Charting The Atlantic: A Comprehensive Exploration Of The Second Largest Ocean
Charting the Atlantic: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Second Largest Ocean
Related Articles: Charting the Atlantic: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Second Largest Ocean
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Charting the Atlantic: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Second Largest Ocean. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Atlantic: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Second Largest Ocean
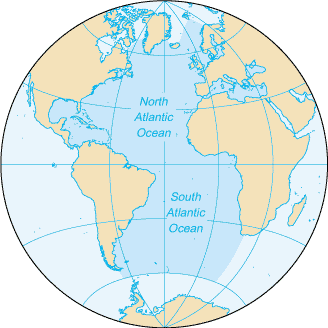
The Atlantic Ocean, the second largest of Earth’s five oceans, stretches across a vast expanse, connecting continents and influencing global weather patterns. Its waters cradle diverse ecosystems, host rich marine life, and have played a pivotal role in human history. Understanding the Atlantic’s physical geography, its dynamic currents, and its complex ecosystems is crucial for comprehending its influence on our planet and the challenges it faces.
A Glimpse into the Atlantic’s Geography:
The Atlantic Ocean’s boundaries are defined by landmasses and water bodies. To the west lies North and South America, while Europe and Africa border it to the east. The Arctic Ocean marks its northern limit, and the Southern Ocean defines its southern boundary. Its vast area of approximately 106,400,000 square kilometers (41,080,000 square miles) encompasses a diverse range of features:
- Mid-Atlantic Ridge: This underwater mountain range, stretching from Iceland to the South Atlantic, is a defining feature of the Atlantic, marking the boundary between the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates. Its volcanic activity creates new ocean floor, driving the continuous process of seafloor spreading.
- Ocean Trenches: Deepest points in the Atlantic, like the Puerto Rico Trench, are formed by the convergence of tectonic plates. These trenches harbor unique ecosystems, adapted to extreme pressure and darkness.
- Continental Shelves: These relatively shallow areas extend from the coastlines, providing habitats for diverse marine life and supporting important fisheries.
- Islands: The Atlantic is dotted with numerous islands, both volcanic and continental, each with its own unique history and ecosystem.
The Atlantic’s Dynamic Currents:
The Atlantic’s surface currents are driven by prevailing winds and the Earth’s rotation, forming a complex network of interconnected currents. These currents play a crucial role in regulating global climate by transporting heat and moisture:
- The Gulf Stream: This warm current, originating in the Gulf of Mexico, carries warm water northward along the eastern coast of North America, moderating the climate of western Europe.
- The North Atlantic Drift: An extension of the Gulf Stream, this current carries warm water across the Atlantic, influencing the climate of northwest Europe.
- The Canary Current: This cool current flows southward along the western coast of Africa, carrying cold water from the north.
- The Benguela Current: Another cool current, flowing northward along the western coast of Africa, supports a rich ecosystem and influences the climate of the region.
A World of Life in the Atlantic:
The Atlantic’s diverse ecosystems support a rich array of marine life, ranging from microscopic plankton to massive whales:
- Plankton: These tiny organisms form the base of the Atlantic’s food web, supporting all other marine life.
- Fish: The Atlantic is home to a vast array of fish species, including tuna, cod, herring, and sharks, many of which are commercially important.
- Whales: The Atlantic is a crucial habitat for various whale species, including humpback whales, blue whales, and sperm whales.
- Sea Turtles: Several species of sea turtles, including loggerhead turtles and leatherback turtles, nest on Atlantic beaches and migrate across the ocean.
- Coral Reefs: While not as extensive as in the Pacific, coral reefs exist in the Atlantic, particularly in the Caribbean Sea, providing vital habitats for marine life.
Challenges Facing the Atlantic:
Despite its vastness and resilience, the Atlantic Ocean faces significant challenges, primarily driven by human activities:
- Climate Change: Rising ocean temperatures and acidification threaten marine ecosystems, impacting coral reefs, fish populations, and other species.
- Pollution: Plastic pollution, oil spills, and chemical runoff from land contaminate the ocean, harming marine life and ecosystems.
- Overfishing: Unsustainable fishing practices deplete fish stocks, disrupting the balance of marine ecosystems.
- Habitat Loss: Coastal development, dredging, and other activities destroy critical habitats for marine life.
The Importance of Understanding the Atlantic:
Understanding the Atlantic Ocean’s geography, currents, ecosystems, and challenges is crucial for several reasons:
- Climate Regulation: The Atlantic’s currents play a vital role in regulating global climate, making it essential to monitor their changes and impacts.
- Marine Conservation: Protecting the Atlantic’s diverse ecosystems and its rich marine life requires understanding their vulnerabilities and the threats they face.
- Sustainable Resource Management: Managing fisheries and other resources sustainably requires knowledge of the ocean’s dynamics and the impacts of human activities.
- Navigation and Transportation: The Atlantic serves as a major shipping route, connecting continents and facilitating global trade.
FAQs about the Atlantic Ocean:
Q: What is the deepest point in the Atlantic Ocean?
A: The deepest point in the Atlantic Ocean is the Puerto Rico Trench, reaching a depth of approximately 8,605 meters (28,232 feet).
Q: What is the average depth of the Atlantic Ocean?
A: The average depth of the Atlantic Ocean is approximately 3,688 meters (12,100 feet).
Q: What are the main currents in the Atlantic Ocean?
A: The main currents in the Atlantic Ocean include the Gulf Stream, the North Atlantic Drift, the Canary Current, and the Benguela Current.
Q: What are the major threats to the Atlantic Ocean?
A: The major threats to the Atlantic Ocean include climate change, pollution, overfishing, and habitat loss.
Q: How can we protect the Atlantic Ocean?
A: Protecting the Atlantic Ocean requires efforts to mitigate climate change, reduce pollution, manage fisheries sustainably, and conserve habitats.
Tips for Understanding the Atlantic Ocean:
- Explore interactive maps and oceanographic data: Websites and applications provide detailed information on the Atlantic’s geography, currents, and ecosystems.
- Read books and articles about oceanography and marine biology: Gaining knowledge about the Atlantic’s science will deepen your understanding.
- Support organizations dedicated to ocean conservation: Contribute to organizations working to protect the Atlantic’s health and resources.
- Reduce your own environmental footprint: Make conscious choices to minimize your impact on the ocean, such as reducing plastic use and supporting sustainable seafood.
Conclusion:
The Atlantic Ocean, a vast and dynamic body of water, plays a vital role in shaping our planet and supporting life. Understanding its geography, currents, ecosystems, and challenges is crucial for protecting its health and ensuring its continued role in sustaining life on Earth. By embracing knowledge, promoting responsible stewardship, and fostering a sense of global responsibility, we can ensure the Atlantic Ocean remains a vibrant and healthy part of our planet for generations to come.



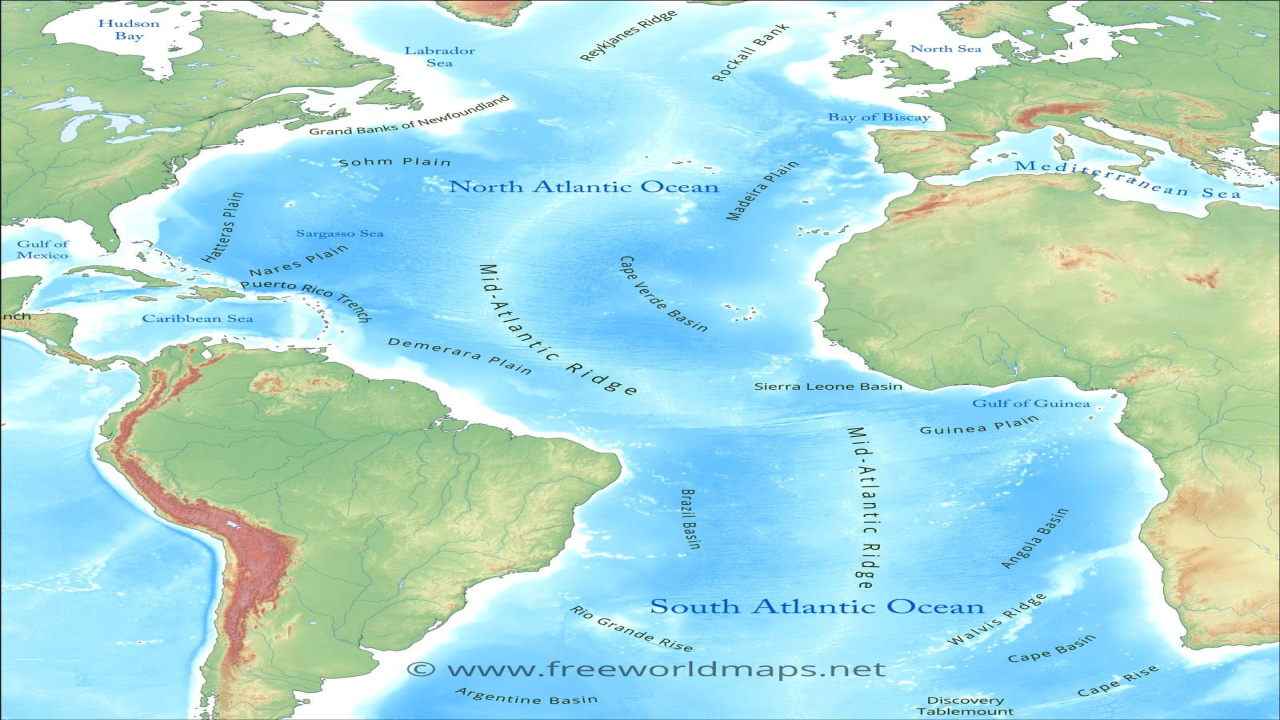

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Atlantic: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Second Largest Ocean. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!