A Geographic Tapestry: Understanding The Border Between South Dakota And Montana
A Geographic Tapestry: Understanding the Border Between South Dakota and Montana
Related Articles: A Geographic Tapestry: Understanding the Border Between South Dakota and Montana
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Tapestry: Understanding the Border Between South Dakota and Montana. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Tapestry: Understanding the Border Between South Dakota and Montana

The border between South Dakota and Montana is more than just a line on a map. It is a physical and cultural boundary that has shaped the history, environment, and communities of both states. This border, etched across the vast landscapes of the Great Plains and the rugged peaks of the Rocky Mountains, is a testament to the interplay of nature and human endeavor.
A Border Defined by Geography and History
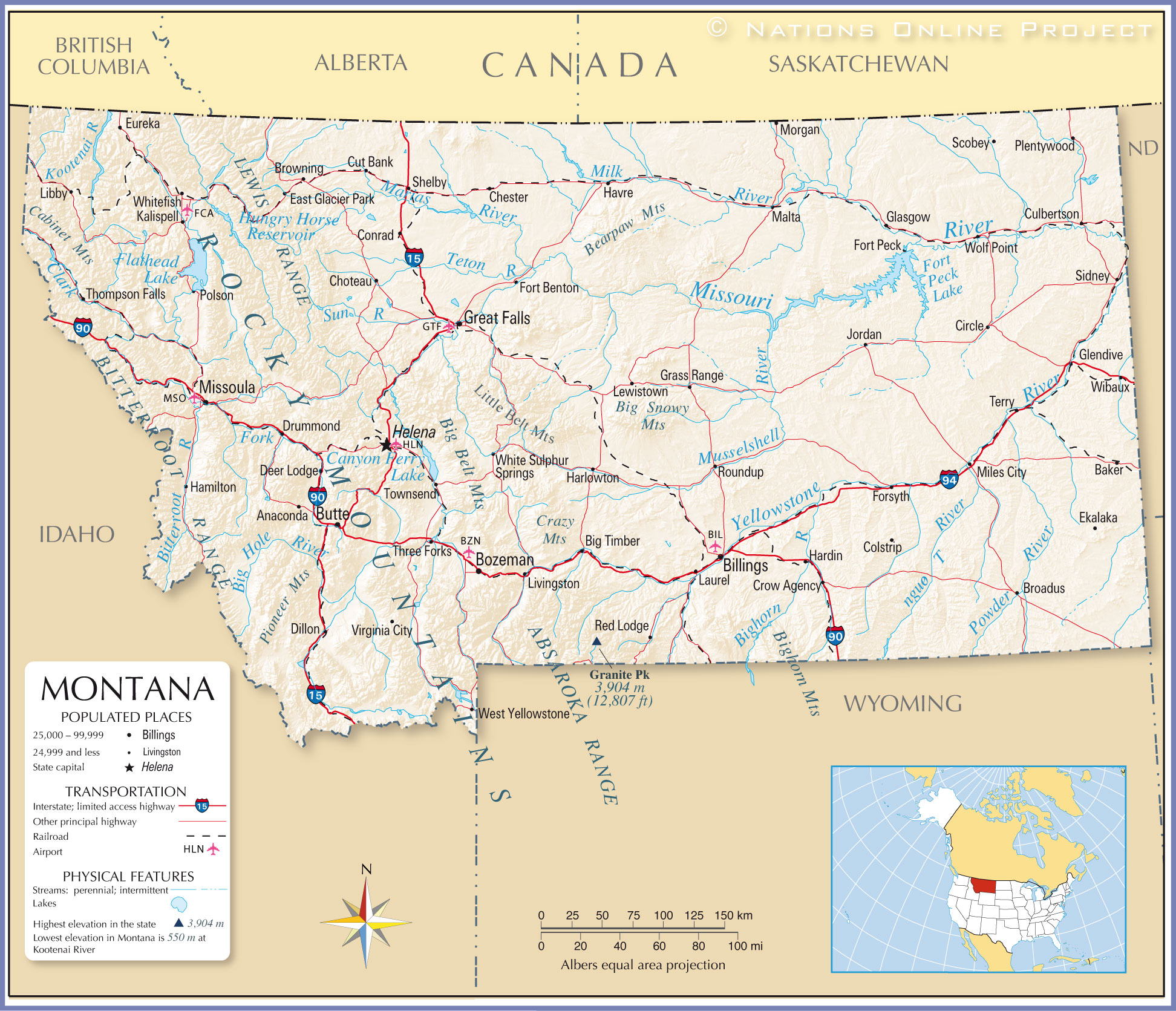
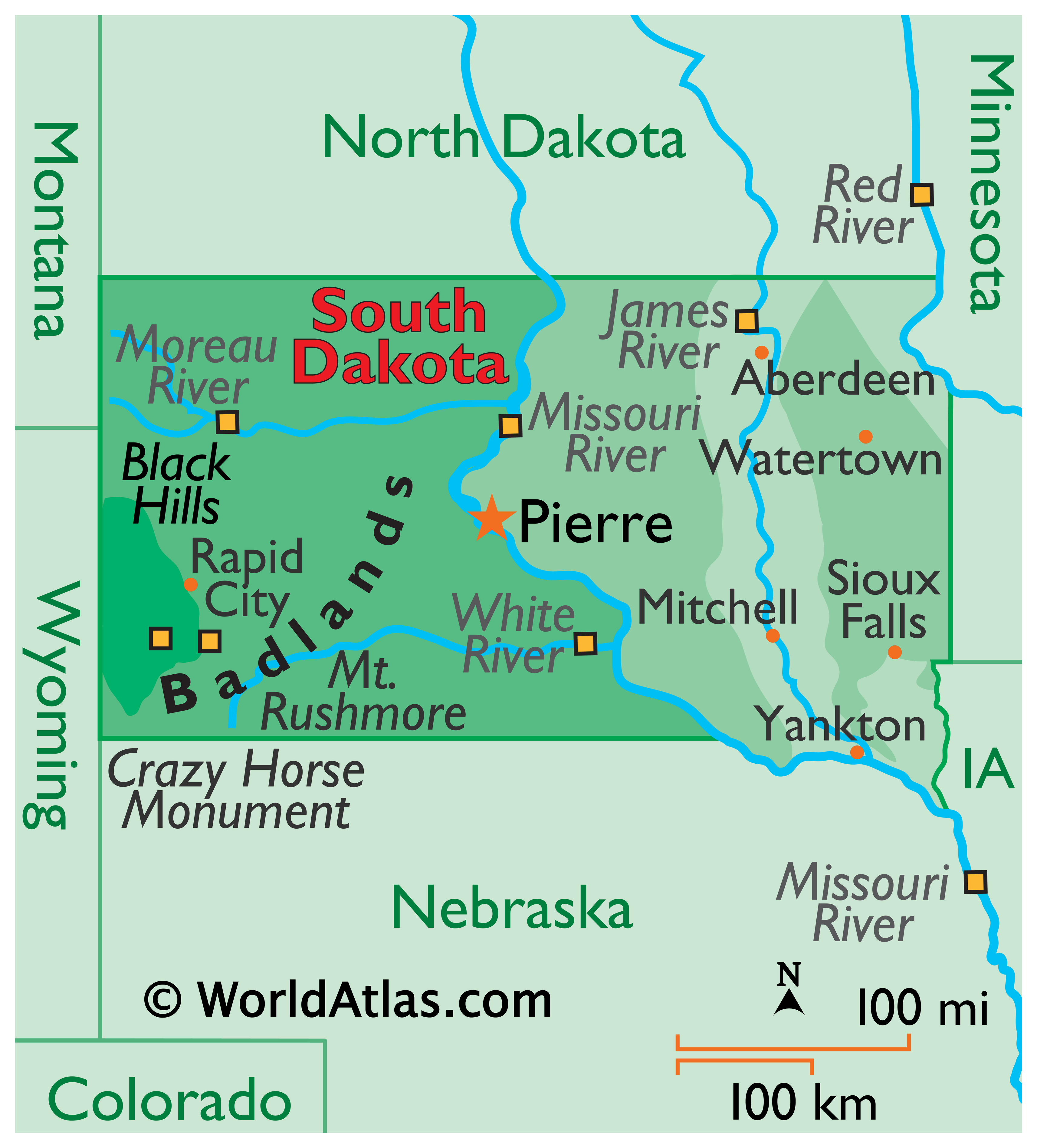
The South Dakota-Montana border traces a complex path, reflecting the natural features and historical events that have shaped the region. The most prominent feature is the Missouri River, which serves as a natural boundary for much of the border’s length. The river’s course, meandering through the heartland, has played a pivotal role in the settlement and development of both states.
Beyond the Missouri, the border extends westward through the rugged terrain of the Black Hills, encompassing the iconic Mount Rushmore National Memorial. This section of the border showcases the dramatic contrast between the rolling plains and the majestic mountain ranges, highlighting the geological diversity of the region.
The historical significance of the border is equally compelling. The establishment of the border in the late 19th century coincided with the westward expansion of the United States, a period marked by Native American displacement and the influx of settlers. The border became a dividing line between different cultures and ways of life, impacting the social and economic landscape of both states.
The Importance of the Border: A Crossroads of Culture and Ecology
The South Dakota-Montana border is not merely a geographical divide; it is a vital corridor for wildlife migration, cultural exchange, and economic activity. The region’s diverse ecosystems, ranging from grasslands and forests to the high alpine meadows of the Rocky Mountains, support a rich tapestry of flora and fauna.
The border serves as a critical migratory route for numerous species, including elk, deer, and pronghorn antelope. The presence of these animals underscores the interconnectedness of the region’s ecosystems and the need for collaborative conservation efforts between the two states.
The border also facilitates cultural exchange between the communities of South Dakota and Montana. The shared history and heritage of the region have fostered a strong sense of connection between the residents of both states. The border region is home to numerous Native American tribes, whose cultural traditions and perspectives continue to shape the identity of the area.
Economic Interdependence and Shared Resources
The South Dakota-Montana border is a hub of economic activity, with both states relying on the shared resources and infrastructure of the region. The agriculture industry, particularly cattle ranching, is a major contributor to the economies of both states, with ranchers utilizing the vast grasslands and open spaces of the border region.
The energy sector also plays a significant role in the border’s economy, with the extraction of oil and natural gas contributing to the economic well-being of both states. The development of energy resources necessitates collaboration between South Dakota and Montana, ensuring the efficient and sustainable management of these shared assets.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the South Dakota-Montana border presents numerous opportunities, it also faces challenges, such as the need for sustainable development, environmental protection, and the preservation of cultural heritage. The region’s unique ecosystems are vulnerable to climate change, habitat fragmentation, and invasive species, requiring coordinated efforts to mitigate these threats.
The preservation of Native American cultural sites and traditions is another crucial challenge. The border region is rich in archaeological and cultural resources, necessitating the development of strategies to protect these sites and ensure the continuation of Native American cultural practices.
Understanding the Border: A Key to Informed Decision-Making
A comprehensive understanding of the South Dakota-Montana border is essential for informed decision-making in the areas of resource management, environmental protection, and cultural preservation. By recognizing the interconnectedness of the region’s ecosystems, the importance of cultural exchange, and the need for collaboration between the states, we can foster a sustainable and prosperous future for the border region.
FAQs
1. What are the major cities and towns located on the South Dakota-Montana border?
The major cities and towns located on the South Dakota-Montana border include:
- South Dakota: Belle Fourche, Spearfish, Sturgis, Rapid City
- Montana: Miles City, Billings, Glendive
2. What are the main industries located in the border region?
The main industries in the border region include:
- Agriculture (cattle ranching, farming)
- Energy (oil and natural gas extraction)
- Tourism (Mount Rushmore, Black Hills National Forest, Badlands National Park)
3. What are some of the environmental challenges facing the border region?
The border region faces environmental challenges such as:
- Climate change
- Habitat fragmentation
- Invasive species
- Water scarcity
4. How does the border region contribute to the cultural heritage of both states?
The border region is home to numerous Native American tribes, whose cultural traditions and perspectives continue to shape the identity of the area. The region also has a rich history of ranching and frontier life, which has contributed to the cultural identity of both South Dakota and Montana.
5. What are some of the opportunities for collaboration between South Dakota and Montana in the border region?
Opportunities for collaboration between South Dakota and Montana in the border region include:
- Joint conservation efforts to protect shared ecosystems
- Economic development initiatives to promote tourism and industry
- Cultural exchange programs to foster understanding and appreciation of shared heritage
Tips
- Visit the border region: Experience the diverse landscapes and cultural heritage of the South Dakota-Montana border firsthand.
- Learn about the history of the region: Explore the historical events and figures that have shaped the border and its communities.
- Support local businesses and organizations: Contribute to the economic vitality and cultural richness of the border region.
- Engage in conservation efforts: Participate in initiatives to protect the region’s unique ecosystems and wildlife.
- Promote cultural exchange: Foster understanding and appreciation of the shared heritage of South Dakota and Montana.
Conclusion
The South Dakota-Montana border is a dynamic region that embodies the interplay of geography, history, culture, and economy. Understanding the complexities of this border is crucial for informed decision-making, ensuring the sustainable development and preservation of the region’s natural and cultural resources. By fostering collaboration between the states and engaging in responsible stewardship of the border region, we can ensure a prosperous and vibrant future for the communities and ecosystems that call this unique landscape home.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Tapestry: Understanding the Border Between South Dakota and Montana. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!