A Majestic Spine: The Atlas Mountains On The World Map
A Majestic Spine: The Atlas Mountains on the World Map
Related Articles: A Majestic Spine: The Atlas Mountains on the World Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Majestic Spine: The Atlas Mountains on the World Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Majestic Spine: The Atlas Mountains on the World Map

The Atlas Mountains, a formidable chain of peaks that stretches across northwestern Africa, are a defining feature of the continent’s geography and a testament to the dynamic forces shaping the Earth’s crust. Understanding their location on the world map unlocks insights into their geological significance, ecological diversity, cultural influence, and economic potential.
A Tapestry of Mountains:
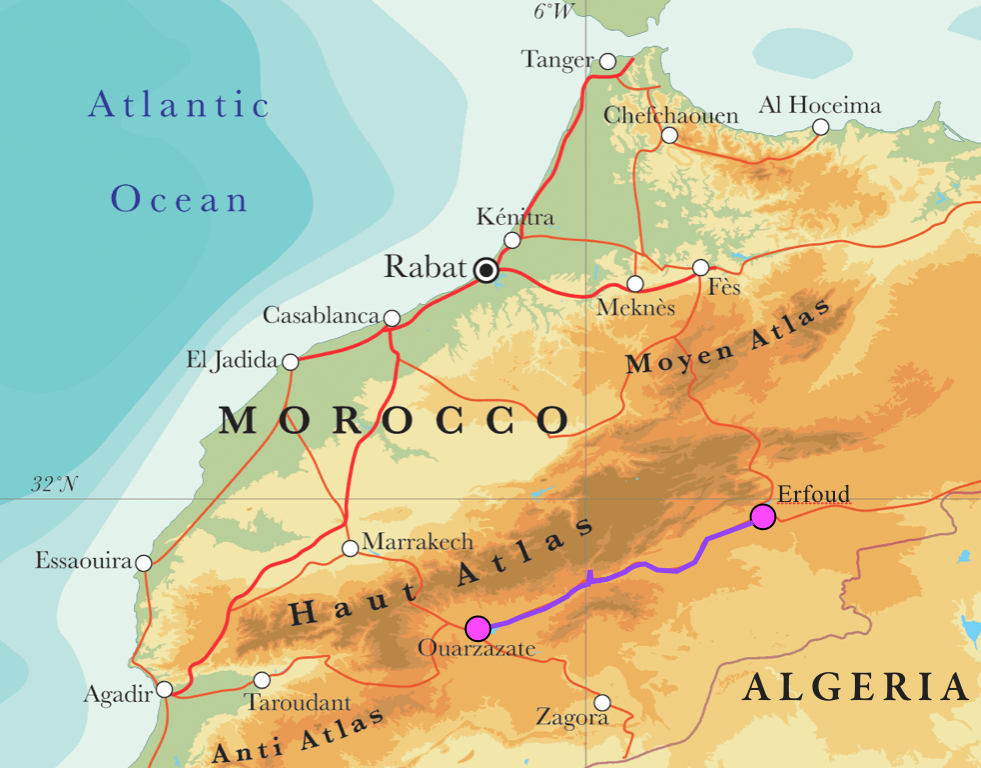
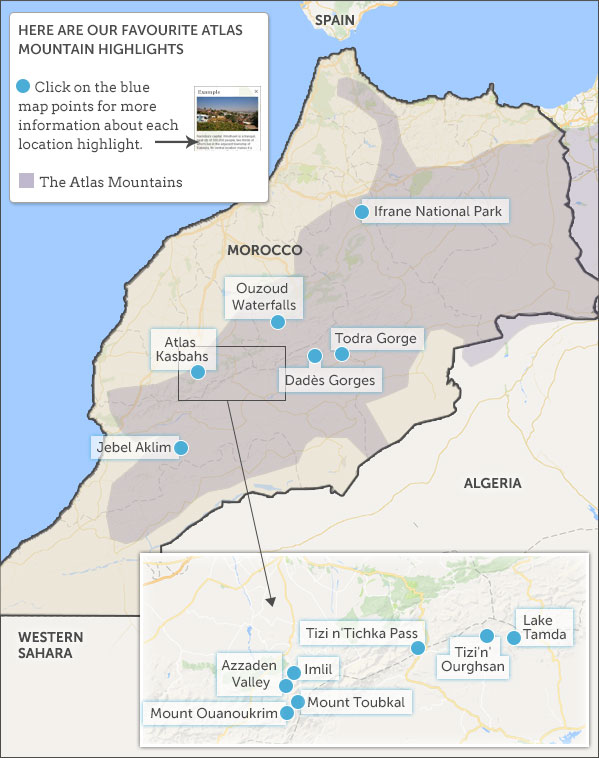
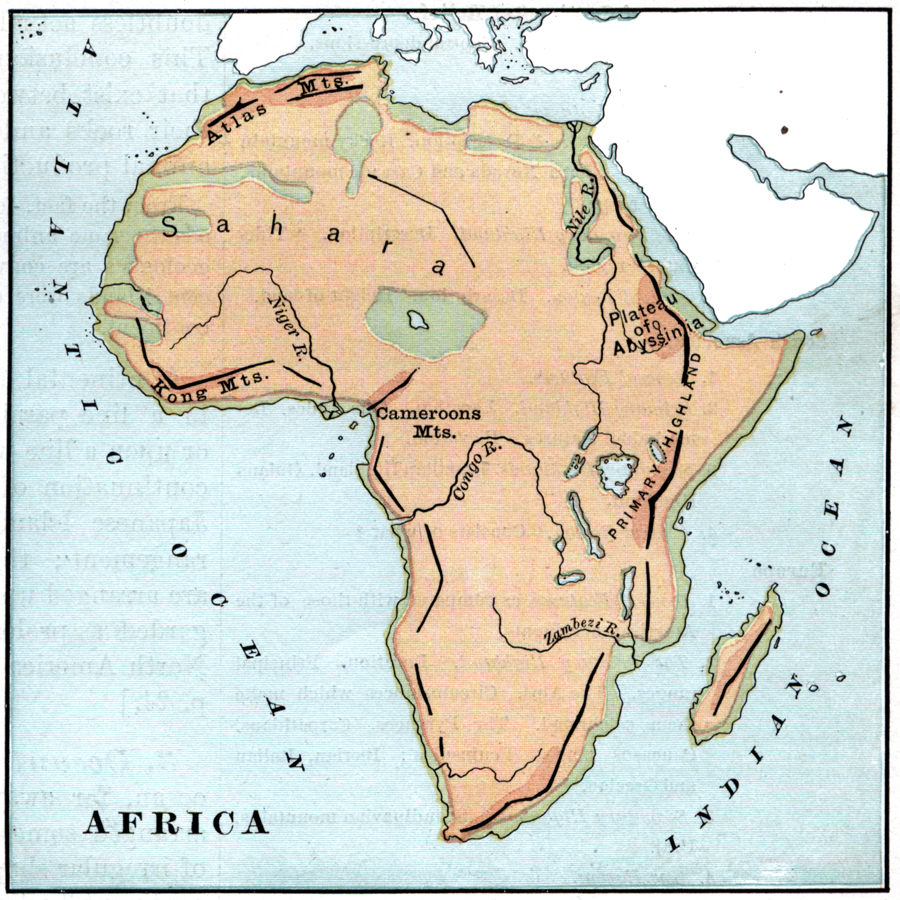
The Atlas Mountains extend for over 2,000 kilometers, spanning Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. They are a complex system of ranges, plateaus, and valleys, divided into three main sections:
- The High Atlas: The most prominent and highest range, reaching an elevation of 4,167 meters at Mount Toubkal, Morocco’s highest peak.
- The Middle Atlas: Located north of the High Atlas, characterized by gentler slopes and a lower elevation.
- The Anti-Atlas: Situated southwest of the High Atlas, known for its rugged terrain and ancient rock formations.
Geological Origins and Tectonic Significance:
The Atlas Mountains are the result of a collision between the African and Eurasian tectonic plates, a process that began millions of years ago. As these plates converged, the African plate buckled and folded, pushing up the landmass to form the towering peaks we see today. This geological history is evident in the diverse rock formations, including limestone, sandstone, and granite, that make up the mountain ranges.
Ecological Diversity and Biodiversity:
The Atlas Mountains are a haven for biodiversity, supporting a wide range of ecosystems and a rich tapestry of flora and fauna. The lower slopes are characterized by Mediterranean forests, while higher elevations feature alpine meadows and grasslands. The mountains are home to numerous endemic species, including the Barbary macaque, the Atlas cedar, and the Atlas blue sheep, highlighting their unique ecological significance.
Cultural Significance and Historical Legacy:
The Atlas Mountains have played a crucial role in shaping the cultures and histories of the surrounding regions. Berber communities, known for their traditional way of life, have inhabited these mountains for centuries, preserving their distinct customs, languages, and traditions. The Atlas Mountains have also served as a natural barrier, influencing trade routes and political boundaries throughout history.
Economic Importance and Resources:
The Atlas Mountains offer a range of economic opportunities, from agriculture and forestry to tourism and mining. The fertile valleys and slopes provide suitable land for farming, while the forests offer valuable timber resources. The mountains also attract tourists drawn to their stunning scenery, diverse wildlife, and cultural heritage. Mining activities, particularly for phosphates and iron ore, are also significant in the region.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The Atlas Mountains face a number of challenges, including climate change, deforestation, and unsustainable land use practices. These threats pose a risk to the ecological integrity and biodiversity of the region. However, there are also opportunities for sustainable development, such as promoting ecotourism, supporting local communities, and implementing conservation measures to protect the unique natural resources of the Atlas Mountains.
FAQs:
Q: What is the highest peak in the Atlas Mountains?
A: Mount Toubkal in Morocco, with an elevation of 4,167 meters.
Q: What countries do the Atlas Mountains span?
A: Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia.
Q: What is the geological origin of the Atlas Mountains?
A: They were formed by the collision of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing the Atlas Mountains?
A: Climate change, deforestation, and unsustainable land use practices.
Q: What are some of the economic opportunities presented by the Atlas Mountains?
A: Agriculture, forestry, tourism, and mining.
Tips:
- Explore the High Atlas: Hike to the summit of Mount Toubkal or explore the stunning valleys and gorges.
- Visit the Middle Atlas: Discover the Berber villages and the cedar forests.
- Experience the Anti-Atlas: Explore the ancient rock formations and the desert landscapes.
- Learn about the Berber culture: Visit traditional villages and learn about their customs and traditions.
- Support sustainable tourism: Choose eco-friendly accommodations and participate in activities that benefit local communities.
Conclusion:
The Atlas Mountains, a defining feature of northwestern Africa, are a testament to the Earth’s dynamic geological processes and a source of ecological, cultural, and economic significance. Their location on the world map highlights their importance as a region of diverse landscapes, rich biodiversity, and rich cultural heritage. Understanding the Atlas Mountains and the challenges they face is crucial for ensuring their sustainable future and preserving the unique natural and cultural treasures they hold.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Majestic Spine: The Atlas Mountains on the World Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!