A Journey Through Asia: Unveiling The Continent’s Geographic Tapestry
A Journey Through Asia: Unveiling the Continent’s Geographic Tapestry
Related Articles: A Journey Through Asia: Unveiling the Continent’s Geographic Tapestry
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Asia: Unveiling the Continent’s Geographic Tapestry. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Asia: Unveiling the Continent’s Geographic Tapestry

The world atlas map of Asia, a vibrant tapestry of diverse landscapes, cultures, and histories, holds a unique position in global cartography. It serves as a visual gateway to a continent that encompasses nearly one-third of the Earth’s landmass, home to the world’s largest population and a breathtaking spectrum of geographical features. This map is more than just a collection of lines and labels; it is a portal to understanding the complexities and intricacies of the Asian continent.
A Continent of Contrasts: Navigating the Geographic Landscape
Asia’s geographical diversity is staggering, encompassing towering mountain ranges, vast plains, fertile river valleys, arid deserts, and sprawling coastlines. The map reveals the continent’s defining physical features:
- The Himalayas: A formidable mountain range that stretches across the northern border of India, Nepal, Bhutan, and China, marking the world’s highest peaks, including Mount Everest.
- The Tibetan Plateau: A high-altitude plateau, known as the "Roof of the World," that covers much of western China and forms the headwaters of major Asian rivers.
- The Siberian Plain: A vast, flat expanse in northern Russia, characterized by its cold climate and abundant natural resources.
- The Indus River Valley: A fertile plain in Pakistan, home to one of the world’s oldest civilizations.
- The Ganges River Delta: A densely populated region in India and Bangladesh, known for its fertile agricultural land and rich cultural heritage.
- The Southeast Asian Islands: A chain of islands stretching from Myanmar to Indonesia, characterized by their tropical climate, volcanic landscapes, and diverse biodiversity.
- The Arabian Peninsula: A vast desert region in the Middle East, home to the world’s largest oil reserves.
Beyond these prominent features, the map unveils a myriad of smaller, equally important geographical elements. From the volcanic peaks of Japan to the vast steppes of Central Asia, each region offers a unique glimpse into the continent’s diverse landscape.
A Mosaic of Cultures: Exploring the Human Landscape
The world atlas map of Asia is not just a representation of physical geography; it also serves as a visual guide to the continent’s rich cultural tapestry. The map reveals the diverse ethnicities, languages, religions, and traditions that shape the Asian landscape:
- The Indian Subcontinent: Home to a vibrant blend of cultures, religions, and languages, including Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, Sikhism, and Christianity.
- East Asia: A region characterized by its Confucian values, strong family ties, and advanced technological development.
- Southeast Asia: A melting pot of cultures, influenced by Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, and Christianity, with a strong emphasis on community and family.
- Central Asia: A region with a rich history of nomadic cultures, influenced by Islam and Persian traditions.
- The Middle East: A region with a long history of trade and cultural exchange, known for its Islamic heritage and diverse ethnicities.
The map underscores the interconnectedness of these diverse cultures, highlighting the historical and contemporary flows of people, ideas, and goods across the continent.
A Journey Through Time: Unveiling the Historical Landscape
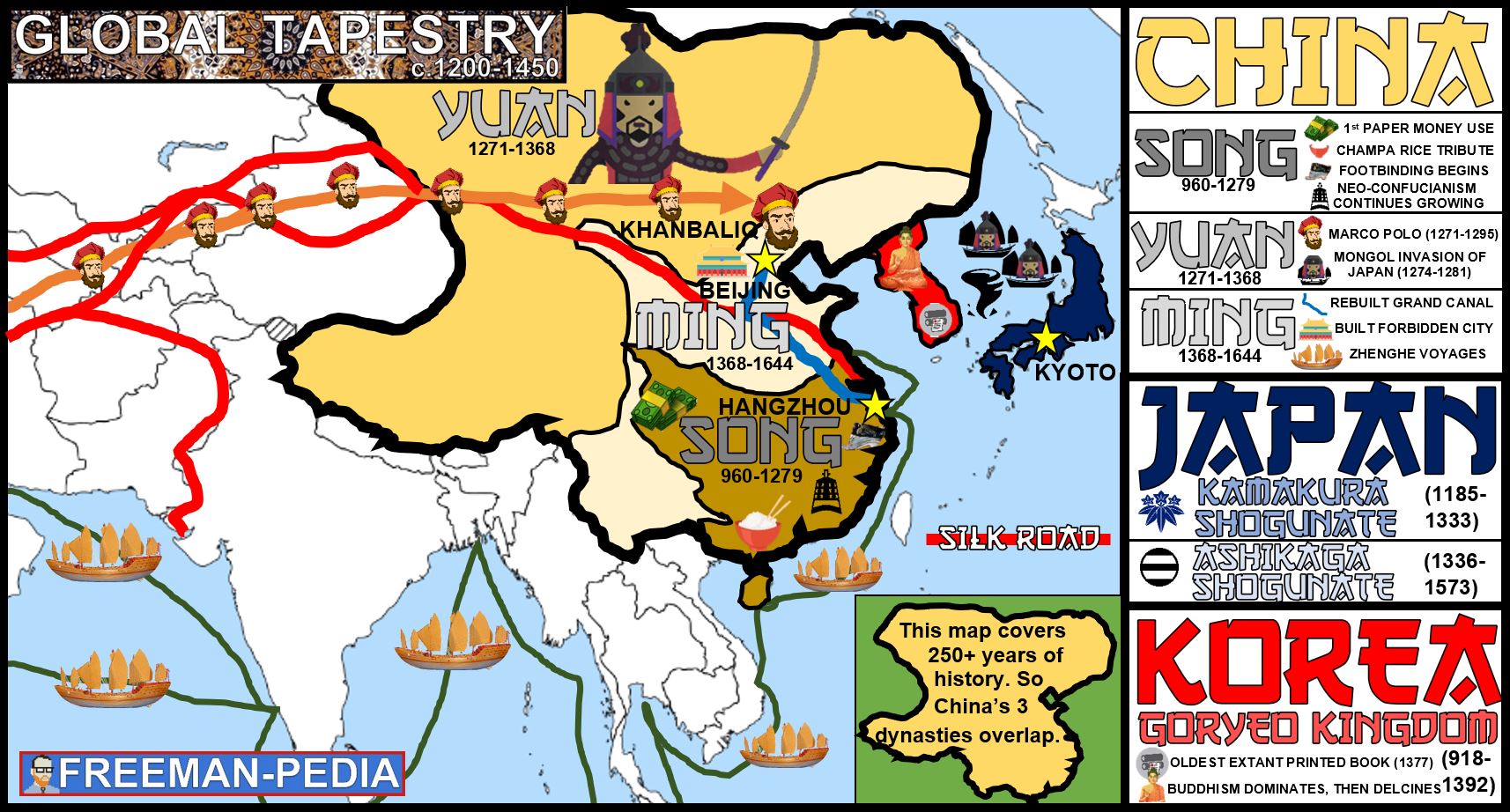
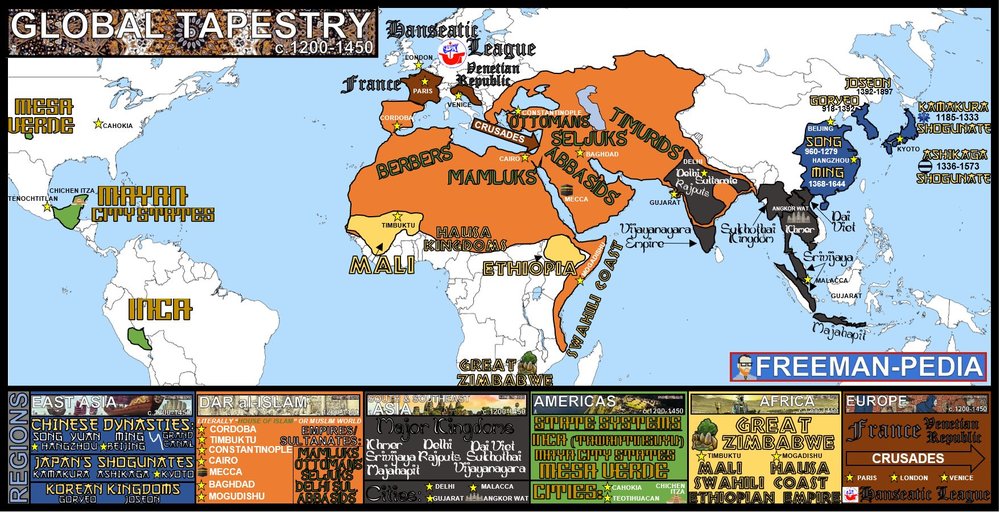
The world atlas map of Asia is also a historical document, revealing the continent’s long and complex past. It showcases the rise and fall of empires, the development of major trade routes, and the evolution of cultural centers:
- The Silk Road: A network of trade routes that connected the East and West for centuries, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- The Mongol Empire: One of the largest empires in history, spanning from Eastern Europe to Southeast Asia, leaving a lasting impact on the cultural and political landscape of Asia.
- The British Raj: The British colonial rule in India, which had a profound impact on the political, economic, and social landscape of the subcontinent.
- The Cold War: A period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union, which had a significant impact on the political and economic landscape of Asia.
The map serves as a reminder of the historical forces that have shaped the continent, highlighting the interconnectedness of past and present.
The Importance of the World Atlas Map of Asia
The world atlas map of Asia is an invaluable tool for understanding the continent’s geography, culture, and history. It provides a visual framework for:
- Education: The map is an essential resource for students and educators, providing a comprehensive overview of the continent’s physical, cultural, and historical features.
- Research: Researchers across various disciplines, from geography and history to political science and economics, rely on the map to gain insights into the Asian landscape and its complexities.
- Global Awareness: The map promotes global awareness by highlighting the diversity and interconnectedness of the Asian continent, fostering understanding and appreciation of different cultures.
- Decision-Making: Policymakers and business leaders use the map to understand the geopolitical landscape of Asia, inform strategic decisions, and navigate the complexities of the region.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the major geographical features of Asia?
Asia is home to a diverse range of geographical features, including the Himalayas, the Tibetan Plateau, the Siberian Plain, the Indus River Valley, the Ganges River Delta, the Southeast Asian Islands, and the Arabian Peninsula.
2. What are the major cultural regions of Asia?
Asia is home to a wide range of cultures, including the Indian Subcontinent, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Central Asia, and the Middle East.
3. What are some of the major historical events that have shaped Asia?
Some of the major historical events that have shaped Asia include the Silk Road, the Mongol Empire, the British Raj, and the Cold War.
4. What are the benefits of using a world atlas map of Asia?
A world atlas map of Asia is a valuable tool for education, research, global awareness, and decision-making.
5. What are some tips for using a world atlas map of Asia?
When using a world atlas map of Asia, it is important to pay attention to the scale, the legend, and the different types of information presented. It is also helpful to use the map in conjunction with other resources, such as books, articles, and websites.
Conclusion
The world atlas map of Asia is an essential tool for navigating the continent’s complex geography, culture, and history. It serves as a visual gateway to understanding the diverse landscapes, vibrant cultures, and rich history that make Asia a unique and fascinating region of the world. By providing a comprehensive overview of the continent’s physical, cultural, and historical features, the map fosters global awareness, promotes understanding, and informs decision-making.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Asia: Unveiling the Continent’s Geographic Tapestry. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!