Charting The Depths: Exploring The Topography Of The Atlantic Ocean
Charting the Depths: Exploring the Topography of the Atlantic Ocean
Related Articles: Charting the Depths: Exploring the Topography of the Atlantic Ocean
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the Depths: Exploring the Topography of the Atlantic Ocean. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Depths: Exploring the Topography of the Atlantic Ocean

The Atlantic Ocean, a vast expanse of water covering nearly 20% of the Earth’s surface, is far from a flat, uniform plane. Beneath its surface lies a complex and dynamic topography, shaped by geological forces spanning millions of years. Understanding this topography is crucial for navigation, resource management, and understanding the ocean’s role in global climate.
A World Beneath the Waves:
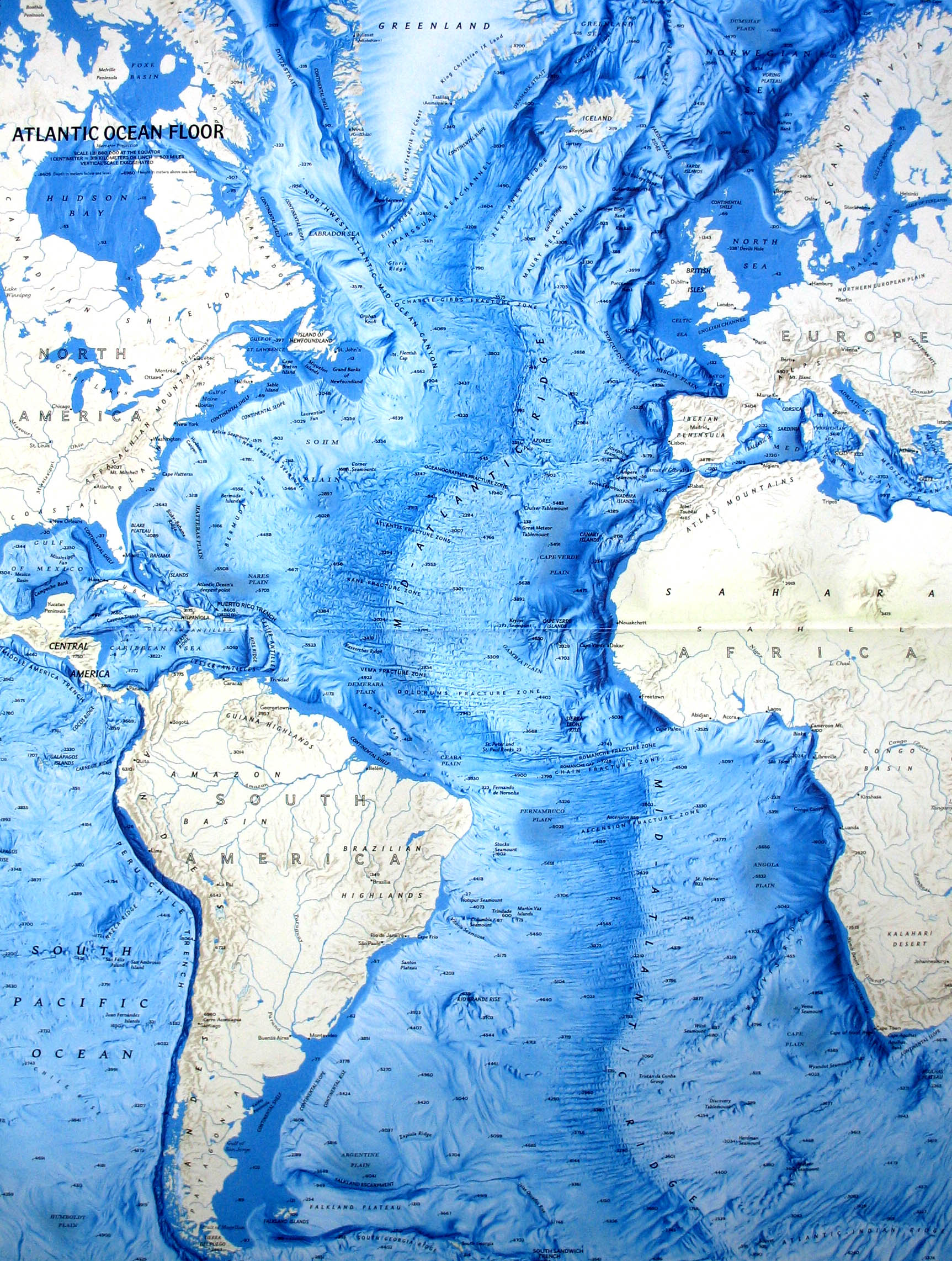
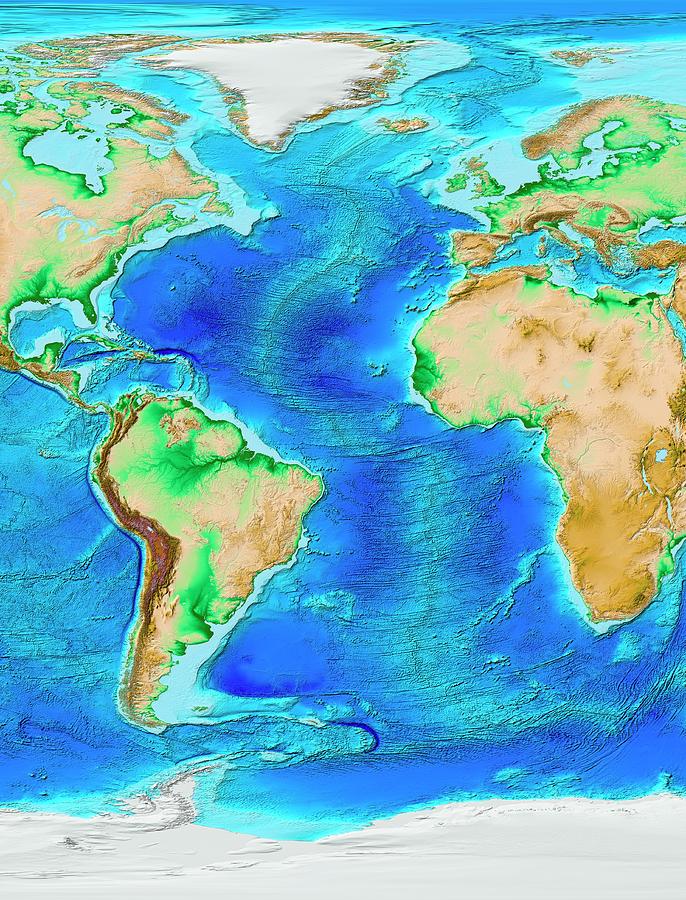
Topographical maps of the Atlantic Ocean reveal a landscape of dramatic features, including:
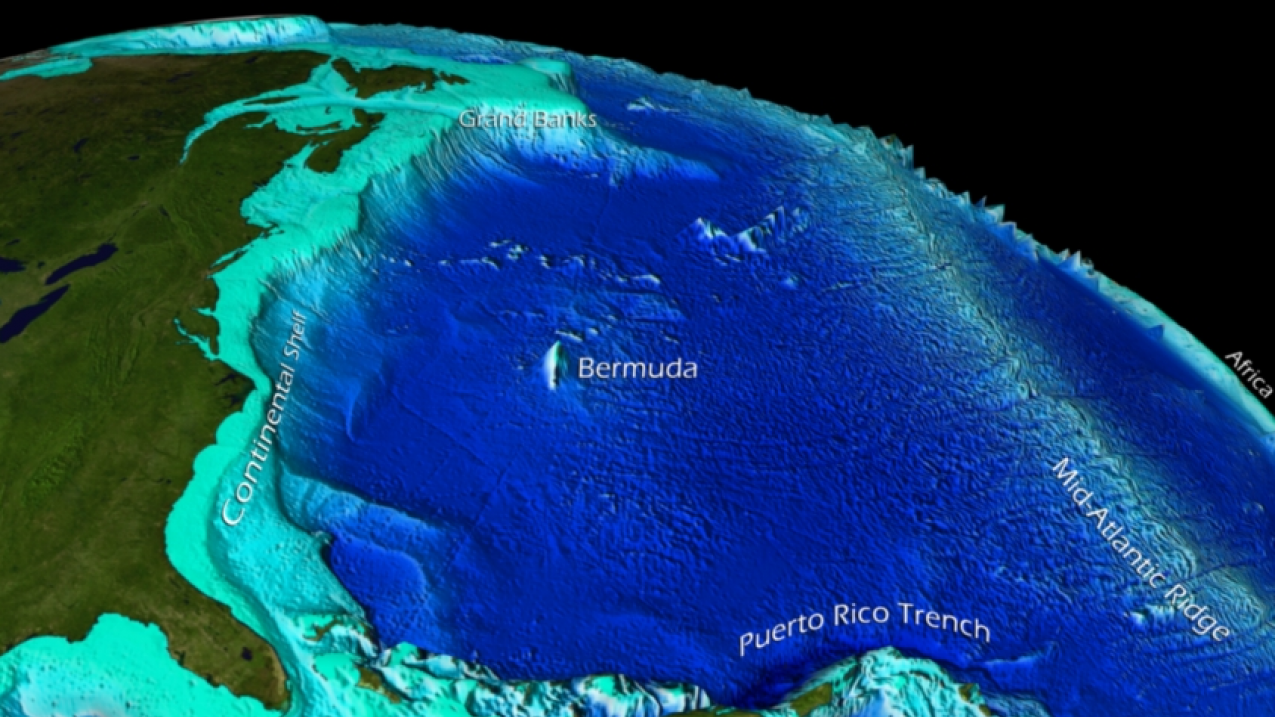
- Mid-Atlantic Ridge: This massive undersea mountain range, running like a spine down the center of the ocean, is a testament to the Earth’s tectonic plates. It marks the boundary where the North American and Eurasian plates, and the South American and African plates, are slowly pulling apart.
- Ocean Trenches: Deep, narrow depressions in the ocean floor, like the Puerto Rico Trench and the Romanche Trench, are formed where tectonic plates collide. These trenches are among the deepest points on Earth.
- Seamounts and Guyots: Isolated volcanic mountains rising from the ocean floor, often with flat tops, these features are remnants of past volcanic activity.
- Abyssal Plains: Vast, flat expanses of the ocean floor, covered in sediments, represent the accumulation of millions of years of deposition.
- Continental Shelves and Slopes: The transition zone between the continents and the deep ocean floor, these features are crucial for marine life and resource exploration.
The Importance of Mapping the Atlantic Ocean:
Mapping the Atlantic’s topography is not just an academic exercise; it holds significant practical applications:
- Navigation: Accurate charts depicting ocean depths and underwater features are essential for safe and efficient marine navigation. This is especially crucial for shipping routes, submarine operations, and underwater exploration.
- Resource Exploration: The ocean floor holds vast reserves of natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals. Topographical maps help identify potential resource deposits, guiding exploration and extraction efforts.
- Environmental Management: Understanding the ocean’s topography is vital for marine conservation and environmental protection. It helps identify areas of unique biodiversity, fragile ecosystems, and potential pollution hotspots.
- Climate Research: The ocean floor plays a crucial role in global climate regulation. Topography influences ocean currents, heat distribution, and carbon cycling. Mapping the ocean floor provides valuable data for understanding and modeling climate change.
- Disaster Preparedness: Topographical maps help predict the impact of tsunamis, storm surges, and other natural disasters. They reveal areas vulnerable to flooding and help guide evacuation efforts.
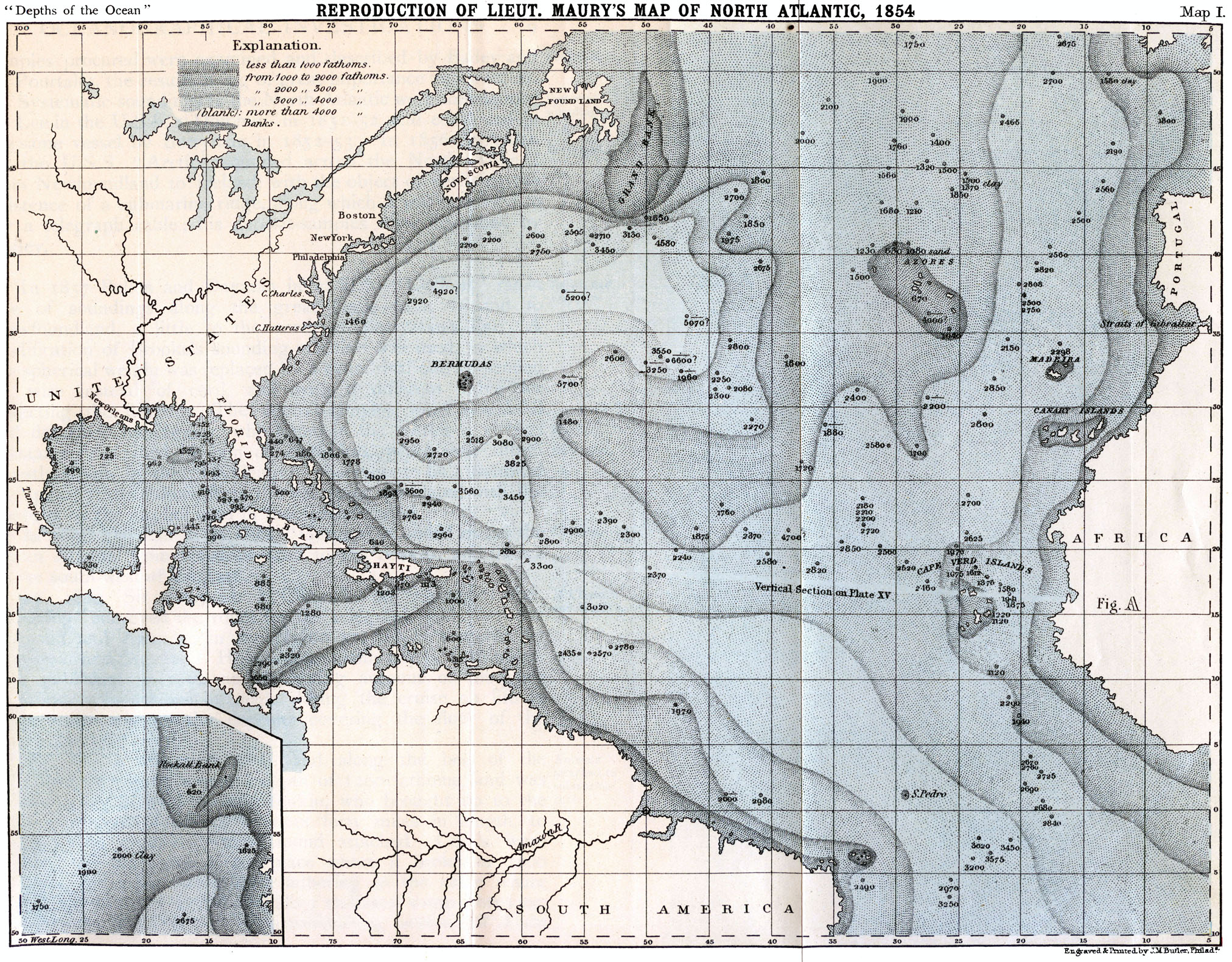
The Evolution of Atlantic Ocean Mapping:
The mapping of the Atlantic Ocean has evolved significantly over time, from rudimentary early attempts to sophisticated modern techniques:
- Early Exploration: Early navigators relied on rudimentary methods like soundings and lead lines to determine ocean depth. These methods were imprecise and limited to shallow waters.
- Echo Sounding: The invention of echo sounding in the early 20th century revolutionized ocean mapping. This technology uses sound waves to measure depth, providing a more accurate and comprehensive picture of the ocean floor.
- Satellite Altimetry: Satellite-based altimetry, developed in the late 20th century, uses radar pulses to measure the height of the ocean surface. This technology allows for mapping the ocean floor over large areas with high accuracy.
- Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs): Modern AUVs equipped with sophisticated sensors and mapping equipment are capable of exploring the ocean floor in detail, providing unprecedented insights into its topography.
FAQs about Topographical Maps of the Atlantic Ocean:
Q: What are the key features of the Atlantic Ocean’s topography?
A: The Atlantic Ocean features a diverse topography, including the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, ocean trenches, seamounts, abyssal plains, and continental shelves and slopes.
Q: How do topographical maps benefit navigation?
A: Topographical maps provide accurate information about ocean depths and underwater features, crucial for safe and efficient navigation of ships and submarines.
Q: What role does ocean topography play in climate change?
A: Ocean topography influences ocean currents, heat distribution, and carbon cycling, making it a vital factor in understanding and modeling climate change.
Q: How are topographical maps used in resource exploration?
A: Topographical maps help identify potential resource deposits like oil, gas, and minerals, guiding exploration and extraction efforts.
Q: What are the latest technologies used in mapping the Atlantic Ocean?
A: Modern technologies like satellite altimetry and autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) provide highly accurate and detailed maps of the ocean floor.
Tips for Understanding Topographical Maps of the Atlantic Ocean:
- Pay attention to the scale: The scale of the map determines the level of detail and the size of features depicted.
- Look for contour lines: Contour lines connect points of equal elevation, revealing the shape of the ocean floor.
- Identify key features: Locate the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, ocean trenches, seamounts, and other prominent features.
- Consider the context: Relate the topographical features to geological processes and their impact on marine life and resources.
Conclusion:
Topographical maps of the Atlantic Ocean are essential tools for understanding the ocean’s complex and dynamic environment. They provide a window into the hidden world beneath the waves, revealing the geological forces that shape the planet and the vital role the ocean plays in global systems. By continuing to explore and map the Atlantic’s depths, we gain valuable insights that inform navigation, resource management, environmental protection, and our understanding of the Earth’s interconnected systems.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Depths: Exploring the Topography of the Atlantic Ocean. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!