A Journey Through The Atlas Mountains: A Geographic Exploration
A Journey Through the Atlas Mountains: A Geographic Exploration
Related Articles: A Journey Through the Atlas Mountains: A Geographic Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through the Atlas Mountains: A Geographic Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through the Atlas Mountains: A Geographic Exploration
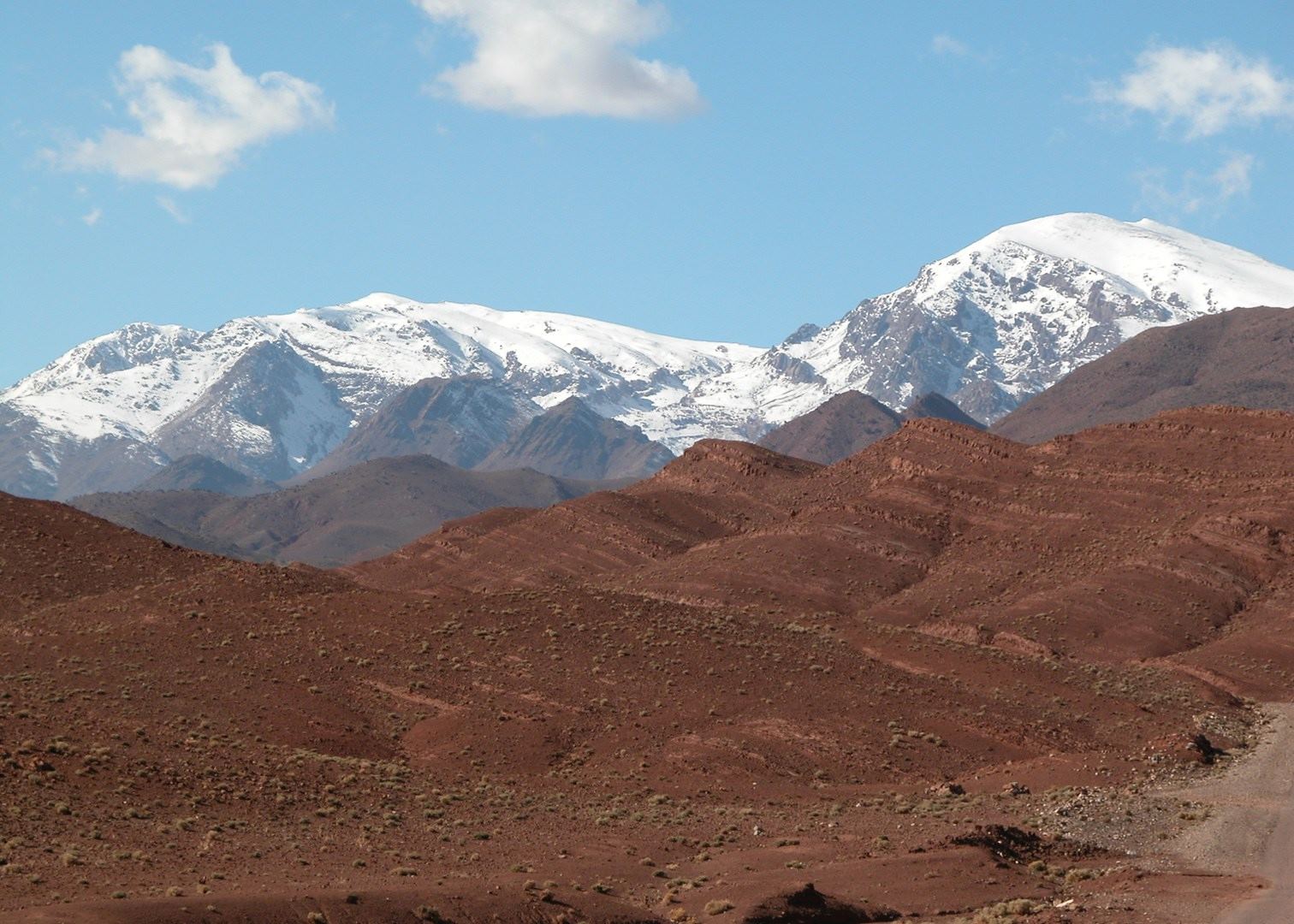
The Atlas Mountains, a formidable range that dominates the landscape of Northwest Africa, stand as a testament to the Earth’s geological dynamism. Spanning across Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia, this mountain range is a remarkable geographical feature, offering a diverse landscape of towering peaks, fertile valleys, and arid deserts.
A Geographic Perspective:
The Atlas Mountains, extending for approximately 2,500 kilometers, are a prominent feature on the map of North Africa. They are a young mountain range, geologically speaking, formed during the Tertiary Period through the collision of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates. This collision resulted in the uplift of the landmass, creating the dramatic peaks and valleys that characterize the Atlas.
Locating the Atlas on a Map:
To understand the Atlas Mountains’ location, one must first visualize the geography of Northwest Africa. The range stretches across three countries, with each section possessing distinct characteristics.
-
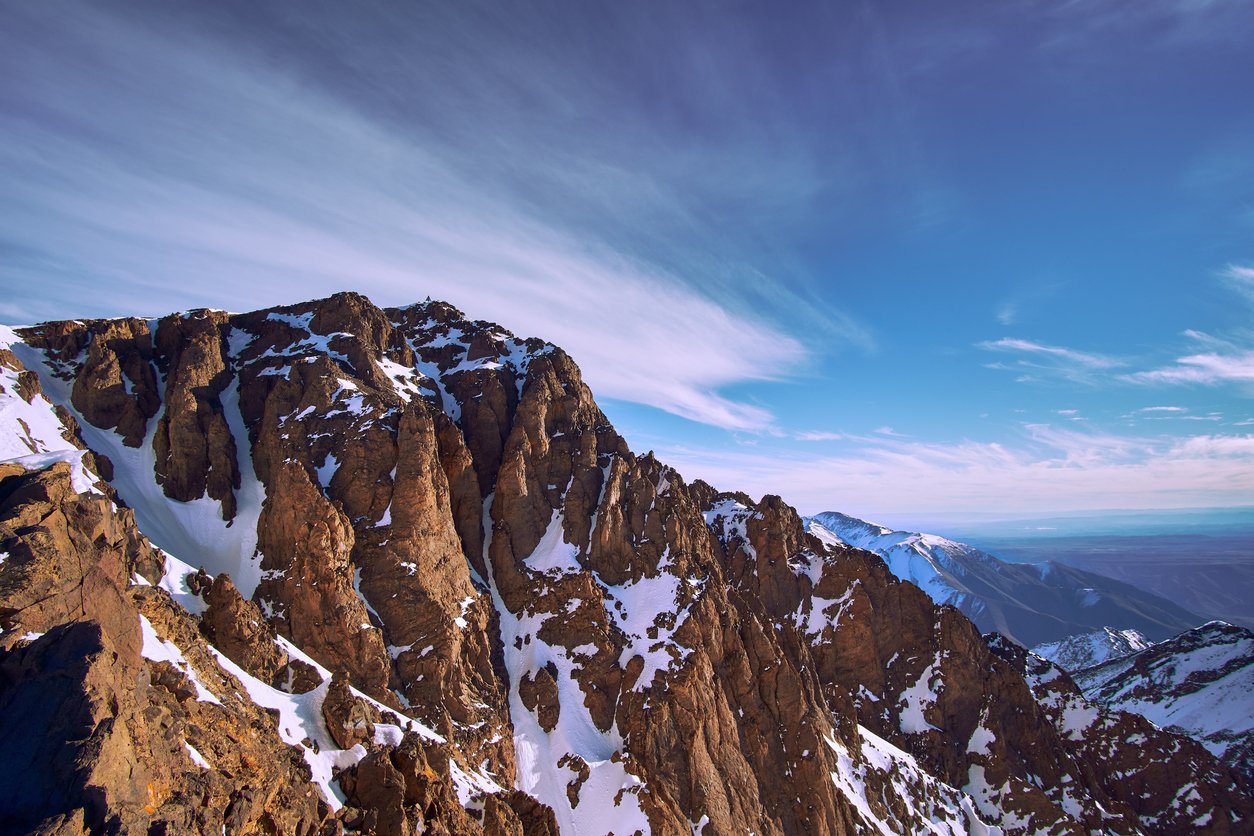
The High Atlas: This section, the highest and most prominent part of the range, lies primarily in Morocco. It is home to the highest peak in North Africa, Mount Toubkal, reaching an impressive elevation of 4,167 meters. The High Atlas stretches from the Atlantic coast in the west to the Sahara Desert in the east, forming a natural barrier between the Mediterranean climate of the north and the arid climate of the south.
-
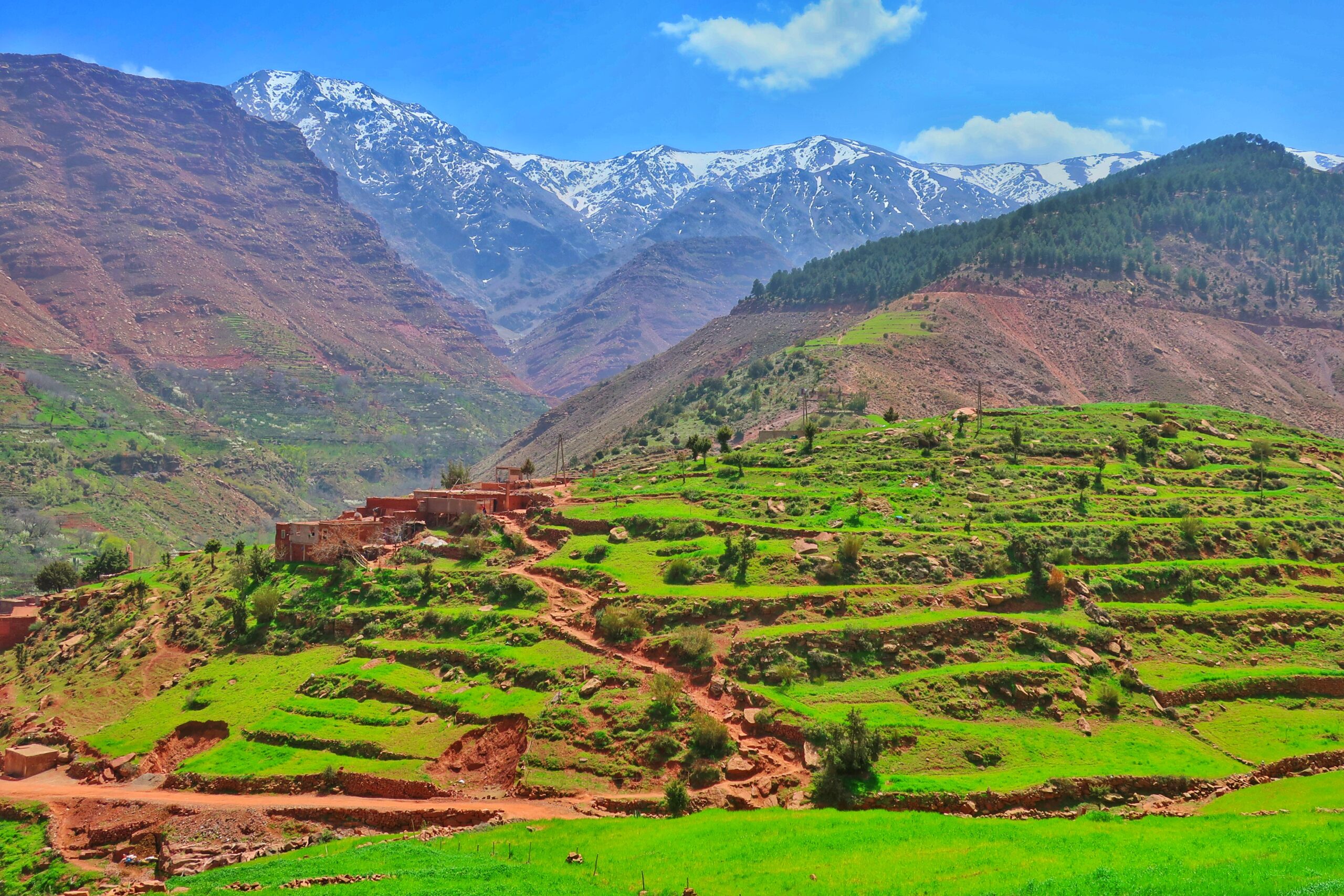
The Middle Atlas: This section, located in the north-central part of Morocco, is less elevated than the High Atlas. It features rolling hills, plateaus, and forested areas. The Middle Atlas is known for its cedar forests and its rich biodiversity.
-
The Anti-Atlas: Situated in southwestern Morocco, the Anti-Atlas is a lower and older section of the range. It is characterized by its rugged, eroded terrain and its distinctive red sandstone formations.
-
The Saharan Atlas: This section, extending across Algeria and Tunisia, is the easternmost part of the range. It is characterized by its arid climate and its role as a transition zone between the Atlas Mountains and the Sahara Desert.
Beyond the Map: The Significance of the Atlas Mountains:
The Atlas Mountains are not merely a geographical feature; they are a vital component of the North African ecosystem and a source of cultural and economic significance.
Ecological Importance:
- Biodiversity Hotspot: The Atlas Mountains are a biodiversity hotspot, harboring a wide range of flora and fauna, including endemic species found nowhere else on Earth.
- Water Resource: The Atlas Mountains are a crucial source of water for North Africa. They act as a natural reservoir, capturing rainfall and feeding rivers and streams that irrigate surrounding areas.
- Climate Regulation: The mountains play a significant role in regulating the climate of North Africa. They act as a barrier, blocking moisture-laden winds from the Atlantic and Mediterranean, creating distinct microclimates within their valleys and slopes.
Cultural and Economic Significance:
- Berber Culture: The Atlas Mountains have been home to the Berber people for centuries. Their unique culture, traditions, and language have been shaped by the rugged landscape and the challenges of living in a mountainous environment.
- Tourism: The Atlas Mountains are a popular destination for tourists seeking adventure, cultural immersion, and stunning natural beauty. The mountains offer opportunities for hiking, trekking, skiing, and exploring ancient villages and Berber communities.
- Natural Resources: The Atlas Mountains are rich in natural resources, including minerals, timber, and fertile land. These resources contribute significantly to the economies of the countries they traverse.
FAQs:
-
Q: What is the highest peak in the Atlas Mountains?
A: The highest peak in the Atlas Mountains is Mount Toubkal, located in the High Atlas of Morocco, reaching a height of 4,167 meters.
-
Q: What countries do the Atlas Mountains traverse?
A: The Atlas Mountains extend across Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia.
-
Q: Are the Atlas Mountains a popular tourist destination?
A: Yes, the Atlas Mountains are a popular tourist destination, offering opportunities for hiking, trekking, skiing, and cultural immersion.
-
Q: What is the climate like in the Atlas Mountains?
A: The climate in the Atlas Mountains varies depending on altitude and location. The higher peaks experience snow and cold temperatures, while the lower valleys have a more Mediterranean climate.
-
Q: What is the significance of the Atlas Mountains for the Berber people?
A: The Atlas Mountains have been home to the Berber people for centuries. Their culture, traditions, and language are deeply intertwined with the mountainous landscape.
Tips for Exploring the Atlas Mountains:
- Plan your trip in advance: The Atlas Mountains are a vast and diverse region, requiring careful planning. Research different areas, choose suitable activities, and ensure you have the necessary permits and equipment.
- Be prepared for varying weather conditions: The weather in the Atlas Mountains can change rapidly. Pack for all seasons, including warm clothing, rain gear, and sturdy footwear.
- Respect local culture and traditions: The Atlas Mountains are home to a rich and diverse culture. Be respectful of local customs, traditions, and way of life.
- Hire a local guide: A local guide can provide valuable insights into the region, its history, culture, and natural wonders. They can also help with navigation, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience.
- Consider the environment: Be mindful of the environment while exploring the mountains. Pack out all your trash, avoid disturbing wildlife, and stay on designated trails.
Conclusion:
The Atlas Mountains are a magnificent geographical feature, offering a unique blend of natural beauty, cultural richness, and ecological significance. From the towering peaks of the High Atlas to the rolling hills of the Middle Atlas, this mountain range provides a captivating glimpse into the diverse landscape and history of North Africa. Understanding the Atlas Mountains’ location and significance allows us to appreciate their role in shaping the region’s environment, culture, and economy. As a testament to the Earth’s geological processes, the Atlas Mountains continue to inspire and captivate those who venture into their rugged and breathtaking terrain.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through the Atlas Mountains: A Geographic Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!