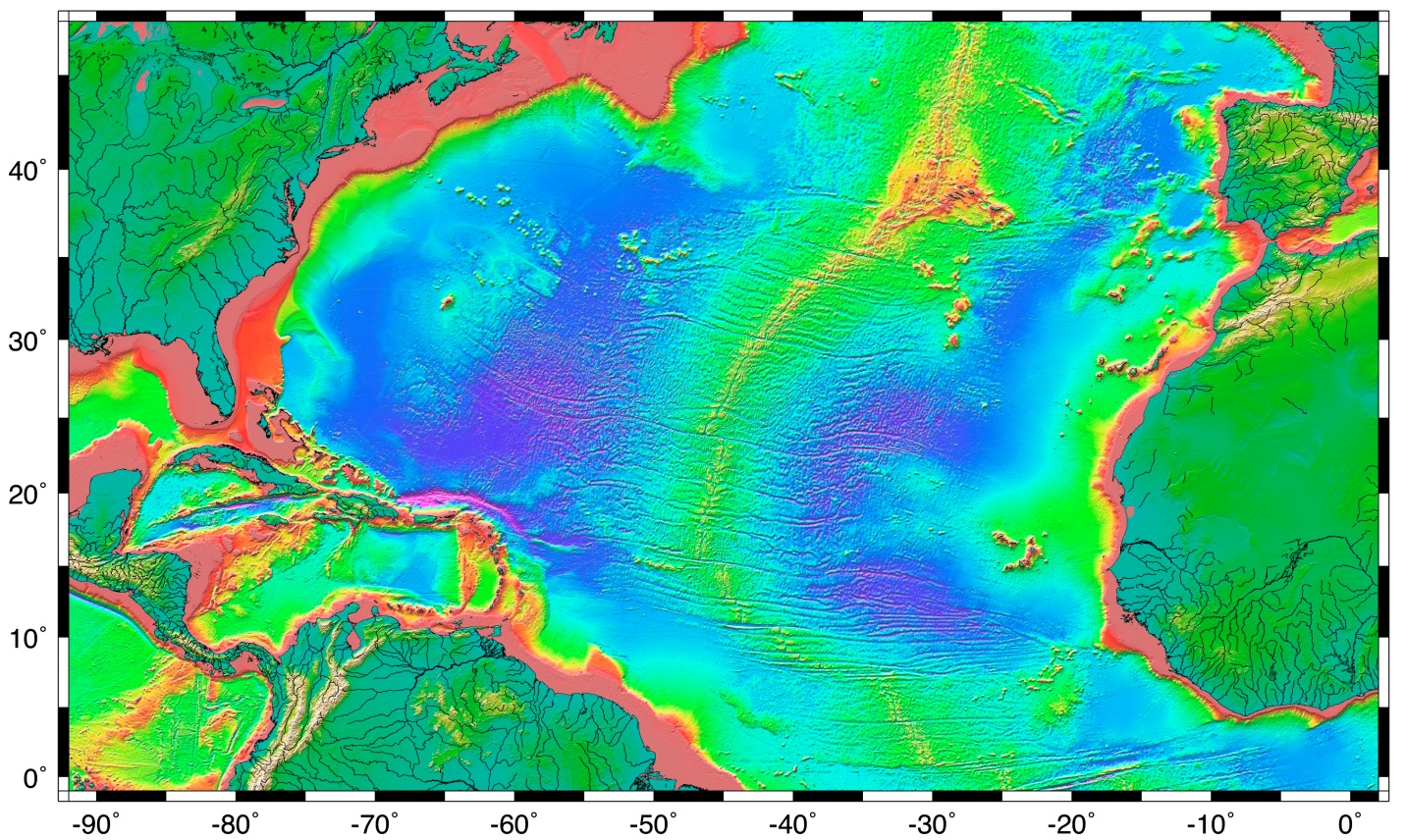
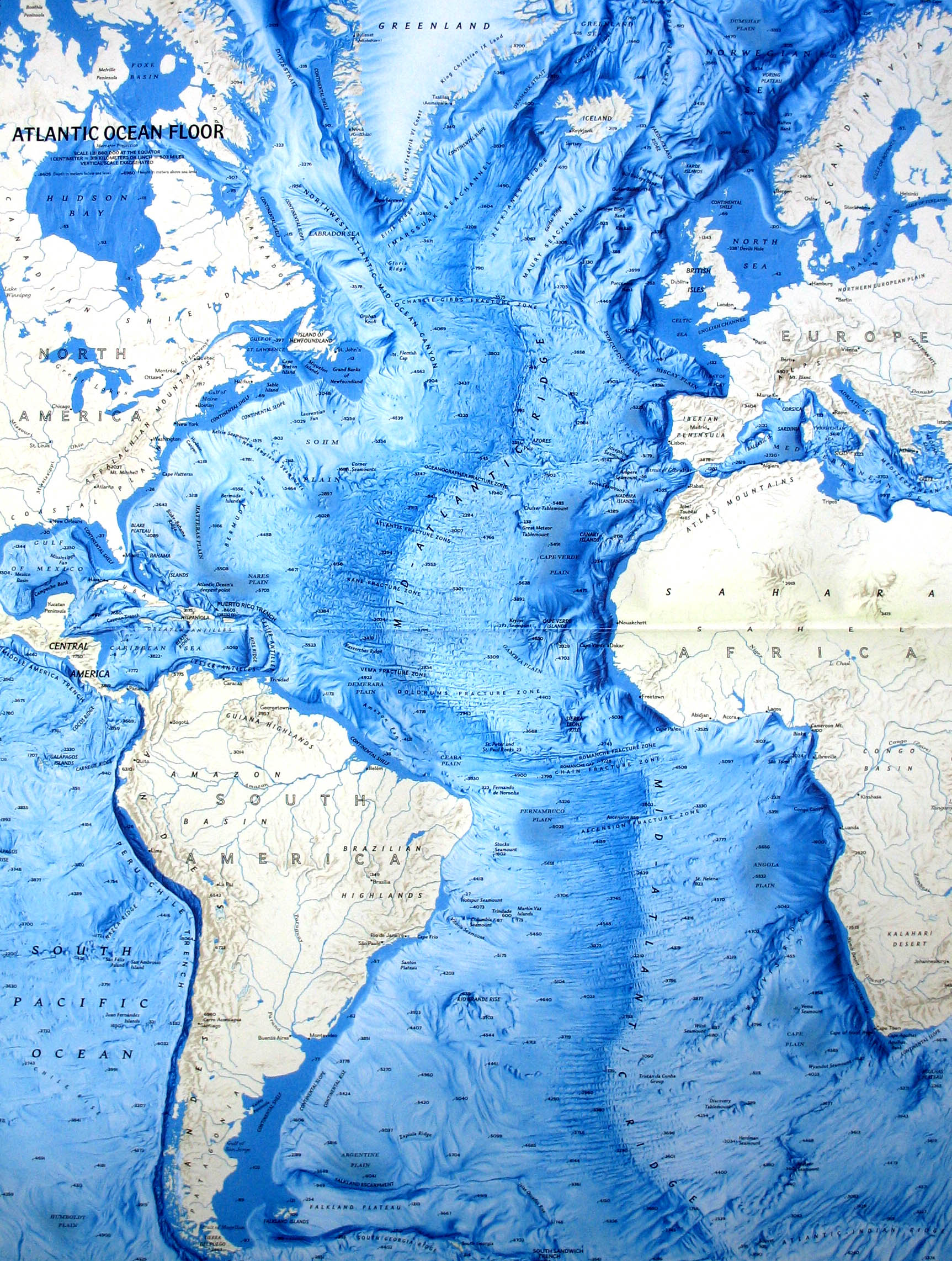
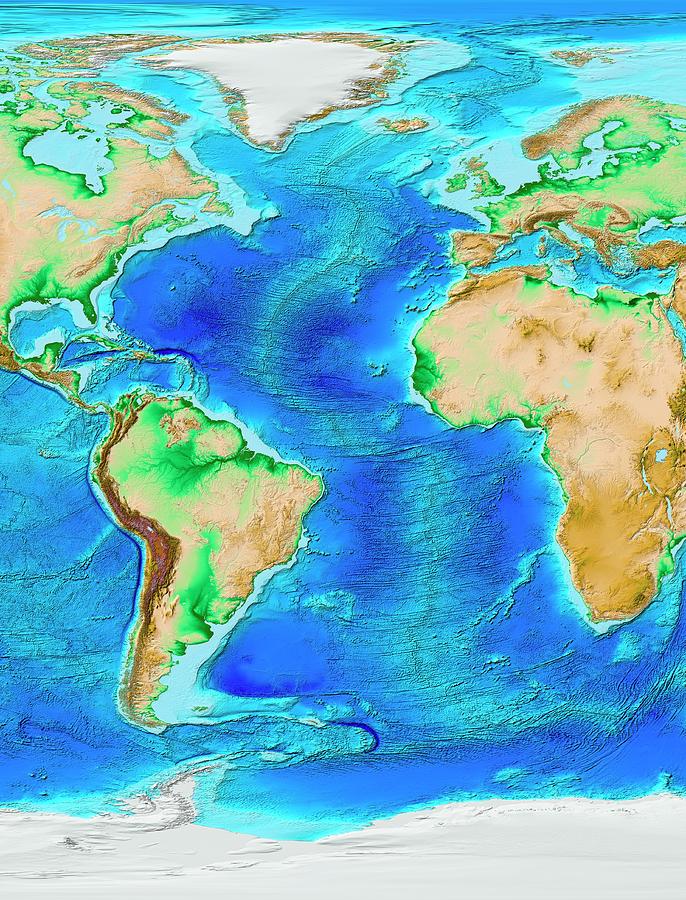

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Depths: A Comprehensive Look at the Atlantic Ocean’s Topography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!