Deciphering The Atlantic Ocean’s Thermal Tapestry: A Comprehensive Exploration Of Temperature Maps
Deciphering the Atlantic Ocean’s Thermal Tapestry: A Comprehensive Exploration of Temperature Maps
Related Articles: Deciphering the Atlantic Ocean’s Thermal Tapestry: A Comprehensive Exploration of Temperature Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Atlantic Ocean’s Thermal Tapestry: A Comprehensive Exploration of Temperature Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Atlantic Ocean’s Thermal Tapestry: A Comprehensive Exploration of Temperature Maps
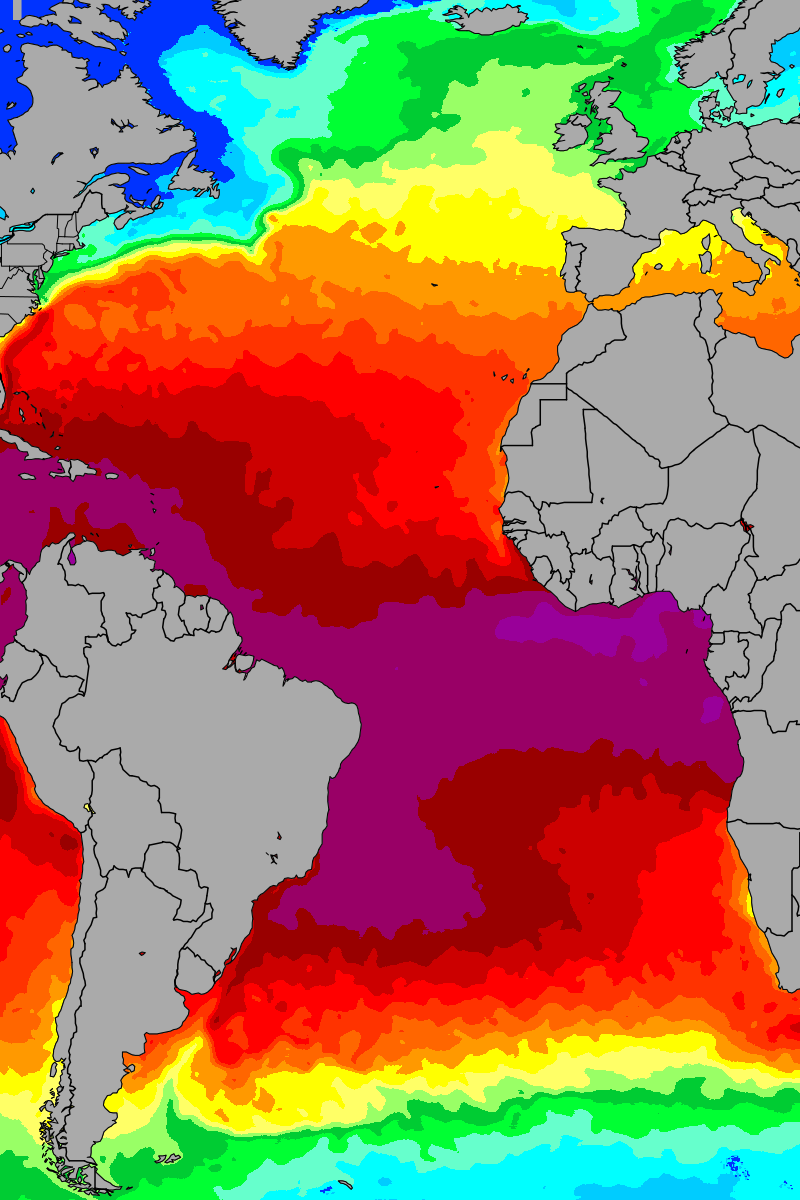
The Atlantic Ocean, spanning vast distances and encompassing diverse ecosystems, is a dynamic entity constantly in flux. Its intricate thermal patterns, driven by complex interactions between solar energy, atmospheric circulation, and oceanic currents, are crucial for understanding the ocean’s role in global climate regulation and its impact on marine life.
Mapping the Ocean’s Heat:
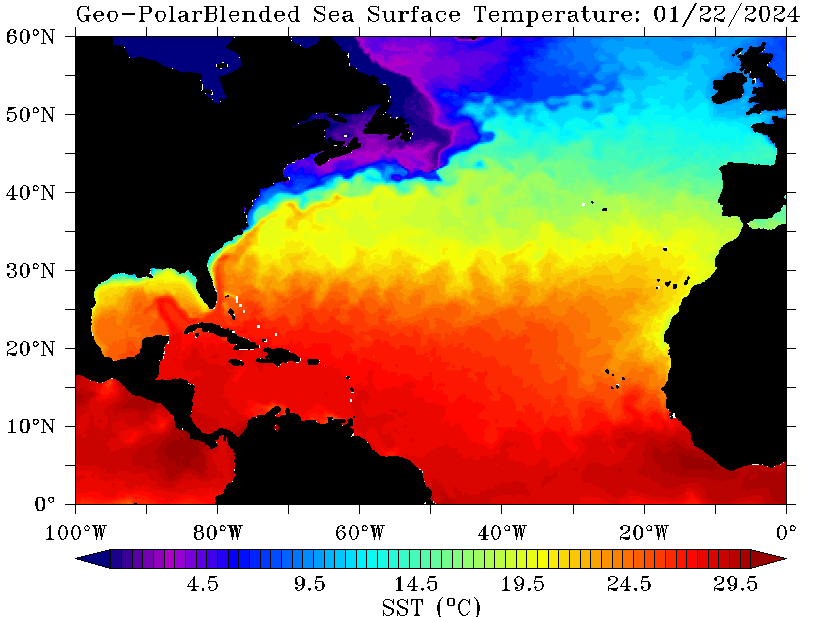
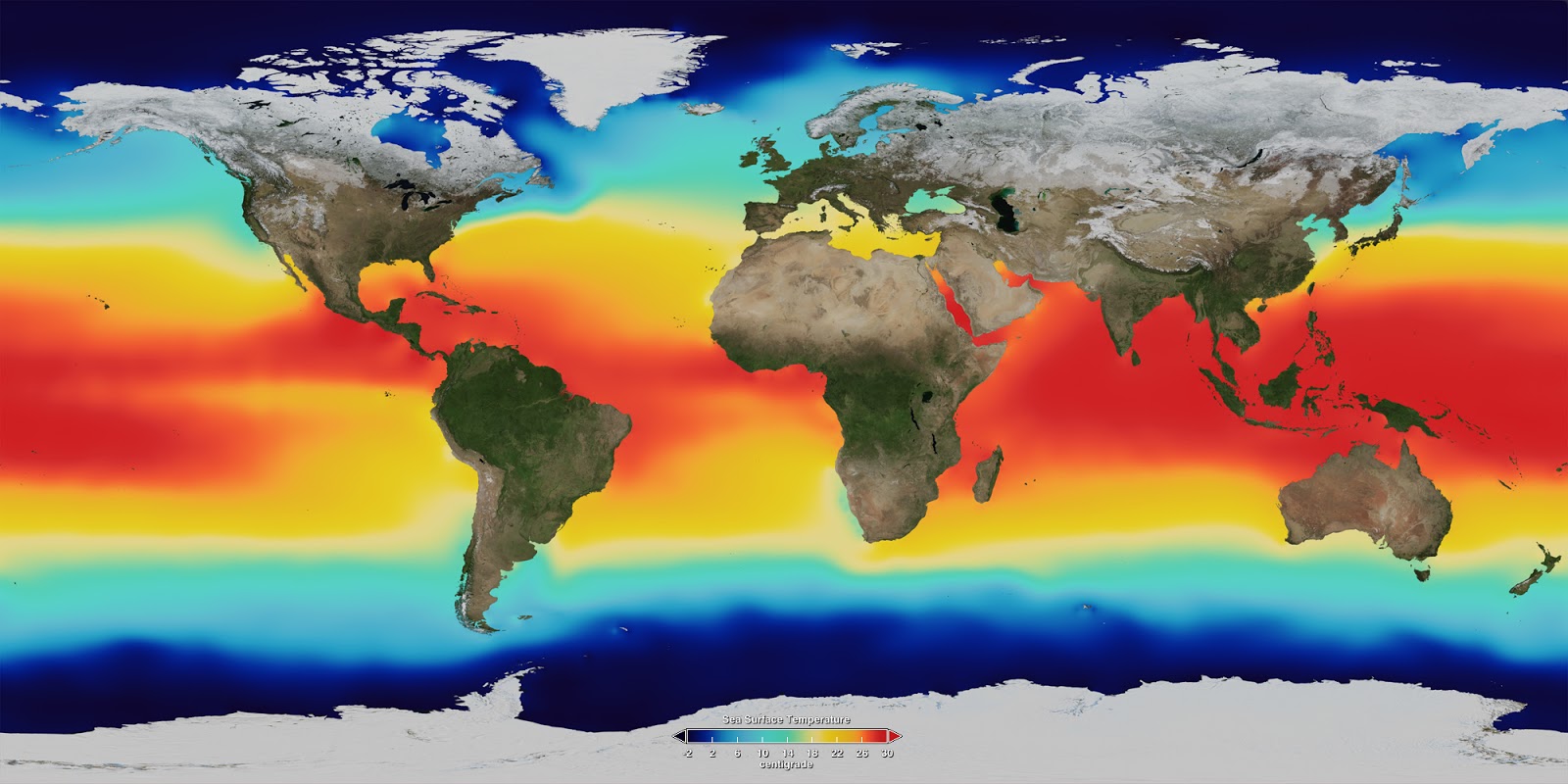
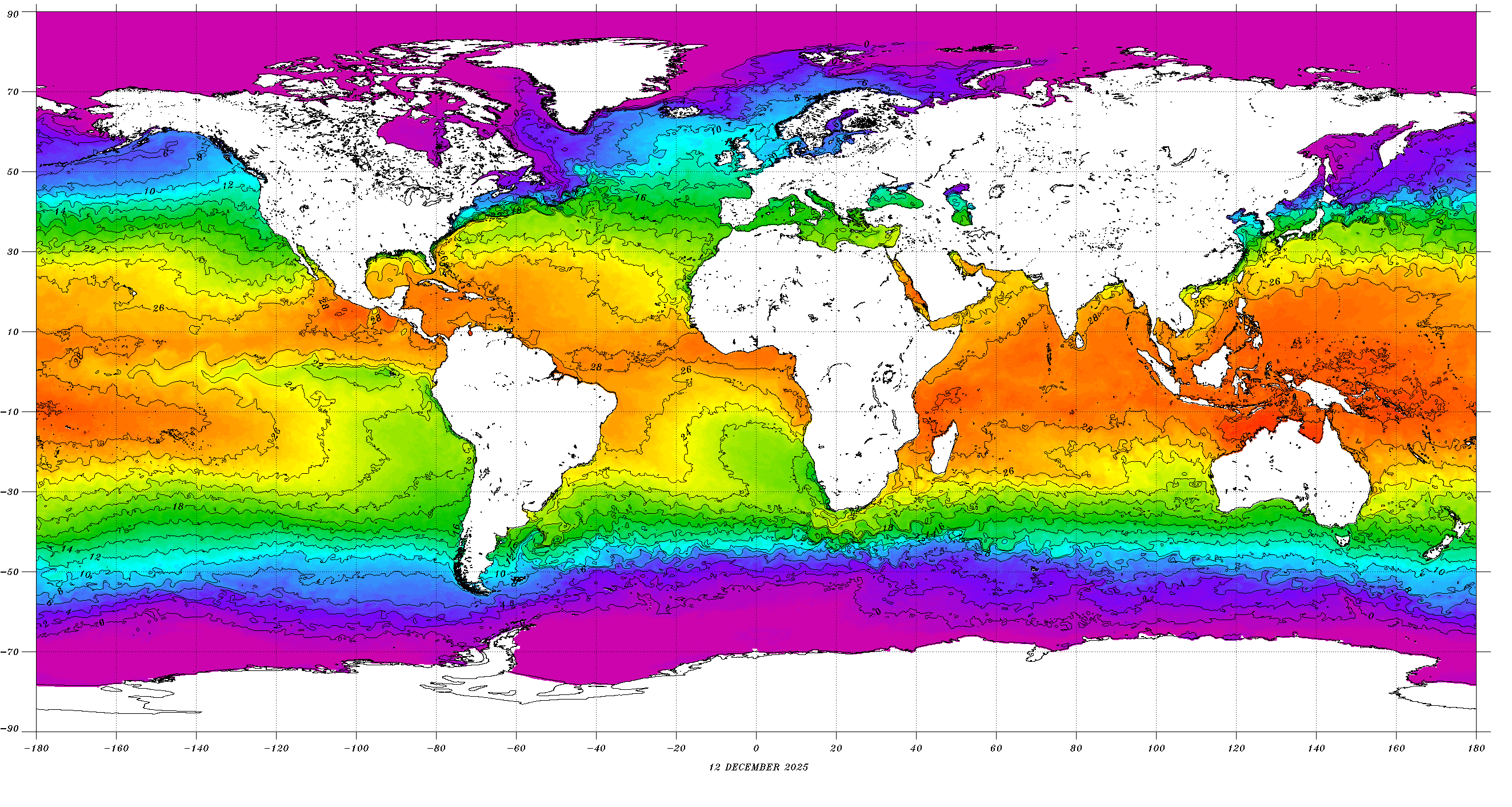
Atlantic Ocean temperature maps are visual representations of the ocean’s thermal distribution at a given time. These maps, generated using data collected from satellites, buoys, and research vessels, offer a snapshot of the ocean’s thermal landscape, highlighting areas of warm and cold water. The maps utilize color gradients, where warmer waters are typically depicted in shades of red and orange, while cooler waters are represented in blues and greens.
Unveiling the Ocean’s Thermal Rhythms:
The Atlantic Ocean’s temperature patterns are not static. They exhibit seasonal variations, influenced by the Earth’s tilt and its journey around the sun. During summer, the sun’s rays strike the northern hemisphere more directly, leading to warmer surface temperatures in the North Atlantic. Conversely, the Southern Hemisphere experiences its winter, resulting in colder surface temperatures in the South Atlantic.
Beyond seasonal variations, long-term trends in Atlantic Ocean temperatures are closely monitored. These trends, influenced by natural cycles like the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and human-induced climate change, have significant implications for weather patterns, marine ecosystems, and human activities.
The Significance of Atlantic Ocean Temperature Maps:
Understanding the ocean’s thermal patterns is crucial for a multitude of reasons:
1. Climate Monitoring and Prediction:
Atlantic Ocean temperature maps provide vital insights into the ocean’s role in global climate regulation. They help scientists monitor and predict changes in weather patterns, such as the intensity and frequency of hurricanes and the occurrence of extreme weather events.
2. Marine Ecosystem Health:
The ocean’s temperature directly affects marine life. Fish, coral reefs, and other marine organisms thrive within specific temperature ranges. Temperature maps help scientists understand how temperature variations impact the distribution, abundance, and health of marine species.
3. Fisheries Management:
Fish populations are sensitive to temperature changes. Temperature maps assist in identifying areas of suitable temperatures for different fish species, aiding in sustainable fisheries management and preventing overfishing.
4. Navigation and Shipping:
Ocean temperature variations can affect the efficiency of shipping routes. Warmer waters can lead to increased fuel consumption, while colder waters can affect ship performance. Temperature maps help optimize shipping routes and minimize fuel consumption.
5. Coastal Protection:
Sea level rise, driven by warming ocean temperatures, poses a significant threat to coastal communities. Temperature maps provide crucial data for understanding and mitigating the impacts of sea level rise on coastal infrastructure and ecosystems.
Exploring the Depths of Ocean Temperature Data:
Beyond surface temperatures, Atlantic Ocean temperature maps can depict the thermal structure of the ocean’s depths. These maps reveal the presence of thermoclines, distinct layers of water with different temperatures, and provide insights into the ocean’s vertical circulation patterns.
FAQs:
1. What is the average temperature of the Atlantic Ocean?
The average surface temperature of the Atlantic Ocean varies significantly depending on latitude and season. Generally, it ranges from approximately 27°C (81°F) in tropical regions to near-freezing temperatures in polar regions.
2. How do ocean currents affect Atlantic Ocean temperatures?
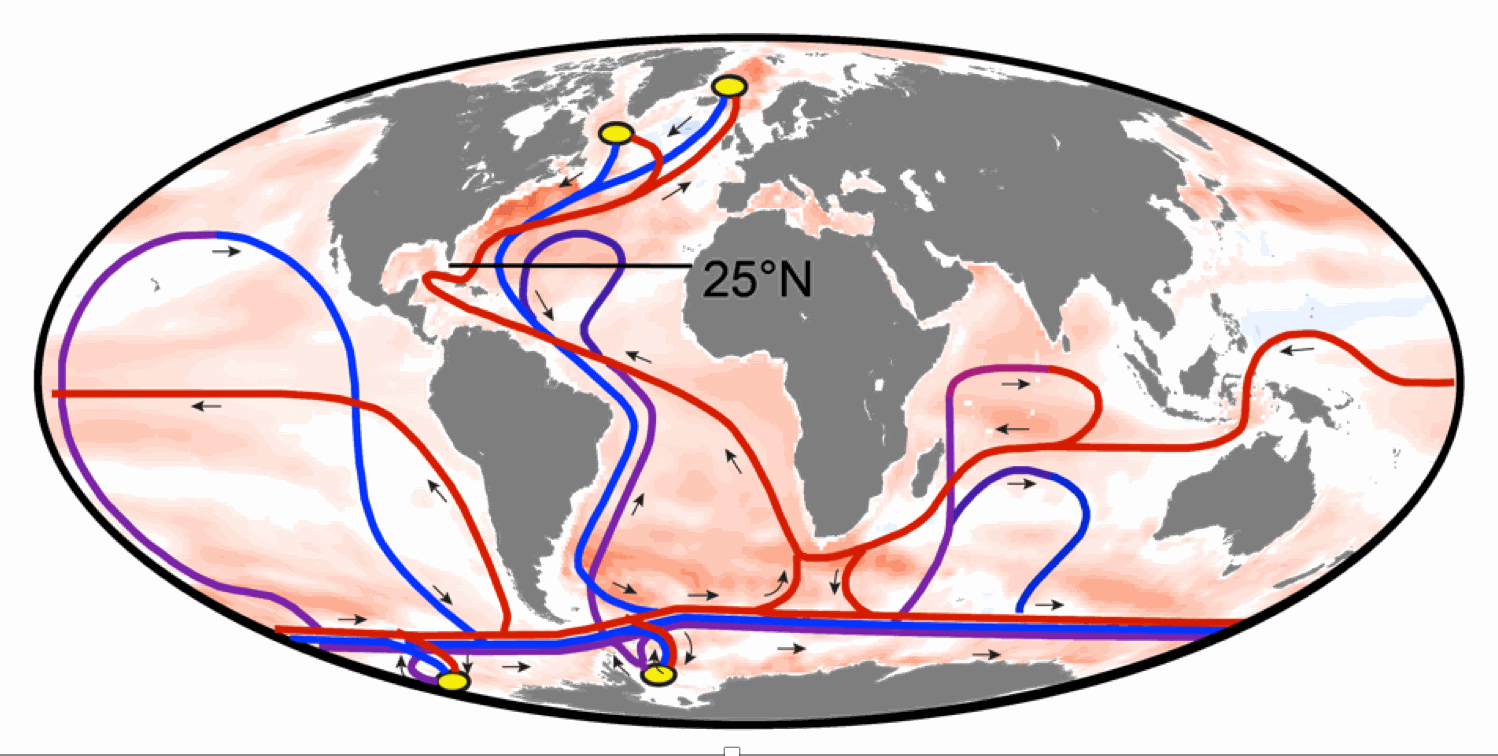
Ocean currents play a vital role in distributing heat throughout the Atlantic Ocean. Warm currents, like the Gulf Stream, transport warm water from the tropics towards higher latitudes, moderating the climate of Western Europe. Cold currents, like the Labrador Current, carry cold water from polar regions towards lower latitudes.
3. How do human activities impact Atlantic Ocean temperatures?
Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, trapping heat and causing global warming. This warming trend is evident in rising Atlantic Ocean temperatures, with significant implications for marine ecosystems and human societies.
4. How are Atlantic Ocean temperature maps created?
Atlantic Ocean temperature maps are created using data collected from various sources:
- Satellites: Satellites equipped with infrared sensors measure the temperature of the ocean’s surface.
- Buoys: Buoys deployed throughout the ocean collect data on temperature, salinity, and other oceanographic parameters.
- Research Vessels: Research vessels equipped with sophisticated instruments measure temperature at different depths.
5. What are the potential consequences of rising Atlantic Ocean temperatures?
Rising Atlantic Ocean temperatures have a wide range of potential consequences:
- Increased frequency and intensity of hurricanes: Warmer ocean temperatures provide more energy for hurricanes to form and intensify.
- Sea level rise: As ocean water warms, it expands, contributing to sea level rise.
- Marine heatwaves: Prolonged periods of unusually warm water can cause widespread coral bleaching and harm marine ecosystems.
- Changes in ocean currents: Rising temperatures can disrupt ocean currents, affecting climate patterns and marine life.
Tips for Understanding Atlantic Ocean Temperature Maps:
- Pay attention to the color scale: The color scale indicates the temperature range represented on the map.
- Consider the time of year: Seasonal variations in temperature are significant.
- Look for patterns: Identify areas of warm and cold water, and consider how they might be influenced by ocean currents, weather patterns, or other factors.
- Compare maps from different times: Observing changes in temperature over time can reveal long-term trends.
Conclusion:
Atlantic Ocean temperature maps are essential tools for understanding the ocean’s thermal dynamics and their impact on climate, marine ecosystems, and human activities. By deciphering the ocean’s thermal tapestry, we gain valuable insights into the intricate workings of our planet and the challenges we face in a changing climate.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Atlantic Ocean’s Thermal Tapestry: A Comprehensive Exploration of Temperature Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!